|
Proxemics
Proxemics is the study of human use of space and the effects that population density has on behavior, communication, and social interaction. Proxemics is one among several subcategories in the study of nonverbal communication, including Haptic communication, haptics (touch), kinesics (body movement), paralanguage, vocalics (paralanguage), and chronemics (structure of time). Edward T. Hall, the Cultural anthropology, cultural anthropologist who coined the term in 1963, defined proxemics as "the interrelated observations and theories of humans' use of space as a specialized elaboration of culture". In his foundational work on proxemics, ''The Hidden Dimension'', Hall emphasized the impact of proxemic behavior (the use of space) on interpersonal communication. According to Hall, the study of proxemics is valuable in evaluating not only the way people interact with others in daily life, but also "the organization of space in [their] houses and buildings, and ultimately the layout of [ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonverbal Communication
Nonverbal communication is the transmission of messages or signals through a nonverbal platform such as eye contact (oculesics), body language (kinesics), social distance (proxemics), touch (Haptic communication, haptics), voice (prosody (linguistics), prosody and paralanguage), physical environments/appearance, and use of objects. When communicating, nonverbal channels are utilized as means to convey different messages or signals, whereas others interpret these messages. The study of nonverbal communication started in 1872 with the publication of ''The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals'' by Charles Darwin. Darwin began to study nonverbal communication as he noticed the interactions between animals such as lions, tigers, dogs etc. and realized they also communicated by gestures and expressions. For the first time, nonverbal communication was studied and its relevance noted. Today, scholars argue that nonverbal communication can convey more meaning than verbal communica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
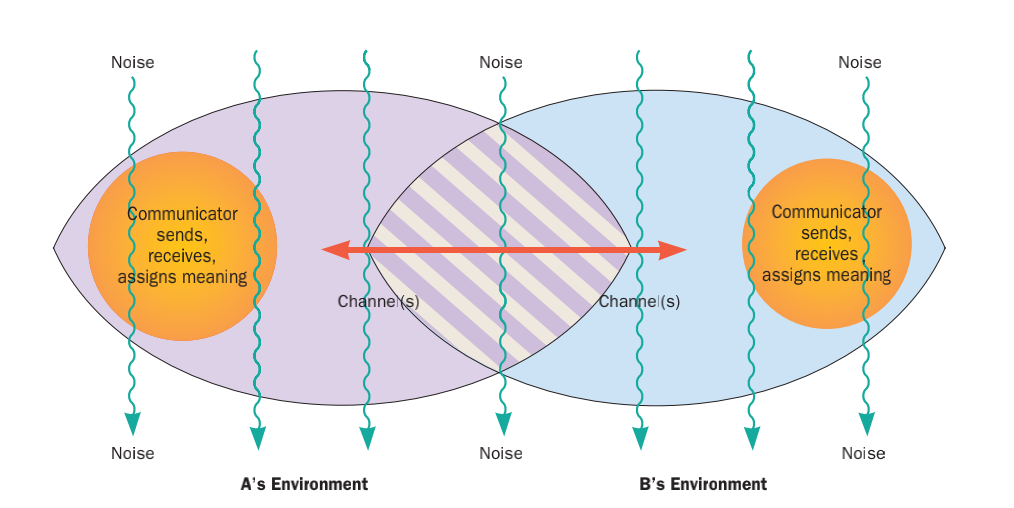
Interpersonal Communication
Interpersonal communication is an exchange of information between two or more people. It is also an area of research that seeks to understand how humans use verbal and nonverbal cues to accomplish several personal and relational goals. Communication includes utilizing communication skills within one's surroundings, including physical and psychological spaces. It is essential to see the visual/nonverbal and verbal cues regarding the physical spaces. In the psychological spaces, self-awareness and awareness of the emotions, cultures, and things that are not seen are also significant when communicating. Interpersonal communication research addresses at least six categories of inquiry: 1) how humans adjust and adapt their verbal communication and nonverbal communication during Face-to-face interaction, face-to-face communication; 2) how messages are produced; 3) how uncertainty influences behavior and information-management strategies; 4) Interpersonal deception theory, deceptive com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haptic Communication
Haptic communication is nonverbal communication and interaction via the sense of touch. Touch can come in many different forms, some can promote physical and psychological well-being. A warm, loving touch can lead to positive outcomes while a violent touch can ultimately lead to a negative outcome. The sense of touch allows one to experience different sensations such as pleasure, pain, heat, or cold. One of the most significant aspects of touch is the ability to convey and enhance physical intimacy. The sense of touch is the fundamental component of haptic communication for interpersonal relationships. Touch can be categorized in many terms such as positive, playful, control, ritualistic, task-related or unintentional. It can be both sexual ( kissing is one example that some perceive as sexual), and platonic (such as hugging or a handshake). Striking, pushing, pulling, pinching, kicking, strangling and hand-to-hand fighting are forms of touch in the context of physica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paralanguage
Paralanguage, also known as vocalics, is a component of meta-communication that may modify meaning, give nuanced meaning, or convey emotion, by using suprasegmental techniques such as prosody, pitch, volume, intonation, etc. It is sometimes defined as relating to nonphonemic properties only. Paralanguage may be expressed consciously or unconsciously. The study of paralanguage is known as paralinguistics and was invented by George L. Trager in the 1950s, while he was working at the Foreign Service Institute of the U.S. Department of State. His colleagues at the time included Henry Lee Smith, Charles F. Hockett (working with him on using descriptive linguistics as a model for paralanguage), Edward T. Hall developing proxemics, and Ray Birdwhistell developing kinesics. Trager published his conclusions in 1958, 1960 and 1961. His work has served as a basis for all later research, especially those investigating the relationship between paralanguage and culture (since par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinematics
In physics, kinematics studies the geometrical aspects of motion of physical objects independent of forces that set them in motion. Constrained motion such as linked machine parts are also described as kinematics. Kinematics is concerned with systems of specification of objects' positions and velocities and mathematical transformations between such systems. These systems may be rectangular like Cartesian coordinate system, cartesian, Curvilinear coordinates like polar coordinates or other systems. The object trajectories may be specified with respect to other objects which may themselve be in motion relative to a standard reference. Rotating systems may also be used. Numerous practical problems in kinematics involve constraints, such as mechanical linkages, ropes, or rolling disks. Overview Kinematics is a subfield of physics and mathematics, developed in classical mechanics, that describes the motion of points, Physical object, bodies (objects), and systems of bodies (group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amygdala
The amygdala (; : amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek language, Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is a paired nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclear complex present in the Cerebral hemisphere, cerebral hemispheres of vertebrates. It is considered part of the limbic system. In Primate, primates, it is located lateral and medial, medially within the temporal lobes. It consists of many nuclei, each made up of further subnuclei. The subdivision most commonly made is into the Basolateral amygdala, basolateral, Central nucleus of the amygdala, central, cortical, and medial nuclei together with the intercalated cells of the amygdala, intercalated cell clusters. The amygdala has a primary role in the processing of memory, decision making, decision-making, and emotions, emotional responses (including fear, anxiety, and aggression). The amygdala was first identified and named by Karl Friedrich Burdach in 1822. Structure Thirteen Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei have been identif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Graziano
Michael Steven Anthony Graziano (born May 22, 1967) is an American scientist A scientist is a person who Scientific method, researches to advance knowledge in an Branches of science, area of the natural sciences. In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a modern scientist. Instead, philosophers engag ... and novelist who is currently a professor of psychology and neuroscience at Princeton University. His scientific research focuses on the brain basis of awareness. He has proposed the attention schema theory, "attention schema" theory, an explanation of how, and for what adaptive advantage, brains attribute the property of awareness to themselves. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caressing
Physical intimacy is sensuous proximity or touching. It is an act or reaction, such as an expression of feelings (including close friendship, platonic love, romantic love, or sexual attraction), between people. Examples of physical intimacy include being inside someone's personal space, holding hands, hugging, kissing, caressing and sexual activity. Physical intimacy can often convey the real meaning or intention of an interaction in a way that accompanying speech cannot do. Physical intimacy can be exchanged between any people but as it is often used to communicate positive and intimate feelings, it most often occurs in people who have a preexisting relationship, whether familial, platonic or romantic, with romantic relationships having increased physical intimacy. Several forms of romantic touch have been noted including holding hands, hugging, kissing, cuddling, as well as caressing and massaging. Physical affection is highly correlated with overall relationship and par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odour
An odor (American English) or odour (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, see spelling differences) is a smell or a scent caused by one or more volatilized chemical compounds generally found in low concentrations that humans and many animals can perceive via their olfactory system. While ''smell'' can refer to pleasant and unpleasant odors, the terms ''scent'', ''aroma'', and ''fragrance'' are usually reserved for pleasant-smelling odors and are frequently used in the food and cosmetic industry to describe floral scents or to refer to perfumes. Odor physiology Sense of smell The perception of odors, or sense of smell, is mediated by the olfactory nerve. The olfactory receptor (OR) cells are neurons present in the olfactory epithelium, which is a small patch of tissue at the back of the nasal cavity. There are millions of olfactory receptor neurons that act as sensory signaling cells. Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olfaction
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste. In humans, it occurs when an odor binds to a receptor within the nasal cavity, transmitting a signal through the olfactory system. Glomeruli aggregate signals from these receptors and transmit them to the olfactory bulb, where the sensory input will start to interact with parts of the brain responsible for smell identification, memory, and emotion. There are many different things which can interfere with a normal sense of smell, including damage to the nose or smell receptors, anosmia, upper respiratory infections, traumatic brain injury, and neurodegenerative disease. History of study Early scientific study of the sense of smell includes the extensive doctoral dissertation of Eleanor Gamble, published in 1898, which compared olfactory to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation emitted by the thermal motion of particles in matter. All matter with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. The emission of energy arises from a combination of electronic, molecular, and lattice oscillations in a material. Kinetic energy is converted to electromagnetism due to charge-acceleration or dipole oscillation. At room temperature, most of the emission is in the infrared (IR) spectrum, though above around 525 °C (977 °F) enough of it becomes visible for the matter to visibly glow. This visible glow is called incandescence. Thermal radiation is one of the fundamental mechanisms of heat transfer, along with conduction and convection. The primary method by which the Sun transfers heat to the Earth is thermal radiation. This energy is partially absorbed and scattered in the atmosphere, the latter process being the reason why the sky is visibly blue. Much of the Sun's radiation tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |