|
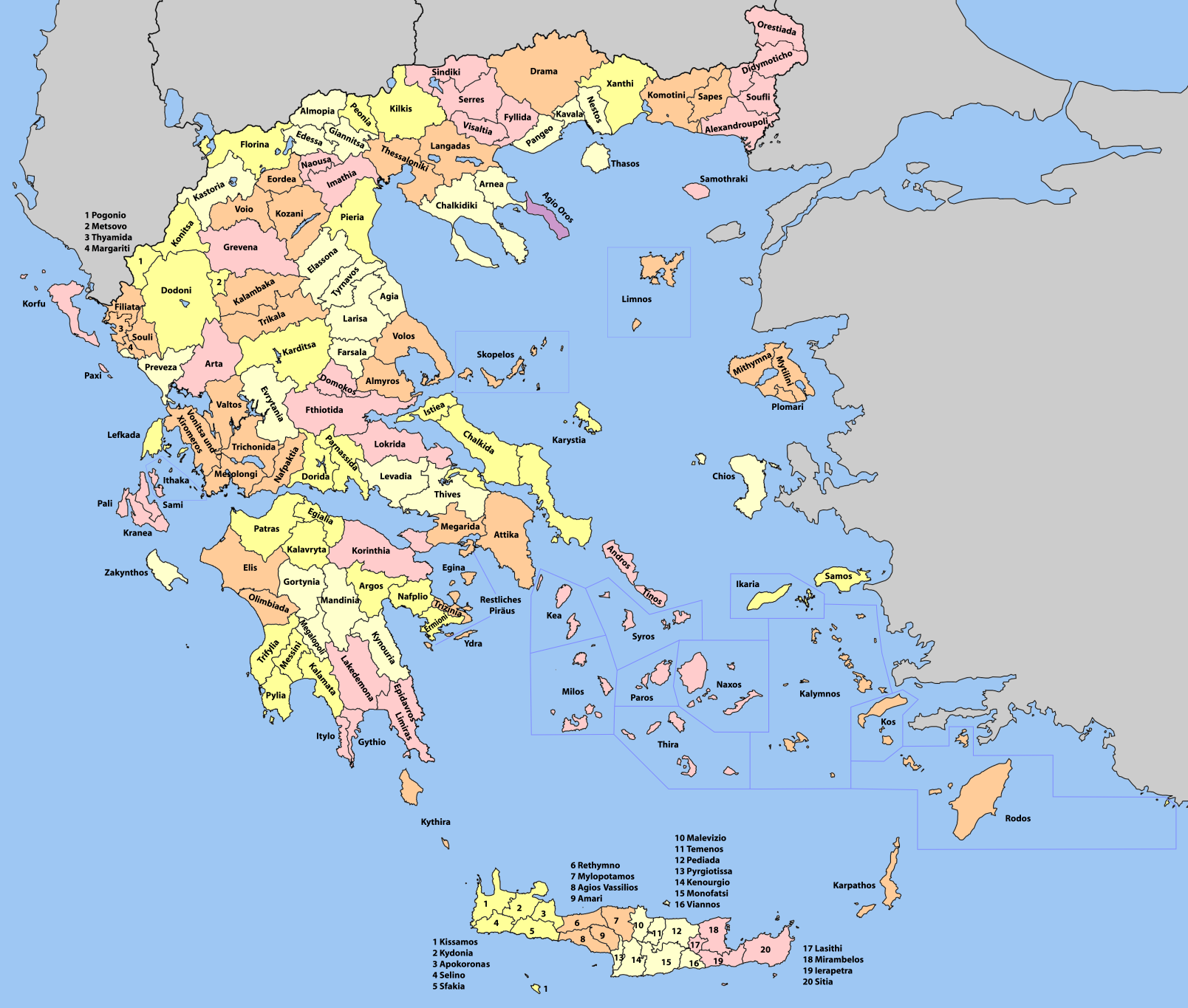
Provinces Of Greece
The provinces of Greece ( el, επαρχία, "eparchy") were sub-divisions of some the country's prefectures of Greece, prefectures. From 1887, the provinces were abolished as actual administrative units, but were retained for some state services, especially financial and educational services, as well as for electoral purposes. Before the Second World War, there were 139 provinces, and after the war, with the addition of the Dodecanese, Dodecanese Islands, their number grew to 147. According to the Article 7 of the Code of Prefectural Self-Government (Presidential Decree 30/1996), the provinces constituted a "particular administrative district" within the wider "administrative district" of the prefectures. The provinces were finally abolished after the 2006 Greek local elections, 2006 local elections, in line with Law 2539/1997, as part of the wide-ranging administrative reform known as the "Kapodistrias reform, Kapodistrias Project", and replaced by enlarged Municipalities and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greece Former German Provinces
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the northeast. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the Geography of Greece, mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Sea of Crete and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin, featuring List of islands of Greece, thousands of islands. The country consists of nine Geographic regions of Greece, traditional geographic regions, and has a population of approximately 10.4 million. Athens is the nation's capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city, followed by Thessaloniki and Patras. Greece is considered the cradle of Western culture, Western civilization, being the birthplace of Athenian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missolonghi
Missolonghi or Messolonghi ( el, Μεσολόγγι, ) is a municipality of 34,416 people (according to the 2011 census) in western Greece. The town is the capital of Aetolia-Acarnania regional unit, and the seat of the municipality of Iera Polis Messolongiou ( el, Ιερά Πόλις Μεσολογγίου, , Sacred Town of Missolonghi). Missolonghi is known as the site of Third Siege of Missolonghi, a dramatic siege during the Greek War of Independence, and of the death of poet Lord Byron. Geography The town is located between the Achelous River, Achelous and the Evinos rivers and has a port on the Gulf of Patras. It trades in fish, wine, and tobacco. The Arakynthos mountains lie to the northeast. The town is almost canalized but houses are within the gulf and the swamplands. The Missolonghi–Aitoliko Lagoons complex lies to the west. In the ancient times, the land was part of the gulf. Climate Summers are long, hot and humid, with temperatures often surpassing 40 °C and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonidio
Leonidio ( el, Λεωνίδιο, Katharevousa: Λεωνίδιον, Tsakonian: Αγιελήδι) is a town and a former municipality in Arcadia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality South Kynouria, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 418.65 km2, the community 102.67 km2. It is considered a traditional settlement. Name In the local Tsakonian language, the only surviving descendant of Doric Greek, the town is called ''Agie Lidi''.*. Page 19. Landscape The town of Leonidio, with a population of 3,826, emerges from a spectacular landscape, bound by two abrupt mountainsides enclosing the town from the north and south. The River Dafnon passes through the town, and its banks are linked with three bridges. The town is capital of the Tsakonia region, notable for its cultural and linguistic particularities, and the settlement itself offers striking and picturesque architecture; now a protected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cynuria
Cynuria ( – ''Kynouria'' or – ''Kynouriake'') is an ancient district on the eastern coast of the Peloponnese, between the Argolis and Laconia, so called from the Cynurians, one of the most ancient tribes in the peninsula. It was believed to have taken its name from the mythical Cynurus. Location and history Herodotus regarded the Cynurians as autochthones, but at the same time called them Ionians. There can be little doubt, however, that they were Pelasgians; but in consequence of their maritime position, they were regarded as a different race from the Arcadian Pelasgians, and came to be looked upon as Ionians, which was the case with the Pelasgians dwelling upon the coast of the Gulf of Corinth, in the district afterwards called Achaia. They were a semi-barbarous and predatory tribe, dwelling chiefly in the eastern slopes of Mount Parnon; but their exact boundaries cannot be defined, as they were only a tribe, and never formed a political body. At a later time they were alm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimitsana
Dimitsana ( el, Δημητσάνα) is a mountain village and a former municipality in Arcadia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Gortynia, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 110.759 km2. Dimitsana is built on the ruins of the ancient town Teuthis. The population of the village is 342 (2011 census), while it was 611 in 2001. It has been registered as a traditional settlement. Dimitsana is built on a mountain slope at an elevation of 950 meters. From its southern side a marvelous view of Megalopolis plain and Taygetus is provided. Dimitsana is located 53 km east of Pyrgos, 31 km northwest of Tripoli, 23 km northwest of Megalopoli and 17 km northeast of Andritsaina. The village has a school, a historical library, several churches, a post office, an open-air water-power museum, an open amphitheater, hotels and a square. History At the site of present-day ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gortynia
Gortynia ( el, Γορτυνία) is a municipality in the Arcadia regional unit, Peloponnese, Greece. The seat of the municipality is the town Dimitsana. The municipality has an area of 1,050.882 km2. Municipality The municipality Gortynia was formed at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of the following 8 former municipalities, that became municipal units: *Dimitsana *Iraia *Kleitor *Kontovazaina * Langadia *Trikolonoi *Tropaia *Vytina Province The province of Gortynia ( el, Επαρχία Γορτυνίας) was one of the four provinces of Arcadia Prefecture. It was abolished in 2006. Its territory corresponded with that of the current municipality Gortynia and the municipal unit Gortyna Gortyna ( grc, Γόρτυνα; also known as Gortyn (Γορτύν)) was a town of ancient Crete which appears in the Homeric poems under the form of Γορτύν; but afterwards became usually Gortyna (Γόρτυνα). According to Stephanus of .... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcadia (regional Unit)
Arcadia ( el, Αρκαδία, ''Arkadía'' ) is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the administrative region of Peloponnese. It is in the central and eastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. It takes its name from the mythological figure Arcas. In Greek mythology, it was the home of the god Pan. In European Renaissance arts, Arcadia was celebrated as an unspoiled, harmonious wilderness. Geography Arcadia is a rural, mountainous regional unit comprising about 18% of the land area of the Peloponnese peninsula. It is the peninsula's largest regional unit. According to the 2011 census, it has about 86,000 inhabitants; its capital, Tripoli, has about 30,000 residents in the city proper, and about 47,500 total in the greater metropolitan area. Arcadia consists partly of farmland, and to a larger extent grassland and degenerated shrubland. It also has three mountain ranges, with forestation mainly at altitudes above 1000 meters: Mainalo, a winter ski resort, situat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vonitsa
Vonitsa ( el, Βόνιτσα) is a town in the northwestern part of Aetolia-Acarnania in Greece, seat of the municipality of Aktio-Vonitsa. Population 4,916 (2011). The beach town is situated on the south coast of the Ambracian Gulf, and is dominated by a Venetian fortress on a hill. Vonitsa is southeast of Preveza, northeast of Lefkada (city) and northwest of Agrinio. The Greek National Road 42 (Lefkada - Amfilochia) passes through Vonitsa. Settlements *Vonitsa proper *Aktio, the ancient Actium *Nea Kamarina History Vonitsa is built near the site of ancient Anactorium, an important city of Acarnania, founded by the Corinthians in 630 BC. Like the other cities of Acarnania, it went into decline when the Romans founded Nicopolis on the other side of the Ambracian Gulf after the Battle of Actium, and forced its inhabitants to move to that city. Modern Vonitsa was founded during the Byzantine era. Vonitsa was controlled by the Republic of Venice between 1684 and 1797. After th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vonitsa-Xiromero
Vonitsa-Xiromero was one of the provinces of the Aetolia-Acarnania Prefecture, Greece. Its territory corresponded with that of the current municipalities Aktio-Vonitsa and Xiromero Xiromero municipality ( el, Δήμος Ξηρομέρου) is a municipality in the Aetolia-Acarnania regional unit, West Greece region, Greece. The seat of the municipality is the town Astakos. Its borders do not coincide with the historical regi ..., and part of the municipal unit Oiniades. It was abolished in 2006. References Provinces of Greece {{WestGreece-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amfilochia
Amfilochia ( el, Αμφιλοχία) is a town and a municipality in the northwestern part of Aetolia-Acarnania in Greece, on the site of ancient Amfilochia. Under the Ottoman Empire, it was known as Karvasaras (Καρβασαράς; from '' caravanserai''). Amfilochia is situated by the Ambracian Gulf and features an amphitheatre. Amfilochia dates back to the ancient times and also features the ancient cities of Amphilochian Argos and Limnaia (or Limnaea). History According to Pausanias, it is named after king Amphilochos, son of Amphiaraus. After the fall of Troy, Amphilochos settled in the area, which consequently was called Amphilochoi until the time of Pausanias. Under the Ottoman Empire, Ali Pasha of Ioannina, forcibly relocated residents of another village to the current location of the town and established a motel (''serai'' in Turkish) to serve passing caravans. This was how the name Karvasaras came up. In July 1944 a battle took place in the town between ELAS of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valtos Province
Valtos Province ( el, Επαρχία Βάλτου) is one of the five former provinces of Aetolia-Acarnania in Greece. It lies in the northern part of Aetolia-Acarnania. Its capital was Amfilochia. The Acheloos River was the border of the province to Evrytania. Its territory corresponded with that of the current municipality Amfilochia and the municipal unit Stratos. It was abolished in 2006. During Ottoman rule, the region of Valtos (which means "swamp" in Greek) was a haven for bandits and brigands. During the struggle for the liberation of Greece Valtos contributed many fighters and leaders to the Greek Revolution The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. The Greeks were later assisted by .... References Aetolia-Acarnania Provinces of Greece {{WGreece-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agrinio
Agrinio (Greek: Αγρίνιο, , Latin: ''Agrinium'') is the largest city of the Aetolia-Acarnania regional unit of Greece and its largest municipality, with 106,053 inhabitants. It is the economical center of Aetolia-Acarnania, although its capital is the town of Mesolonghi. The settlement dates back to ancient times. Ancient Agrinion was northeast of the present city; some walls and foundations of which have been excavated. In medieval times and until 1836, the city was known as Vrachori (Βραχώρι). The majority of the local population was occupied for an important period of time in the tobacco industry, from the last decades of 19th till the end of the 20th century. Big tobacco companies were founded in the city, including the famous Papastratos, alongside Panagopoulos and Papapetrou. Agrinion is also agriculturally known for its production of Agrinion olives. History Antiquity According to mythology, the ancient city of Agrinio (situated in the area of Megali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |