|
Proto-writing
Proto-writing consists of visible marks communicating limited information. Such systems emerged from earlier traditions of symbol systems in the early Neolithic, as early as the 7th millennium BC in Eastern Europe and China. They used ideographic or early mnemonic symbols or both to represent a limited number of concepts, in contrast to true writing systems, which record the language of the writer. Neolithic Neolithic China In 2003, tortoise shells were found in 24 Neolithic graves excavated at Jiahu, Henan province, northern China, with radiocarbon dates from the 7th millennium BC. According to some archaeologists, the symbols carved on the shells had similarities to the late 2nd millennium BC oracle bone script.. Others have dismissed this claim as insufficiently substantiated, claiming that simple geometric designs such as those found on the Jiahu shells cannot be linked to early writing. Neolithic Europe The Dispilio tablet is a wooden tablet bearing inscribed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
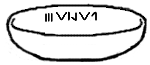
Vinča Symbols
The Vinča symbols, sometimes known as the Danube script, Vinča signs, Vinča script, Vinča–Turdaș script, Old European script, etc., are a set of untranslated symbols found on Neolithic era (6th to 5th millennium BC) artifacts from the Vinča culture and related " Old European" cultures of Central Europe and Southeastern Europe. Whether this is one of the earliest writing systems or simply symbols of some sort is disputed. They have sometimes been described as "pre-writing" or "proto-writing". The symbols went out of use around 3500 BC. Discovery In 1875, archaeological excavations directed by the Hungarian archaeologist Baroness Zsófia Torma (1840–1899) at Tordos (present Turdaș, Romania) unearthed marble and fragments of pottery inscribed with previously unknown symbols. At the site, on the Mureş river, a feeder into a tributary of the Danube, female figurines, pots, and artifacts made of stone were also found. In 1908, a similar cache was found during excava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of civilization in the world, along with ancient Egypt, Elam, the Caral-Supe civilization, Mesoamerica, the Indus Valley civilisation, and ancient China. Living along the valleys of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, Sumerian farmers grew an abundance of grain and other crops, the surplus from which enabled them to form urban settlements. Proto-writing dates back before 3000 BC. The earliest texts come from the cities of Uruk and Jemdet Nasr, and date to between c. 3500 and c. 3000 BC. Name The term "Sumer" (Sumerian: or , Akkadian: ) is the name given to the language spoken by the "Sumerians", the ancient non-Semitic-speaking inhabitants of southern Mesopotamia, by their successors the East Semitic-speaking Akkadians. The Sumerians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Writing Systems
A writing system is a method of visually representing verbal communication, based on a script and a set of rules regulating its use. While both writing and speech are useful in conveying messages, writing differs in also being a reliable form of information storage and transfer. Writing systems require shared understanding between writers and readers of the meaning behind the sets of characters that make up a script. Writing is usually recorded onto a durable medium, such as paper or electronic storage, although non-durable methods may also be used, such as writing on a computer display, on a blackboard, in sand, or by skywriting. Reading a text can be accomplished purely in the mind as an internal process, or expressed orally. Writing systems can be placed into broad categories such as alphabets, syllabaries, or logographies, although any particular system may have attributes of more than one category. In the alphabetic category, a standard set of letters represent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiahu Symbols
The Jiahu symbols () consist of 16 distinct markings on prehistoric artifacts found in Jiahu, a neolithic Peiligang culture site found in Henan, China, and excavated in 1989. The Jiahu symbols are dated to around 6000 BC. The archaeologists who made the original finds believed the markings to be similar in form to some characters used in the much later oracle bone script (e.g. similar markings of "eye", "sun; day"), but most doubt that the markings represent systematic writing. A 2003 report in ''Antiquity'' interpreted them "not as writing itself, but as features of a lengthy period of sign-use which led eventually to a fully-fledged system of writing." The earliest known body of writing in the oracle bone script dates much later to the reign of the late Shang dynasty king Wu Ding, which started in about c. 1250 BC or 1200 BC. See also * Gudi (instrument) * Neolithic signs in China *Undeciphered writing systems An undeciphered writing system is a written form of lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tărtăria Tablets
The Tărtăria tablets () are three tablets, reportedly discovered in 1961 at a Neolithic site in the village of Tărtăria (about from Alba Iulia), in Romania. The tablets bear incised symbols associated with the corpus of the Vinča symbols and have been the subject of considerable controversy among archaeologists, some of whom have argued that the symbols represent the earliest known form of writing in the world. Accurately dating the tablets is difficult as the stratigraphy pertaining to their discovery is disputed, and a heat treatment performed after their discovery has prevented the possibility of directly radiocarbon dating the tablets. Based on the account of their discovery which associates the tablets with the Vinča culture and on indirect radiocarbon evidence, some scientists propose that the tablets date to around , predating Mesopotamian pictographic proto-writing. Some scholars have disputed the authenticity of the account of their discovery, suggesting the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbol
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different concepts and experiences. All communication (and data processing) is achieved through the use of symbols. Symbols take the form of words, sounds, gestures, ideas, or visual images and are used to convey other ideas and beliefs. For example, a red octagon is a common symbol for "STOP"; on maps, blue lines often represent rivers; and a red rose often symbolizes love and compassion. Numerals are symbols for numbers; letters of an alphabet may be symbols for certain phonemes; and personal names are symbols representing individuals. The variable 'x', in a mathematical equation, may symbolize the position of a particle in space. The academic study of symbols is semiotics. In cartography, an organized collection of symbols forms a legend for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo- syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedge-shaped impressions ( Latin: ) which form its signs. Cuneiform was originally developed to write the Sumerian language of southern Mesopotamia (modern Iraq). Cuneiform is the earliest known writing system. Over the course of its history, cuneiform was adapted to write a number of languages in addition to Sumerian. Akkadian texts are attested from the 24th century BC onward and make up the bulk of the cuneiform record. Akkadian cuneiform was itself adapted to write the Hittite language in the early second millennium BC. The other languages with significant cuneiform corpora are Eblaite, Elamite, Hurrian, Luwian, and Urartian. The Old Persian and Ugaritic alphabets feature cuneiform-style signs; however, they are unrelated to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent ( ar, الهلال الخصيب) is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, State of Palestine, Palestine and Jordan, together with the northern region of Kuwait, southeastern region of Turkey and the western portion of Iran. Some authors also include Cyprus and Northern Egypt. The Fertile Crescent is believed to be the very first region where Agriculture, settled farming emerged as people started the process of clearance and modification of natural vegetation to grow newly domesticated plants as crops. Early human civilizations such as Sumer in Mesopotamia flourished as a result. Technological advances in the region include the development of History of agriculture, agriculture and the use of Irrigation#History, irrigation, of History of writing#Bronze Age writing, writing, the Wheel#History, wheel, and History of glass, glass, most emerging first in Mesopotamia. Terminology The term "Fertile Cresce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kish Tablet
The Kish tablet is a limestone tablet found at the site of the ancient Sumerian city of Kish in modern-day Tell al-Uhaymir, Babil Governorate, Iraq. A plaster-cast of the artifact is today in the collection of the Ashmolean Museum. The original is in the Baghdad Museum. It should not be confused with the Scheil dynastic tablet, which contains part of the Sumerian king list and is also sometimes called the Kish tablet. The Kish tablet, which has not yet been deciphered, is inscribed with Proto-Cuneiform signs. It has been dated to the Uruk period (ca. 3500–3200 BC).Hayes, John L., 1990 ''A Manual of Sumerian Grammar and Texts'', Undena Publications, p.266 Several thousand proto-cuneiform documents dating to Uruk IV and III periods (ca. 3350–3000 BC) have been found in Uruk. It is considered the world's oldest known written document. The writing is still purely pictographic, and represents a transitional stage between proto-writing and the emergence of the partly syll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dispilio
Dispilio ( el, Δισπηλιό) is a village near Lake Orestiada, in the Kastoria regional unit of Western Macedonia, Greece. Near the village is an archaeological site containing remains of a Neolithic lakeshore settlement that occupied an artificial island. History The lake settlement was discovered during the dry winter of 1932, which lowered the lake level and revealed traces of the settlement. A preliminary survey was made in 1935 by Antonios Keramopoulos. Excavations began in 1992, led by George Chourmouziadis, professor of prehistoric archaeology at the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki. The site's paleoenvironment, botany, fishing techniques, tools and ceramics were published informally in the June 2000 issue of , a Greek archaeology magazine and by Chourmouziadis in 2002. A recreation of the lake dwellers' settlement has been erected near the site to attract tourists from Greece and abroad. The site appears to have been occupied over a long period, from the final s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Cuneiform
The Proto-Cuneiform script was used in Mesopotamia from roughly 3300 BC to 2900 BC. It arose from the token based system used in the region for the preceding millennia and was replaced by the development of early Cuneiform script in the Early Dynastic I period. While the underlying language of Cuneiform is definitively Sumerian, the language base for Proto-Cuneiform is as yet uncertain. History Beginning around the 9th millennium BC a token based system came into use in various parts of the ancient Near East. These evolved into marked tokens and later marked envelopes, often called clay bullae. It is usually assumed that these were the basis for the development of Proto-Cuneiform. Proto-Cuneiform emerged in the Uruk IV period, circa 3300 BC and continued though the Uruk III times. The script slowly evolved over time with signs changing and merging. It was initially used in Uruk, later spreading to a few additional sites like Jemdet Nasr. Finally, in the Early Dynastic I (c. 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tartaria Amulet
Tartary ( la, Tartaria, french: Tartarie, german: Tartarei, russian: Тартария, Tartariya) or Tatary (russian: Татария, Tatariya) was a blanket term used in Western European literature and cartography for a vast part of Asia bounded by the Caspian Sea, the Ural Mountains, the Pacific Ocean, and the northern borders of China, India and Persia, at a time when this region was largely unknown to European geographers. The active use of the toponym (place name) can be traced from the 13th to the 19th centuries. In European sources, Tartary became the most common name for Central Asia that had no connection with the real polities or ethnic groups of the region; until the 19th century, European knowledge of the area remained extremely scarce and fragmentary. In modern English-speaking tradition, the region formerly known as Tartary is usually called Inner or Central Eurasia. Much of this area consists of arid plains, the main nomadic population of which in the past was eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |