|
Prostatic Venous Plexus
The prostatic veins form a well-marked prostatic plexus which lies partly in the fascial sheath of the prostate and partly between the sheath and the prostatic capsule. It communicates with the pudendal and vesical plexuses. The prostatic venous plexus drains into the internal iliac vein which connects with the vertebral venous plexus, this is thought to be the route of bone metastasis of prostate cancer. It is sometimes known as "Santorini's plexus," named for the Italian anatomist Giovanni Domenico Santorini Giovanni Domenico Santorini (June 6, 1681 – May 7, 1737) was an Italian anatomist. He was a native of Venice, earning his medical doctorate at Pisa in 1701. He is remembered for conducting anatomical dissections of the human body. From 1705 un .... References External links * - "The Male Pelvis: The Prostate Gland" Veins of the torso Prostate {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostate
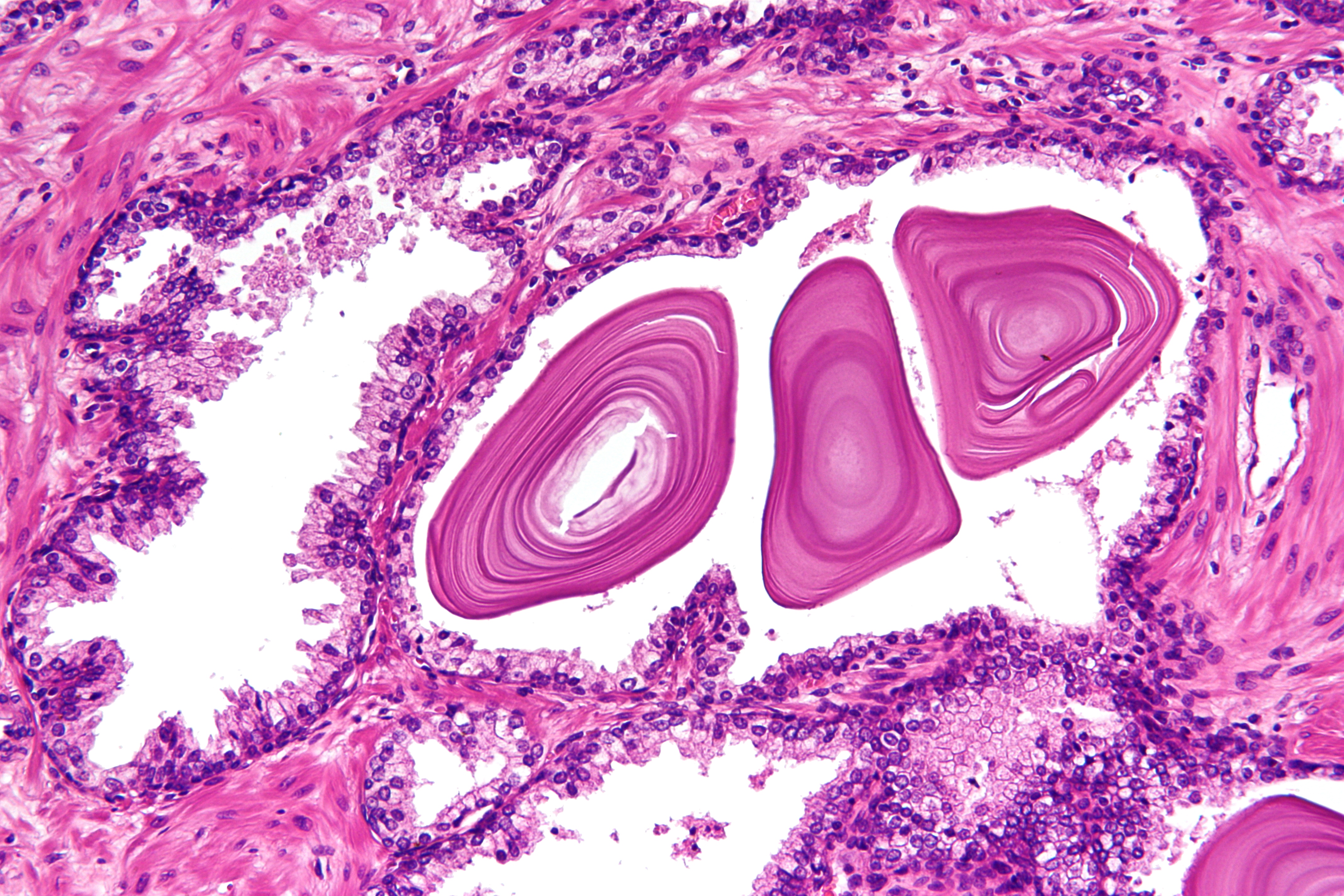
The prostate is both an Male accessory gland, accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found only in some mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and physiologically. Anatomically, the prostate is found below the Urinary bladder, bladder, with the urethra passing through it. It is described in gross anatomy as consisting of lobes and in microanatomy by zone. It is surrounded by an elastic, fibromuscular capsule and contains glandular tissue as well as connective tissue. The prostate glands produce and contain fluid that forms part of semen, the substance emitted during ejaculation as part of the male Human sexual response cycle, sexual response. This prostatic fluid is slightly alkaline, milky or white in appearance. The alkalinity of semen helps neutralize the acidity of the vagina, vaginal tract, prolonging the lifespan of sperm. The prostatic fluid is expelled in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Dorsal Vein Of The Penis
Deep or The Deep may refer to: Places United States * Deep Creek (Appomattox River tributary), Virginia * Deep Creek (Great Salt Lake), Idaho and Utah * Deep Creek (Mahantango Creek tributary), Pennsylvania * Deep Creek (Mojave River tributary), California * Deep Creek (Pine Creek tributary), Pennsylvania * Deep Creek (Soque River tributary), Georgia * Deep Creek (Texas), a tributary of the Colorado River * Deep Creek (Washington), a tributary of the Spokane River * Deep River (Indiana), a tributary of the Little Calumet River * Deep River (Iowa), a minor tributary of the English River * Deep River (North Carolina) * Deep River (Washington), a minor tributary of the Columbia River * Deep Voll Brook, New Jersey, also known as Deep Brook Elsewhere * Deep Creek (Bahamas) * Deep Creek (Melbourne, Victoria), Australia, a tributary of the Maribyrnong River * Deep River (Western Australia) People * Deep (given name) * Deep (rapper), Punjabi rapper from Houston, Texas * Ravi Deep (b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vesical Venous Plexus
The vesical plexus envelops the lower part of the bladder and the base of the prostate and communicates with the pudendal and prostatic plexuses. It is drained, by means of several vesical veins The vesical veins are veins in the pelvis that drain blood from the urinary bladder. The vesical veins receive blood from the vesical venous plexus The vesical plexus envelops the lower part of the bladder and the base of the prostate The ..., into the internal iliac veins. References External links Anatomy at umich.edu Veins of the torso {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pudendal Plexus (veins)
The pudendal venous plexus (vesicoprostatic plexus) lies behind the arcuate pubic ligament and the lower part of the pubic symphysis, and in front of the bladder and prostate. Its chief tributary is the deep dorsal vein of the penis, but it also receives branches from the front of the bladder and prostate. It communicates with the vesical venous plexus and with the internal pudendal vein The internal pudendal veins (internal pudic veins) are a set of veins in the pelvis. They are the venae comitantes of the internal pudendal artery. Internal pudendal veins are enclosed by pudendal canal, with internal pudendal artery and pudenda ... and drains into the vesical and hypogastric veins. See also * Prostatic venous plexus References Veins of the torso {{Portal bar, Anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostatic Capsule
On either side of the urethral crest is a slightly depressed fossa, the prostatic sinus, the floor of which is perforated by numerous apertures, the orifices of the prostatic ducts from the lateral lobes of the prostate The prostate is both an Male accessory gland, accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found only in some mammals. It differs between species anatomically, .... References External links * - "The Male Pelvis: The Prostate Gland" * () Prostate {{genitourinary-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Metastasis
Bone metastasis, or osseous metastatic disease, is a category of cancer metastases that results from primary tumor invasion to bone. Bone-originating primary tumors such as osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, and Ewing's sarcoma are rare; the most common bone tumor is a metastasis Bone metastases can be classified as osteolytic, osteoblastic, or both. Unlike hematologic malignancies which originate in the blood and form non-solid tumors, bone metastases generally arise from epithelial tumors and form a solid mass inside the bone. Bone metastases, especially in a state of advanced disease, can cause severe pain, characterized by a dull, constant ache with periodic spikes of incident pain. Types of lesions Under normal conditions, bone undergoes continuous remodeling through osteoclast-mediated bone resorption and osteoblast-mediated bone deposition. These processes are normally tightly regulated within bone to maintain bone structure and calcium homeostasis in the body. Dysregulation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Domenico Santorini
Giovanni Domenico Santorini (June 6, 1681 – May 7, 1737) was an Italian anatomist. He was a native of Venice, earning his medical doctorate at Pisa in 1701. He is remembered for conducting anatomical dissections of the human body. From 1705 until 1728, Santorini performed anatomical demonstrations in Venice. His best written work was the 1724 publication of ''Observationes anatomicae'', a detailed work involving anatomical aspects of the human body. He is credited for providing descriptions of several anatomical structures, including the following: * Santorini's cartilage: The corniculate cartilage of the larynx. * Santorini's concha: The supreme nasal concha (turbinate).Supreme nasal concha. (n.d.) ''Medical Eponyms''. (2012). Retrieved April 16 2015 fro/ref> * Duct of Santorini: An accessory duct of the pancreas. * Santorini's fissures: Vertical fissures in the anterior part of the cartilage of the external acoustic meatus (ear canal). * Santorini's minor caruncle: Loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veins Of The Torso
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In contrast to veins, arteries carry blood away from the heart. Veins are less muscular than arteries and are often closer to the skin. There are valves (called ''pocket valves'') in most veins to prevent backflow. Structure Veins are present throughout the body as tubes that carry blood back to the heart. Veins are classified in a number of ways, including superficial vs. deep, pulmonary vs. systemic, and large vs. small. * Superficial veins are those closer to the surface of the body, and have no corresponding arteries. *Deep veins are deeper in the body and have corresponding arteries. *Perforator veins drain from the superficial to the deep veins. These are usually referred to in the lower limbs and feet. *Communic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_CIPB2104.jpg)
