|
Principle Of Transformation Groups
The principle of transformation groups is a rule for assigning ''epistemic'' probabilities in a statistical inference problem. It was first suggested by Edwin T. Jaynes and can be seen as a generalisation of the principle of indifference. This can be seen as a method to create ''objective ignorance probabilities'' in the sense that two people who apply the principle and are confronted with the same information will assign the same probabilities. Motivation and description of the method The method is motivated by the following normative principle, or desideratum: ''In two problems where we have the same prior information we should assign the same prior probabilities'' The method then comes about from "transforming" a given problem into an equivalent one. This method has close connections with group theory, and to a large extent is about finding symmetry in a given problem, and then exploiting this symmetry to assign prior probabilities. In problems with discrete variables (e.g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edwin Thompson Jaynes
Edwin Thompson Jaynes (July 5, 1922 – April 30, 1998) was the Wayman Crow Distinguished Professor of Physics at Washington University in St. Louis. He wrote extensively on statistical mechanics and on foundations of probability and statistical inference, initiating in 1957 the maximum entropy interpretation of thermodynamics as being a particular application of more general Bayesian/information theory techniques (although he argued this was already implicit in the works of Josiah Willard Gibbs). Jaynes strongly promoted the interpretation of probability theory as an extension of logic. In 1963, together with Fred Cummings, he modeled the evolution of a two-level atom in an electromagnetic field, in a fully quantized way. This model is known as the Jaynes–Cummings model. A particular focus of his work was the construction of logical principles for assigning prior probability distributions; see the principle of maximum entropy, the principle of maximum caliber, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sampling Probability
In statistics, in the theory relating to sampling from finite populations, the sampling probability (also known as inclusion probability) of an element or member of the population, is its probability of becoming part of the sample during the drawing of a single sample. For example, in simple random sampling the probability of a particular unit i to be selected into the sample is :p_ = \frac = \frac where n is the sample size and N is the population size. Each element of the population may have a different probability of being included in the sample. The inclusion probability is also termed the "first-order inclusion probability" to distinguish it from the "second-order inclusion probability", i.e. the probability of including a pair of elements. Generally, the first-order inclusion probability of the ''i''th element of the population is denoted by the symbol π''i'' and the second-order inclusion probability that a pair consisting of the ''i''th and ''j''th element of the populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Improper Prior
In Bayesian statistical inference, a prior probability distribution, often simply called the prior, of an uncertain quantity is the probability distribution that would express one's beliefs about this quantity before some evidence is taken into account. For example, the prior could be the probability distribution representing the relative proportions of voters who will vote for a particular politician in a future election. The unknown quantity may be a parameter of the model or a latent variable rather than an observable variable. Bayes' theorem calculates the renormalized pointwise product of the prior and the likelihood function, to produce the ''posterior probability distribution'', which is the conditional distribution of the uncertain quantity given the data. Similarly, the prior probability of a random event or an uncertain proposition is the unconditional probability that is assigned before any relevant evidence is taken into account. Priors can be created using a nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deductive Logic
Deductive reasoning is the mental process of drawing deductive inferences. An inference is deductively valid if its conclusion follows logically from its premises, i.e. if it is impossible for the premises to be true and the conclusion to be false. For example, the inference from the premises "all men are mortal" and "Socrates is a man" to the conclusion "Socrates is mortal" is deductively valid. An argument is ''sound'' if it is ''valid'' and all its premises are true. Some theorists define deduction in terms of the intentions of the author: they have to intend for the premises to offer deductive support to the conclusion. With the help of this modification, it is possible to distinguish valid from invalid deductive reasoning: it is invalid if the author's belief about the deductive support is false, but even invalid deductive reasoning is a form of deductive reasoning. Psychology is interested in deductive reasoning as a psychological process, i.e. how people ''actually'' draw i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axioms
An axiom, postulate, or assumption is a statement that is taken to be true, to serve as a premise or starting point for further reasoning and arguments. The word comes from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning 'that which is thought worthy or fit' or 'that which commends itself as evident'. The term has subtle differences in definition when used in the context of different fields of study. As defined in classic philosophy, an axiom is a statement that is so evident or well-established, that it is accepted without controversy or question. As used in modern logic, an axiom is a premise or starting point for reasoning. As used in mathematics, the term ''axiom'' is used in two related but distinguishable senses: "logical axioms" and "non-logical axioms". Logical axioms are usually statements that are taken to be true within the system of logic they define and are often shown in symbolic form (e.g., (''A'' and ''B'') implies ''A''), while non-logical axioms (e.g., ) are actual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bertrand Paradox (probability)
The Bertrand paradox is a problem within the classical interpretation of probability theory. Joseph Bertrand introduced it in his work ''Calcul des probabilités'' (1889), as an example to show that the principle of indifference may not produce definite, well-defined results for probabilities if it is applied uncritically when the domain of possibilities is infinite. Bertrand's formulation of the problem The Bertrand paradox is generally presented as follows: Consider an equilateral triangle inscribed in a circle. Suppose a chord of the circle is chosen at random. What is the probability that the chord is longer than a side of the triangle? Bertrand gave three arguments (each using the principle of indifference), all apparently valid, yet yielding different results: # The "random endpoints" method: Choose two random points on the circumference of the circle and draw the chord joining them. To calculate the probability in question imagine the triangle rotated so its vertex coin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fisher Information
In mathematical statistics, the Fisher information (sometimes simply called information) is a way of measuring the amount of information that an observable random variable ''X'' carries about an unknown parameter ''θ'' of a distribution that models ''X''. Formally, it is the variance of the score, or the expected value of the observed information. In Bayesian statistics, the asymptotic distribution of the posterior mode depends on the Fisher information and not on the prior (according to the Bernstein–von Mises theorem, which was anticipated by Laplace for exponential families). The role of the Fisher information in the asymptotic theory of maximum-likelihood estimation was emphasized by the statistician Ronald Fisher (following some initial results by Francis Ysidro Edgeworth). The Fisher information is also used in the calculation of the Jeffreys prior, which is used in Bayesian statistics. The Fisher information matrix is used to calculate the covariance matrices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeffreys Prior
In Bayesian probability, the Jeffreys prior, named after Sir Harold Jeffreys, is a non-informative (objective) prior distribution for a parameter space; its density function is proportional to the square root of the determinant of the Fisher information matrix: : p\left(\vec\theta\right) \propto \sqrt.\, It has the key feature that it is invariant under a change of coordinates for the parameter vector \vec\theta. That is, the relative probability assigned to a volume of a probability space using a Jeffreys prior will be the same regardless of the parameterization used to define the Jeffreys prior. This makes it of special interest for use with ''scale parameters''. Reparameterization One-parameter case If \theta and \varphi are two possible parametrizations of a statistical model, and \theta is a continuously differentiable function of \varphi, we say that the prior p_\theta(\theta) is "invariant" under a reparametrization if :p_\varphi(\varphi) = p_\theta(\theta) \left, \fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
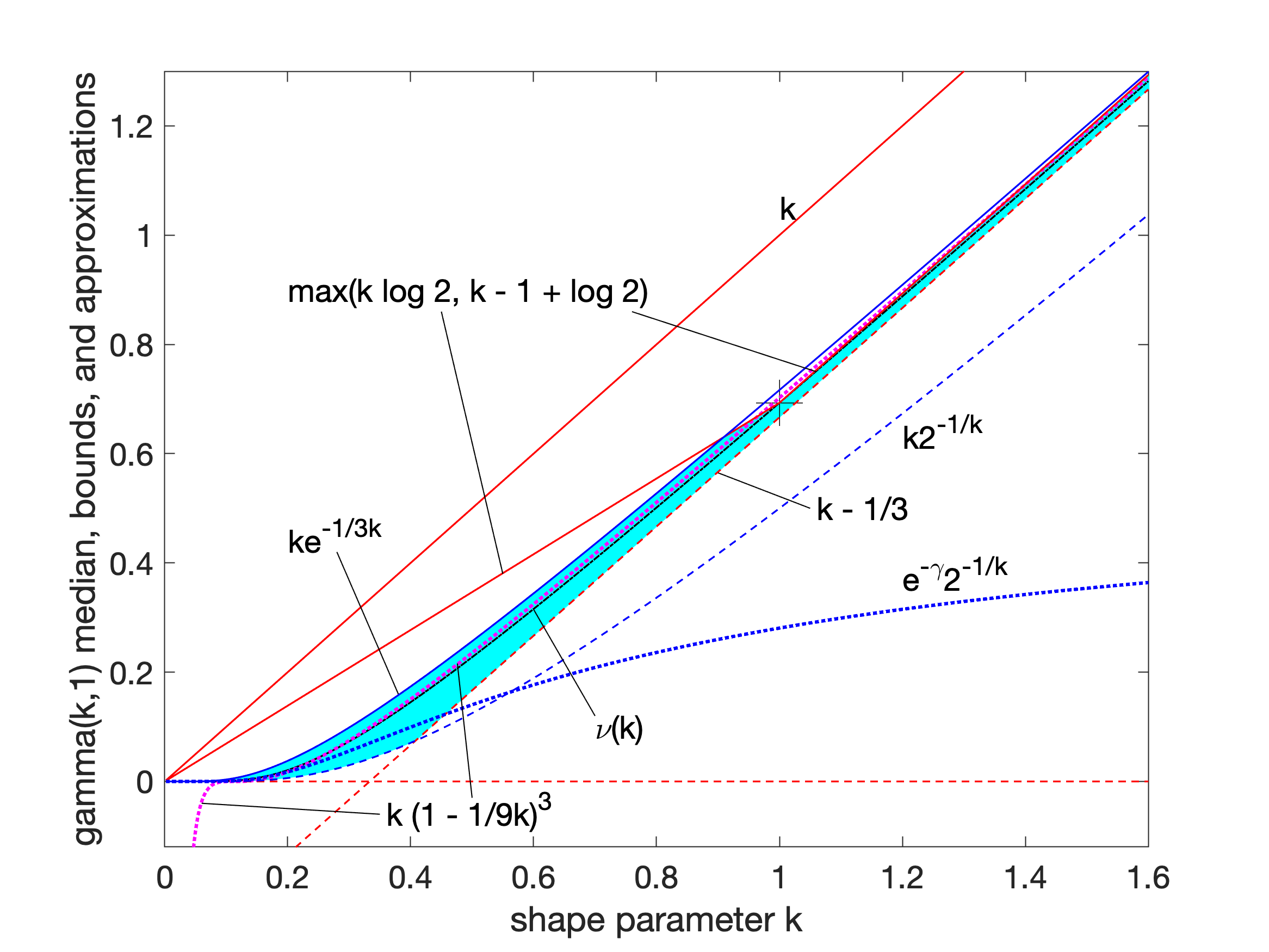
Gamma Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the gamma distribution is a two- parameter family of continuous probability distributions. The exponential distribution, Erlang distribution, and chi-square distribution are special cases of the gamma distribution. There are two equivalent parameterizations in common use: #With a shape parameter k and a scale parameter \theta. #With a shape parameter \alpha = k and an inverse scale parameter \beta = 1/ \theta , called a rate parameter. In each of these forms, both parameters are positive real numbers. The gamma distribution is the maximum entropy probability distribution (both with respect to a uniform base measure and a 1/x base measure) for a random variable X for which E 'X''= ''kθ'' = ''α''/''β'' is fixed and greater than zero, and E n(''X'')= ''ψ''(''k'') + ln(''θ'') = ''ψ''(''α'') − ln(''β'') is fixed (''ψ'' is the digamma function). Definitions The parameterization with ''k'' and ''θ'' appears to be more common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principle Of Indifference
The principle of indifference (also called principle of insufficient reason) is a rule for assigning epistemic probabilities. The principle of indifference states that in the absence of any relevant evidence, agents should distribute their credence (or 'degrees of belief') equally among all the possible outcomes under consideration. In Bayesian probability, this is the simplest non-informative prior. The principle of indifference is meaningless under the frequency interpretation of probability, in which probabilities are relative frequencies rather than degrees of belief in uncertain propositions, conditional upon state information. Examples The textbook examples for the application of the principle of indifference are coins, dice, and cards. In a macroscopic system, at least, it must be assumed that the physical laws that govern the system are not known well enough to predict the outcome. As observed some centuries ago by John Arbuthnot (in the preface of ''Of the Laws of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacobian Matrix And Determinant
In vector calculus, the Jacobian matrix (, ) of a vector-valued function of several variables is the matrix of all its first-order partial derivatives. When this matrix is square, that is, when the function takes the same number of variables as input as the number of vector components of its output, its determinant is referred to as the Jacobian determinant. Both the matrix and (if applicable) the determinant are often referred to simply as the Jacobian in literature. Suppose is a function such that each of its first-order partial derivatives exist on . This function takes a point as input and produces the vector as output. Then the Jacobian matrix of is defined to be an matrix, denoted by , whose th entry is \mathbf J_ = \frac, or explicitly :\mathbf J = \begin \dfrac & \cdots & \dfrac \end = \begin \nabla^ f_1 \\ \vdots \\ \nabla^ f_m \end = \begin \dfrac & \cdots & \dfrac\\ \vdots & \ddots & \vdots\\ \dfrac & \cd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cauchy Distribution
The Cauchy distribution, named after Augustin Cauchy, is a continuous probability distribution. It is also known, especially among physicists, as the Lorentz distribution (after Hendrik Lorentz), Cauchy–Lorentz distribution, Lorentz(ian) function, or Breit–Wigner distribution. The Cauchy distribution f(x; x_0,\gamma) is the distribution of the -intercept of a ray issuing from (x_0,\gamma) with a uniformly distributed angle. It is also the distribution of the ratio of two independent normally distributed random variables with mean zero. The Cauchy distribution is often used in statistics as the canonical example of a " pathological" distribution since both its expected value and its variance are undefined (but see below). The Cauchy distribution does not have finite moments of order greater than or equal to one; only fractional absolute moments exist., Chapter 16. The Cauchy distribution has no moment generating function. In mathematics, it is closely related to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |