|
Portative Organ
A portative organ (from the Latin verb , "to carry"), also known during Italian Trecento as the , is a small pipe organ that consists of one rank of flue pipes, sometimes arranged in two rows, to be played while strapped to the performer at a right angle. The performer manipulates the bellows with one hand and fingers the keys with the other. The portative organ lacks a reservoir to retain a supply of wind and so it produces sound only while the bellows are being operated. The instrument was commonly used in European secular music from the 12th to the 16th centuries. The Italian composer Francesco Landini is known to have played the instrument. There are performers on the instrument again as a result of the Early Music Revival. Some contemporary music has been written for it, for example by José María Sánchez-Verdú. Dolly Collins also used it in modern English folk music. Terminology The portative organ is also called a portatif organ, portativ organ, or simply portative, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reed Pipe
A reed pipe (also referred to as a ''lingual'' pipe) is an organ pipe that is sounded by a vibrating brass strip known as a '' reed''. Air under pressure (referred to as ''wind'') is directed towards the reed, which vibrates at a specific pitch. This is in contrast to flue pipes, which contain no moving parts and produce sound solely through the vibration of air molecules. Reed pipes are common components of pipe organs. Stop Reed pipes include all stops of the "Reed" class, and some stops from the "Hybrid" class. The reed stops of an organ are collectively called the "reed-work". Construction A reed pipe comprises a metal ''tongue'' (the reed) which rests against a ''shallot'', in which is carved a tunnel. The reed and shallot are held in place by a wooden ''wedge''. This assembly protrudes from the underside of the ''block'' and hangs down into the ''boot''. A ''tuning wire'' is inserted through the boot and is bent to hold the reed against the shallot. The wire is moved u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Organ
A positive organ (also positiv organ, positif organ, portable organ, chair organ, or simply positive, positiv, positif, or chair) (from the Latin verb ''ponere'', "to place") is a small, usually one-manual, pipe organ that is built to be more or less mobile. It was common in sacred and secular music between the 10th and the 18th centuries, in chapels and small churches, as a chamber organ and for the basso continuo in ensemble works. The smallest common kind of positive, hardly higher than the keyboard, is called chest or box organ and is especially popular for basso continuo work; positives for more independent use tend to be higher. From the Middle Ages through Renaissance and Baroque the instrument came in many different forms, including processional and tabletop organs that have profited relatively less from the renewed popularity the type in general has enjoyed from the Orgelbewegung onwards. History A well-known instance of an early positive or portable organ of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contorniate
A contorniate, or contourniate (UK pronunciation: ), is a type of ancient Roman medal or medallion of bronze issued in the fourth and fifth centuries CE, having a deep furrow on the contour or edge, as if the object had been turned in a lathe. The extant contorniates show portraits of various earlier emperors (especially Nero and Trajan) or of cultural figures such as Homer, Solon, Euclid, Pythagoras, Socrates, Sallust, Apollonius Tyaneus, and Apuleius, as well as athletes, whose victories are symbolized by palm leaves and chariots, either '' bigae'' or ''quadriga A quadriga is a car or chariot drawn by four horses abreast and favoured for chariot racing in classical antiquity and the Roman Empire. The word derives from the Latin , a contraction of , from ': four, and ': yoke. In Latin the word is almos ...e''. The medals were not used as currency, but may have been distributed as New Year's gifts in association with public spectacles, including chariot races and pantomim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
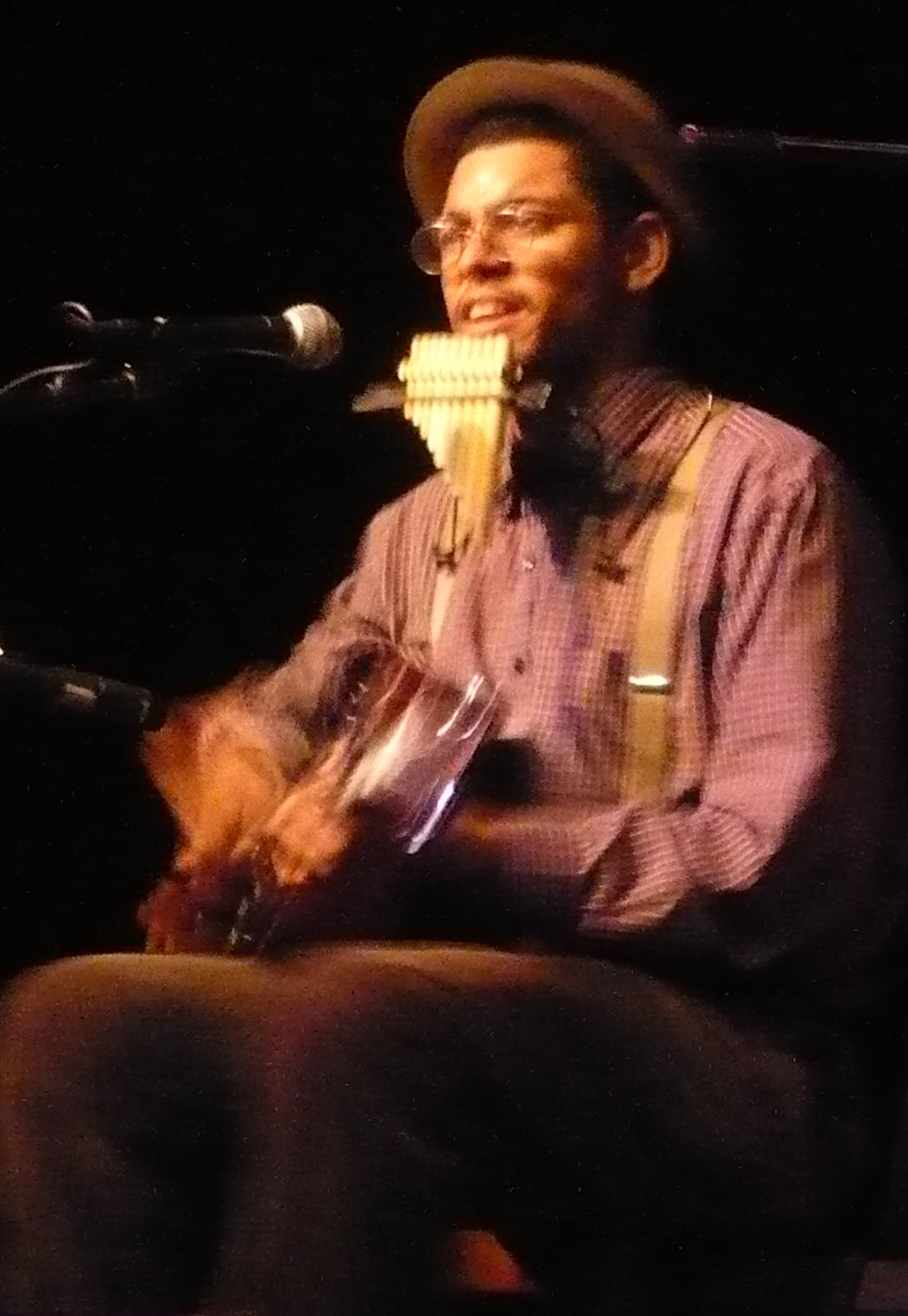
Pan Pipes
A pan flute (also known as panpipes or syrinx) is a musical instrument based on the principle of the closed tube, consisting of multiple pipes of gradually increasing length (and occasionally girth). Multiple varieties of pan flutes have been popular as folk instruments. The pipes are typically made from bamboo, giant cane, or local reeds. Other materials include wood, plastic, metal, and clay. Name The pan flute is named after Pan, the Greek god of nature and shepherds, often depicted with such an instrument. The pan flute has become widely associated with the character Peter Pan created by Sir James Matthew Barrie, whose name was inspired by the god Pan. In Greek mythology Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories conc ..., Syrinx (Σύριγξ) was a forest nymph. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheng (musical Instrument)
Sheng may refer to: Chinese culture * Sheng (instrument) (笙), a Chinese wind instrument * Sheng (surname) (盛), a Chinese surname * Sheng (Chinese opera), a major role in Chinese opera * Sheng (volume) (升), ancient Chinese unit of volume, approximately 1 liter * Sheng pu'er, a type of pu-erh tea * Provinces of China (省), administrative divisions called ''shěng'' in Mandarin East African culture * Sheng slang, a slang dialect of the Swahili language See also *Cheng (other) *Zheng (other) Zheng may refer to: *Zheng (surname), Chinese surname (鄭, 郑, ''Zhèng'') *Zheng County, former name of Zhengzhou, capital of Henan, China * Guzheng (), a Chinese zither instrument with bridges *Qin Shi Huang (259 BC – 210 BC), emperor of the ... * Shen (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museo Archeologico Nazionale Napoli
The National Archaeological Museum of Naples (, ) is an important Italian archaeological museum. Its collection includes works from Greek, Roman and Renaissance times, and especially Roman artifacts from the nearby Pompeii, Stabiae and Herculaneum sites. From 1816 to 1861, it was known as the Royal Bourbon Museum (). Building The building was built as a cavalry barracks in 1585. From 1616 to 1777, it was the seat of the University of Naples. During the 19th century, after it became a museum, it suffered many changes to the main structure. Collections The museum hosts extensive collections of Greek and Roman antiquities. Their core is from the Farnese Collection, which includes a collection of engraved gems (including the Farnese Cup, a Ptolemaic bowl made of sardonyx agate and the most famous piece in the "Treasure of the Magnificent", and is founded upon gems collected by Cosimo de' Medici and Lorenzo il Magnifico in the 15th century) and the Farnese Marbles. Among the no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pompeii
Pompeii ( ; ) was a city in what is now the municipality of Pompei, near Naples, in the Campania region of Italy. Along with Herculaneum, Stabiae, and Villa Boscoreale, many surrounding villas, the city was buried under of volcanic ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. Largely preserved under the ash, Pompeii offers a unique snapshot of Culture of ancient Rome, Roman life, frozen at the moment it was buried, as well as insight into ancient urban planning. It was a wealthy town of 10,000 to 20,000 residents at the time it was destroyed. It hosted many fine public buildings and luxurious private houses with lavish decorations, furnishings and artworks, which were the main attractions for early excavators; subsequent excavations have found hundreds of private homes and businesses reflecting various architectural styles and social classes, as well as numerous public buildings. Organic remains, including wooden objects and human bodies, were interred in the as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), the Roman Republic (50927 BC), and the Roman Empire (27 BC476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic peoples, Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually controlled the Italian Peninsula, assimilating the Greece, Greek culture of southern Italy (Magna Graecia) and the Etruscans, Etruscan culture, and then became the dominant power in the Mediterranean region and parts of Europe. At its hei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantigas De Santa Maria
The ''Cantigas de Santa Maria'' (, ; "Canticles of Holy Mary") are 420 poems with musical notation, written in the medieval Galician-Portuguese language during the reign of Alfonso X of Castile, Alfonso X of Castile ''El Sabio'' (1221–1284). Traditionally, they are all attributed to Alfonso, though scholars have since established that the musicians and poets of his court were responsible for most of them, with Alfonso being credited with a few as well. It is one of the largest collections of monophonic (solo) songs from the Middle Ages and is characterized by the mention of the Mary, the mother of Jesus, Virgin Mary in every song, while every tenth song is a hymn. The ''Cantigas'' have survived in four manuscript codices: two at El Escorial, one at Madrid, Madrid's Biblioteca Nacional de España, National Library, and one in Florence, Italy. The E codex from El Escorial is illuminated with colored Miniature (illuminated manuscript), miniatures showing pairs of musicians playin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miniature (illuminated Manuscript)
A miniature (from the Latin verb 'to colour with minium', a red lead) is a small illustration used to decorate an ancient or medieval illuminated manuscript; the simple illustrations of the early codices having been miniated or delineated with that pigment. The generally small scale of such medieval pictures has led to etymological confusion with minuteness and to its application to small paintings, especially portrait miniatures, which did however grow from the same tradition and at least initially used similar techniques. Apart from the Western, Byzantine and Armenian traditions, there is another group of Asian traditions, which is generally more illustrative in nature, and from origins in manuscript book decoration also developed into single-sheet small paintings to be kept in albums, which are also called miniatures, as the Western equivalents in watercolor and other media are not. These include Arabic miniatures, and their Persian, Mughal, Ottoman and other Indian of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perrin D'Angicourt
Perrin d'Angicourt (''floruit'' 1245–70) was a trouvère associated with the group of poets active in and around Arras. His birthplace was most likely Achicourt, just south of Arras. His surviving oeuvre is large by the standards of the trouvères, and well-distributed in the chansonniers: thirty-five (35) of his songs survive, in some case in as many as eleven different manuscripts. Two or perhaps three, of Perrin's songs "J'ai un joli souvenir", "Quant partis sui" and perhaps "Quant li cincenis s'escrie" are described in their chansonniers as "crowned songs" (''chansons couronnées''), indicating that they had won poetry competitions, probably under the aegis of the '' puy d'Arras''. Twice Perrin composed '' jeux partis''"Perrin d'Angicourt, respondés" and "Prince del pui" with Jehan Bretel, also from Arras, and he is referenced in other ''jeux partis'' by Bretel, Gaidifer d'Avion, Lambert Ferri, Jehan de Grieviler and a certain Audefroi (perhaps the banker Audefroi Louc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |