|
Portable Hyperbaric Bag
A portable hyperbaric bag, of which one brand is the Gamow () bag, is an inflatable pressure bag large enough to accommodate a person. The patient can be placed inside the bag, which is then sealed and inflated with a foot pump. Within minutes, the effective altitude can be decreased by 1000 m to as much as 3000 m (3281 to 9743 feet) depending on the elevation. The bag is pressurised to ; the pressure gradient is regulated by pop-off valves set to the target pressure. History The Gamow bag was named after its inventor, Igor Gamow, son of George Gamow. Igor Gamow originally designed a predecessor to the Gamow bag called "The Bubble" to study the effect of high altitude on stamina and performance in athletes. Gamow later re-designed "The Bubble" into a bag that could be used in high-altitude wilderness. Application It is primarily used for treating severe cases of altitude sickness, Gov't Doc # USARIEM-TN94-2. high-altitude cerebral edema, and high-altitude pulmonary ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portable Hyperbaric Chamber
Portable may refer to: General * Portable building, a manufactured structure that is built off site and moved in upon completion of site and utility work * Portable classroom, a temporary building installed on the grounds of a school to provide additional classroom space where there is a shortage of capacity * Portable toilet, a modern, portable, self-contained outhouse manufactured of molded plastic Computing * Portable object (computing), a distributed computing term for an object which can be accessed through a normal method call while possibly residing in memory on another computer * Software portability, software that can easily be ported to multiple platforms * Portable applications, applications that do not require any kind of installation onto a computer, and can store data in the program's directory Electronics * Portable electronics * Mobile device, Portable device, a wearable or handheld device * Portable audio player, a personal electronic device that allows the user ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igor Gamow
Rustem Igor Gamow (November 4, 1935, in Georgetown, D.C. – April 15, 2021)Gamow, George: ''My World Line: An Informal Autobiography'', The Viking Press, New York, 1970, page 106. was a microbiology professor at the University of Colorado and inventor. His best known inventions included the Gamow bag and the Shallow Underwater Breathing Apparatus. He was fired from CU in 2004 following sexual harassment and assault charges. Early life and education Rustem Igor Gamow was the son of Russian émigré physicists George Gamow and Lyubov Vokhmintseva "Rho" Gamow. Finishing high school at age 17, he joined the National Ballet Company. He worked breaking horses, delivering packages by motorcycle, and teaching karate before enrolling at the University of Colorado in 1958, where his father taught. Igor Gamow received a B.A. and M.S. in biology, and a Ph.D. in biophysics, all at University of Colorado. Research Gamow worked on Phycomyces blakesleeanus during postdoctoral research und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Gamow
George Gamow (March 4, 1904 – August 19, 1968), born Georgiy Antonovich Gamov ( uk, Георгій Антонович Гамов, russian: Георгий Антонович Гамов), was a Russian-born Soviet and American polymath, theoretical physicist and cosmologist. He was an early advocate and developer of Lemaître's Big Bang theory. He discovered a theoretical explanation of alpha decay by quantum tunneling, invented the liquid drop model and the first mathematical model of the atomic nucleus, and worked on radioactive decay, star formation, stellar nucleosynthesis and Big Bang nucleosynthesis (which he collectively called nucleocosmogenesis), and molecular genetics. In his middle and late career, Gamow directed much of his attention to teaching and wrote popular books on science, including '' One Two Three... Infinity'' and the ''Mr Tompkins'' series of books (1939–1967). Some of his books are still in print more than a half-century after their original publicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Altitude
Altitude or height (also sometimes known as depth) is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context (e.g., aviation, geometry, geographical survey, sport, or atmospheric pressure). Although the term ''altitude'' is commonly used to mean the height above sea level of a location, in geography the term elevation is often preferred for this usage. Vertical distance measurements in the "down" direction are commonly referred to as depth. In aviation In aviation, the term altitude can have several meanings, and is always qualified by explicitly adding a modifier (e.g. "true altitude"), or implicitly through the context of the communication. Parties exchanging altitude information must be clear which definition is being used. Aviation altitude is measured using either mean sea level (MSL) or local ground level (above ground level, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altitude Sickness
Altitude sickness, the mildest form being acute mountain sickness (AMS), is the harmful effect of high altitude, caused by rapid exposure to low amounts of oxygen at high elevation. People can respond to high altitude in different ways. Symptoms may include headaches, vomiting, tiredness, confusion, trouble sleeping, and dizziness. Acute mountain sickness can progress to high-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE) with associated shortness of breath or high-altitude cerebral edema (HACE) with associated confusion. Chronic mountain sickness may occur after long-term exposure to high altitude. Altitude sickness typically occurs only above , though some are affected at lower altitudes. Risk factors include a prior episode of altitude sickness, a high degree of activity, and a rapid increase in elevation. Diagnosis is based on symptoms and is supported in those who have more than a minor reduction in activities. It is recommended that at high altitude any symptoms of headache, nausea, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-altitude Cerebral Edema
High-altitude cerebral edema (HACE) is a medical condition in which the brain swells with fluid because of the physiological effects of traveling to a high altitude. It generally appears in patients who have acute mountain sickness and involves disorientation, lethargy, and nausea among other symptoms. It occurs when the body fails to acclimatize while ascending to a high altitude. It appears to be a vasogenic edema (fluid penetration of the blood–brain barrier), although cytotoxic edema (cellular retention of fluids) may play a role as well. Individuals with the condition must immediately descend to a lower altitude or coma and death can occur. Patients are usually given supplemental oxygen and dexamethasone as well. HACE can be prevented by ascending to heights slowly to allow the body more time to acclimatize. Acetazolamide also helps prevent the condition. Untreated patients usually die within 48 hours. Those who receive treatment may take weeks to fully recover. It is a rar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
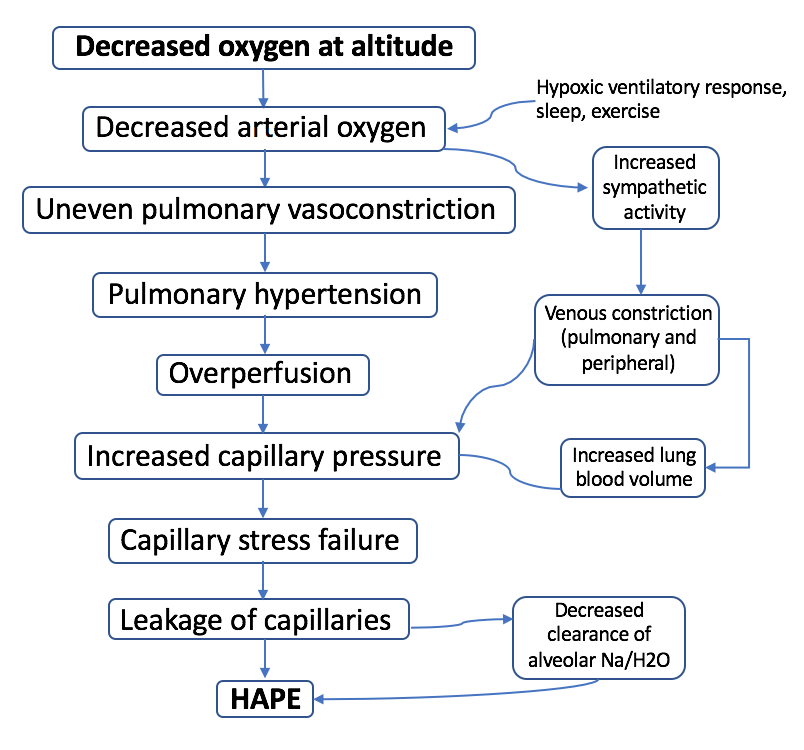
High-altitude Pulmonary Edema
High-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE) is a life-threatening form of non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema that occurs in otherwise healthy people at altitudes typically above . However, cases have also been reported between in more vulnerable subjects. Classically, HAPE occurs in persons normally living at low altitude who travel to an altitude above 2,500 meters (8,200 feet). Re-entry HAPE is also an entity that has been described in persons who normally live at high altitude but who develop pulmonary edema after returning from a stay at low altitude. It is severe presentation of altitude sickness. There are many factors that can make a person more susceptible to developing HAPE, including genetic factors, but detailed understanding is lacking and currently under investigation. HAPE remains the major cause of death related to high-altitude exposure, with a high mortality rate in the absence of adequate emergency treatment. Signs and symptoms Physiological and symptomatic changes ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbaric Medicine
Hyperbaric medicine is medical treatment in which an ambient pressure greater than sea level atmospheric pressure is a necessary component. The treatment comprises hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), the medical use of oxygen at an ambient pressure higher than atmospheric pressure, and therapeutic recompression for decompression illness, intended to reduce the injurious effects of systemic gas bubbles by physically reducing their size and providing improved conditions for elimination of bubbles and excess dissolved gas. The equipment required for hyperbaric oxygen treatment consists of a pressure chamber, which may be of rigid or flexible construction, and a means of delivering 100% oxygen. Operation is performed to a predetermined schedule by trained personnel who monitor the patient and may adjust the schedule as required. HBOT found early use in the treatment of decompression sickness, and has also shown great effectiveness in treating conditions such as gas gangrene and carbon mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Pressure Of Oxygen
Blood gas tension refers to the partial pressure of gases in blood. There are several significant purposes for measuring gas tension. The most common gas tensions measured are oxygen tension (PxO2), carbon dioxide tension (PxCO2) and carbon monoxide tension (PxCO). The subscript ''x'' in each symbol represents the source of the gas being measured: "''a''" meaning arterial, "''A''" being alveolar, "''v''" being venous, and "''c''" being capillary. Blood gas tests (such as arterial blood gas tests) measure these partial pressures. Oxygen tension ;Arterial blood oxygen tension (normal) PaO2 – Partial pressure of oxygen at sea level (160 mmHg in the atmosphere, 21% of standard atmospheric pressure of 760 mmHg) in arterial blood is between 75 mmHg and 100 mmHg. ;Venous blood oxygen tension (normal) PvO2 – Oxygen tension in venous blood at sea level is between 30 mmHg and 40 mmHg. Carbon dioxide tension Carbon dioxide is a by-product of food metaboli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altitude Tent
An altitude tent is a sealed tent used to simulate a higher altitude with reduced oxygen. Living or training at altitude causes the body to adapt to the lower oxygen content by producing more oxygen-carrying red blood cells and hemoglobin, thus causing the body to adapt to the higher altitude and enhancing performance when returning to a lower altitude. Mountain climbers can use them to avoid altitude sickness, and athletes can use them to enhance performance at lower altitudes. History Altitude tents were first marketed in the mid-1990s, and are provided by many different companies in a number of designs. Rationale Sleeping in a simulated altitude environment allows the body to achieve some of the positive adaptations to altitude while still permitting the athlete to perform workouts at an oxygen-rich lower altitude where muscles can perform at their normal work level. An altitude tent is one way to enable athletes living at any elevation to sleep in a high altitude-like envir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilderness Medicine (practice)
Wilderness medicine is a rapidly evolving field and is of increasing importance as more people engage in hiking, climbing, kayaking, and other potentially hazardous activities in the backcountry. The modern definition of wilderness medicine is "medical care delivered in those areas where fixed or transient geographic challenges reduce availability of, or alter requirements for, medical or patient movement resources". A primary focus of the field is the evaluation, prioritization (triage), preliminary treatment of acute injuries or illnesses which occur in those environments and the emergency evacuation of victims. However, back country rescue and wilderness first aid is not the sole activity of wilderness medical professionals, who are also concerned with many additional topics. These include but are not limited to: * Secondary care follow up to first aid in remote settings, such as expeditions * Evaluation of experience and issuance of updated protocols for first response and sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |