|
Porocyte
Porocytes are tubular cells which make up the pores of a sponge known as ostia. Description Covering the sponge is a layer of cells known as the pinacoderm, which is composed of pinacocytes. In a sponge, pinacocytes are a thin, elastic layer which keeps water out. Between the pinacocytes, there are the porocytes that allow water into the sponge. Myocytes are small muscular cells that open and close the porocytes. They also form a circular ring around the osculum and help in closing and opening of it. Once through the pores, water travels down canals. The opening to a porocyte is a pore known as an ostium. In sponges, like Scypha, there are some cells that have an intracellular pore. These cells are known as porocytes. They are present in the Leucosolenia (an asconoid sponge) in the body wall through which water enters the body or they are present in Scypha ''Sycon'' is a genus of calcareous sponges belonging to the family Sycettidae Sycettidae is a family of calcareous spong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Sponge
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. Sponges have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. Sponges do not have nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes. Sponges were first to branch off the evolutionary tree from the last common ancestor of all animals, making them the sister group of all other animals. Etymology The term ''sponge'' derives from the Ancient Greek word ( 'sponge'). Overview Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are multicellular, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostium (sponges)
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. Sponges have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. Sponges do not have nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes. Sponges were first to branch off the evolutionary tree from the last common ancestor of all animals, making them the sister group of all other animals. Etymology The term ''sponge'' derives from the Ancient Greek word ( 'sponge'). Overview Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are multicellular, het ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
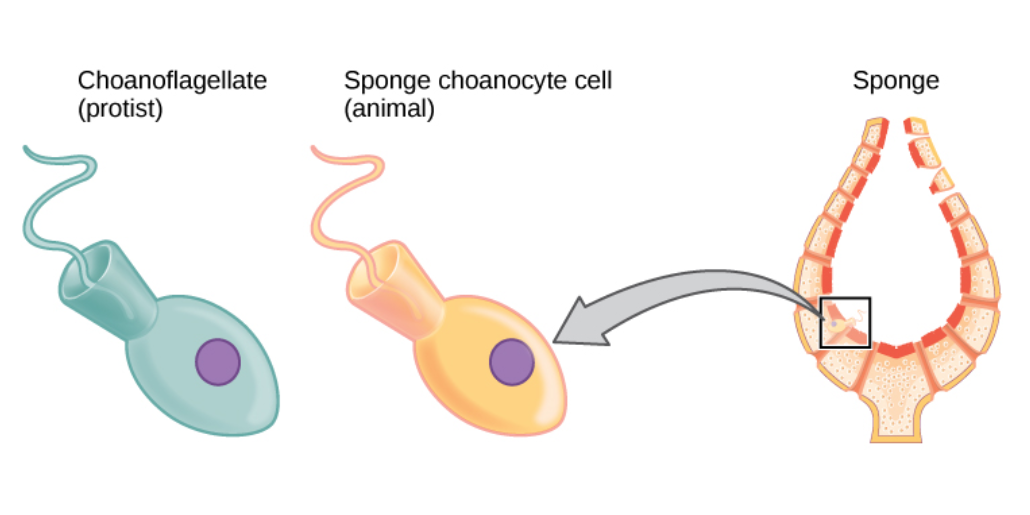
Pinacocytes
The pinacoderm is the outermost layer of body cells (pinacocytes) of organisms of the phylum Porifera (sponges), equivalent to the epidermis in other animals. Structure The pinacoderm is composed of pinacocytes, flattened epithelial cells that can expand or contract to slightly alter the size and shape of the sponge. It also contains porocytes, oval-shaped cells extending from the pinacoderm to the choanoderm (the body layer containing choanocytes Choanocytes (also known as "collar cells") are cells that line the interior of asconoid, syconoid and leuconoid body types of sponges that contain a central flagellum, or ''cilium,'' surrounded by a collar of microvilli which are connected by a t ...). References Sponge anatomy {{animal-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food, energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, H2O, indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. "Water" is also the name of the liquid state of H2O at standard temperature and pressure. A number of natural states of water exist. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice may precipitate in the form of snow. The gaseous state of water is steam or water vapor. Water co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocyte
A muscle cell is also known as a myocyte when referring to either a cardiac muscle cell (cardiomyocyte), or a smooth muscle cell as these are both small cells. A skeletal muscle cell is long and threadlike with many nuclei and is called a muscle fiber. Muscle cells (including myocytes and muscle fibers) develop from embryonic precursor cells called myoblasts. Myoblasts fuse to form multinucleated skeletal muscle cells known as syncytia in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle cells and cardiac muscle cells both contain myofibrils and sarcomeres and form a striated muscle tissue. Cardiac muscle cells form the cardiac muscle in the walls of the heart chambers, and have a single central nucleus. Cardiac muscle cells are joined to neighboring cells by intercalated discs, and when joined in a visible unit they are described as a ''cardiac muscle fiber''. Smooth muscle cells control involuntary movements such as the peristalsis contractions in the esophagus and stomach. Sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scypha
''Sycon'' is a genus of calcareous sponges belonging to the family Sycettidae. These sponges are small, growing up to 7.5 cm and having length from 2.5 to7.5, and are tube-shaped and often white to cream in colour. They are known to aquarium hobbyists as "Pineapple" or "Q-Tip" sponges, and are frequent "hitchhikers" accidentally brought in. Species The following species are recognised in the genus ''Sycon'': *'' Sycon abyssale'' Borojevic & raat-Kleeton, 1965 *'' Sycon acanthoxea'' (Little, 1963) *'' Sycon album'' Tanita, 1942 *'' Sycon ampulla'' (Haeckel, 1870) *'' Sycon antarcticum'' (Jenkin, 1908) *'' Sycon arcticum'' (Haeckel, 1870) *'' Sycon australe'' (Jenkin, 1908) *'' Sycon avus'' Chagas & Cavalcanti, 2017 *'' Sycon barbadense'' (Schuffner, 1877) *'' Sycon bellum'' Chagas & Cavalcanti, 2017 *'' Sycon boreale'' (Schuffner, 1877) *'' Sycon brasiliense'' Borojevic, 1971 *''Sycon calcaravis'' Hozawa, 1929 *''Sycon caminatum'' Thacker, 1908 *'' Sycon capricorn'' Wörheide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Cells
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |