|
Ponderomotive Force
In physics, a ponderomotive force is a nonlinear force that a charged particle experiences in an inhomogeneous oscillating electromagnetic field. It causes the particle to move towards the area of the weaker field strength, rather than oscillating around an initial point as happens in a homogeneous field. This occurs because the particle sees a greater magnitude of force during the half of the oscillation period while it is in the area with the stronger field. The net force during its period in the weaker area in the second half of the oscillation does not offset the net force of the first half, and so over a complete cycle this makes the particle move towards the area of lesser force. The ponderomotive force Fp is expressed by :\mathbf_= -\frac \nabla (E^2) which has units of newtons (in SI units) and where ''e'' is the electrical charge of the particle, ''m'' is its mass, ''ω'' is the angular frequency of oscillation of the field, and ''E'' is the amplitude of the electric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vlasov Equation
The Vlasov equation is a differential equation describing time evolution of the Distribution function (physics), distribution function of plasma (physics), plasma consisting of charged particles with long-range interaction, e.g. Coulomb's law, Coulomb. The equation was first suggested for description of plasma by Anatoly Vlasov in 1938 and later discussed by him in detail in a monograph. Difficulties of the standard kinetic approach First, Vlasov argues that the standard kinetic theory of gases, kinetic approach based on the Boltzmann equation has difficulties when applied to a description of the plasma with long-range Coulomb's law, Coulomb interaction. He mentions the following problems arising when applying the kinetic theory based on pair collisions to plasma dynamics: # Theory of pair collisions disagrees with the discovery by John Strutt, 3rd Baron Rayleigh, Rayleigh, Irving Langmuir and Lewi Tonks of natural vibrations in electron plasma. # Theory of pair collisions is formal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terahertz Time-domain Spectroscopy
In physics, terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS) is a spectroscopic technique in which the properties of matter are probed with short pulses of terahertz radiation. The generation and detection scheme is sensitive to the sample's effect on both the amplitude and the phase of the terahertz radiation. Explanation Typically, an ultrashort pulsed laser is used in the terahertz pulse generation process. In the use of low-temperature grown GaAs as an antenna, the ultrashort pulse creates charge carriers that are accelerated to create the terahertz pulse. In the use of non-linear crystals as a source, a high-intensity ultrashort pulse produces THz radiation from the crystal. A single terahertz pulse can contain frequency components covering much of the terahertz range, often from 0.05 to 4 THz, though the use of an air plasma can contain frequency components up to 40 THz. After THz pulse generation, the pulse is directed by optical techniques, focused through a sample, then mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
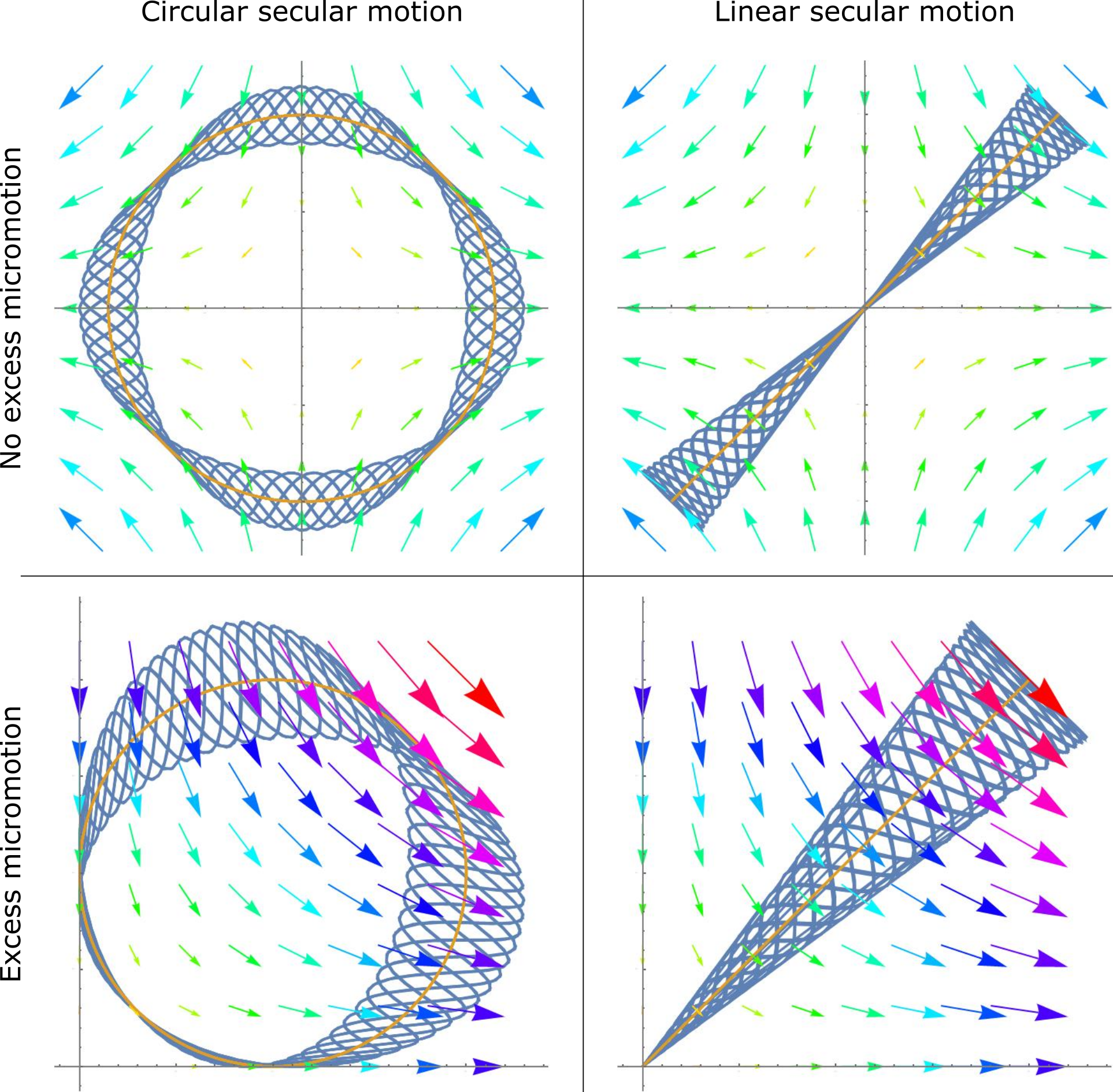
Quadrupole Ion Trap
A quadrupole ion trap or paul trap is a type of ion trap that uses dynamic electric fields to trap charged particles. They are also called radio frequency (RF) traps or Paul traps in honor of Wolfgang Paul, who invented the device and shared the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1989 for this work. It is used as a component of a mass spectrometer or a trapped ion quantum computer. Overview A charged particle, such as an atomic or molecular ion, feels a force from an electric field. It is not possible to create a static configuration of electric fields that traps the charged particle in all three directions (this restriction is known as Earnshaw's theorem). It is possible, however, to create an ''average'' confining force in all three directions by use of electric fields that change in time. To do so, the confining and anti-confining directions are switched at a rate faster than it takes the particle to escape the trap. The traps are also called "radio frequency" traps because the switc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrodeless Plasma Thruster
The electrodeless plasma thruster is a spacecraft propulsion engine commercialized under the acronym "E-IMPAcT" for "Electrodeless-Ionization Magnetized Ponderomotive Acceleration Thruster". It was created by Mr. Gregory Emsellem based on technology developed by French Atomic Energy Commission scientist Dr Richard Geller and Dr. Terenzio Consoli, for high speed plasma beam production. The electrodeless plasma thruster is currently being developed and adapted to various spacecraft propulsion needs bThe Elwing CompanyThe Elwing Company was founded in 2002 by Gregory Emsellem. Operating principle # Propellant is injected at the upstream side of the thruster body. In cases where the propellant used is not gaseous (e.g., alkali metals) at the local temperature, the propellant must be vaporized. # Gaseous propellant is ionized by one of the following methods: #* bombarding the propellant with electrons emitted by a hot cathode or by an electron gun. #* a steady state electrical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Propulsion Engine
A plasma propulsion engine is a type of electric propulsion that generates thrust from a quasi-neutral plasma. This is in contrast with ion thruster engines, which generate thrust through extracting an ion current from the plasma source, which is then accelerated to high velocities using grids/anodes. These exist in many forms (see electric propulsion). However, in the scientific literature, the term "plasma thruster" sometimes encompasses thrusters usually designated as "ion engines". Plasma thrusters do not typically use high voltage grids or anodes/cathodes to accelerate the charged particles in the plasma, but rather use currents and potentials that are generated internally to accelerate the ions, resulting in a lower exhaust velocity given the lack of high accelerating voltages. This type of thruster has a number of advantages. The lack of high voltage grids of anodes removes a possible limiting element as a result of grid ion erosion. The plasma exhaust is 'quasi-neutral', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Acceleration
Plasma acceleration is a technique for accelerating charged particles, such as electrons, positrons, and ions, using the electric field associated with electron plasma wave or other high-gradient plasma structures (like shock and sheath fields). The plasma acceleration structures are created either using ultra-short laser pulses or energetic particle beams that are matched to the plasma parameters. These techniques offer a way to build high performance particle accelerators of much smaller size than conventional devices. The basic concepts of plasma acceleration and its possibilities were originally conceived by Toshiki Tajima and John M. Dawson of UCLA in 1979. The initial experimental designs for a "wakefield" accelerator were conceived at UCLA by Chandrashekhar J. Joshi et al. Current experimental devices show accelerating gradients several orders of magnitude better than current particle accelerators over very short distances, and about one order of magnitude better (1 GeV/m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combined Rf Trap
A quadrupole ion trap or paul trap is a type of ion trap that uses dynamic electric fields to trap charged particles. They are also called radio frequency (RF) traps or Paul traps in honor of Wolfgang Paul, who invented the device and shared the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1989 for this work. It is used as a component of a mass spectrometer or a trapped ion quantum computer. Overview A charged particle, such as an atomic or molecular ion, feels a force from an electric field. It is not possible to create a static configuration of electric fields that traps the charged particle in all three directions (this restriction is known as Earnshaw's theorem). It is possible, however, to create an ''average'' confining force in all three directions by use of electric fields that change in time. To do so, the confining and anti-confining directions are switched at a rate faster than it takes the particle to escape the trap. The traps are also called "radio frequency" traps because the switc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma (physics)
Plasma () 1, where \nu_ is the electron gyrofrequency and \nu_ is the electron collision rate. It is often the case that the electrons are magnetized while the ions are not. Magnetized plasmas are ''anisotropic'', meaning that their properties in the direction parallel to the magnetic field are different from those perpendicular to it. While electric fields in plasmas are usually small due to the plasma high conductivity, the electric field associated with a plasma moving with velocity \mathbf in the magnetic field \mathbf is given by the usual Lorentz force, Lorentz formula \mathbf = -\mathbf\times\mathbf, and is not affected by Debye shielding. Mathematical descriptions To completely describe the state of a plasma, all of the particle locations and velocities that describe the electromagnetic field in the plasma region would need to be written down. However, it is generally not practical or necessary to keep track of all the particles in a plasma. Therefore, plasma physicist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Frequency
In physics, angular frequency "''ω''" (also referred to by the terms angular speed, circular frequency, orbital frequency, radian frequency, and pulsatance) is a scalar measure of rotation rate. It refers to the angular displacement per unit time (for example, in rotation) or the rate of change of the phase of a sinusoidal waveform (for example, in oscillations and waves), or as the rate of change of the argument of the sine function. Angular frequency (or angular speed) is the magnitude of the pseudovector quantity angular velocity.(UP1) One turn is equal to 2''π'' radians, hence \omega = \frac = , where: *''ω'' is the angular frequency (unit: radians per second), *''T'' is the period (unit: seconds), *''f'' is the ordinary frequency (unit: hertz) (sometimes ''ν''). Units In SI units, angular frequency is normally presented in radians per second, even when it does not express a rotational value. The unit hertz (Hz) is dimensionally equivalent, but by convention it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

