|
Polywell
The polywell is a proposed design for a fusion reactor using an electric field to heat ions to fusion conditions. The design is related to the fusor, the high beta fusion reactor, the magnetic mirror, and the biconic cusp. A set of electromagnets generates a magnetic field that traps electrons. This creates a negative voltage, which attracts positive ions. As the ions accelerate towards the negative center, their kinetic energy rises. Ions that collide at high enough energies can fuse. Mechanism Fusor A Farnsworth-Hirsch fusor consists of two wire cages, one inside the other, often referred to as grids, that are placed inside a vacuum chamber. The outer cage has a positive voltage versus the inner cage. A fuel, typically, deuterium gas, is injected into this chamber. It is heated past its ionization temperature, making positive ions. The ions are positive and move towards the negative inner cage. Those that miss the wires of the inner cage fly through the center of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Bussard
Robert W. Bussard (August 11, 1928 – October 6, 2007) was an American physicist who worked primarily in nuclear fusion energy research. He was the recipient of the Schreiber-Spence Achievement Award for STAIF-2004. He was also a fellow of the International Academy of Astronautics and held a Ph.D. from Princeton University. Kiwi (Rover-A) In June 1955 Bussard moved to Los Alamos and joined the Nuclear Propulsion Division's Project Rover designing nuclear thermal rocket engines.Bussard, Robert. "Nuclear Rocketry - The First Bright Hopes", Astronautics, Vol. 7, No. 12, Dec. 1962, pp. 32–35 Bussard and R.D. DeLauer wrote two important monographs on nuclear propulsion, ''Nuclear Rocket Propulsion'' and ''Fundamentals of Nuclear Flight''. Bussard ramjet In 1960, Bussard conceived of the Bussard ramjet, an interstellar space drive powered by hydrogen fusion using hydrogen collected with a magnetic field from the interstellar gas. Due to the presence of high-energy particle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
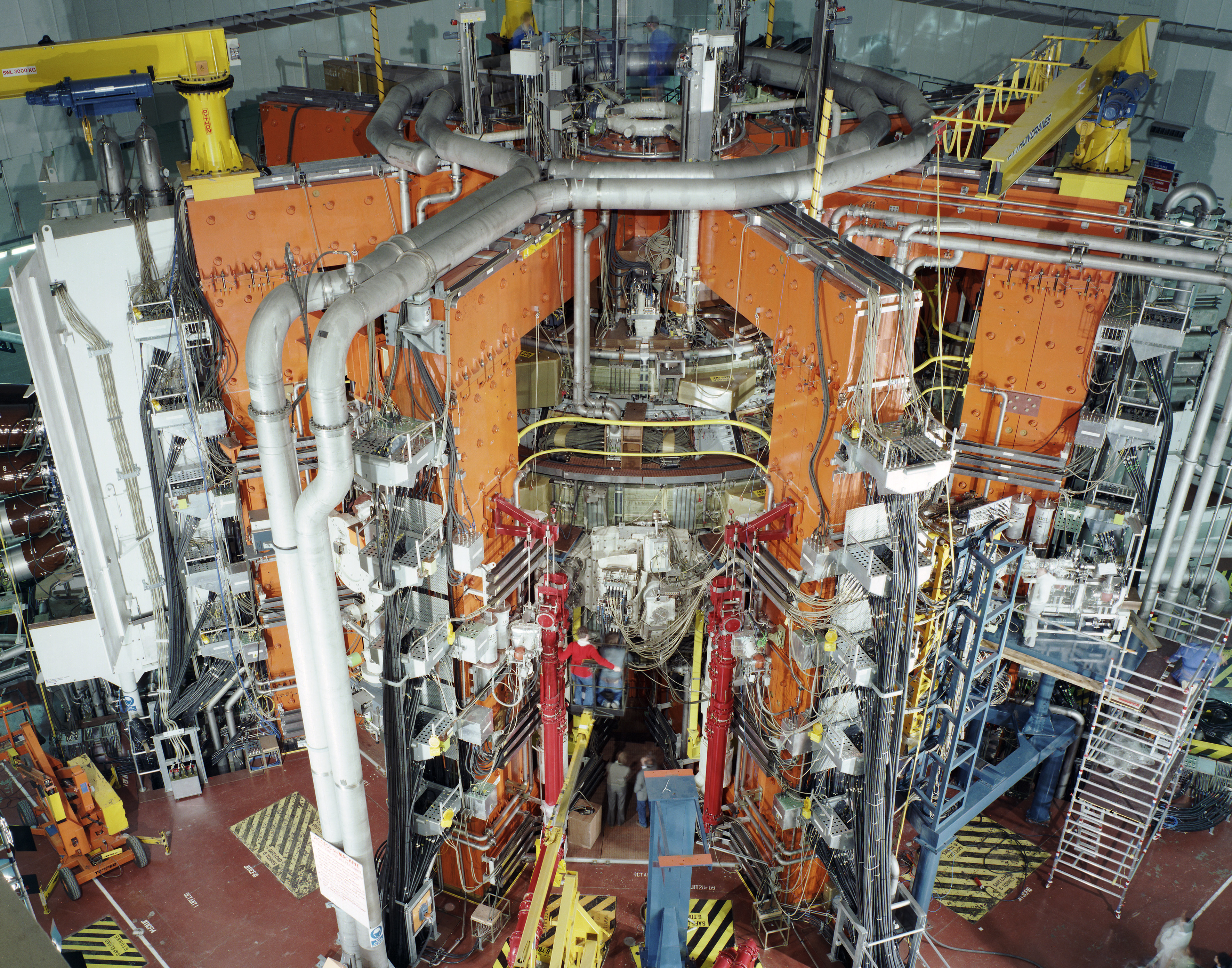
Fusion Reactor
Fusion power is a proposed form of power generation that would generate electricity by using heat from nuclear fusion reactions. In a fusion process, two lighter atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, while releasing energy. Devices designed to harness this energy are known as fusion reactors. Research into fusion reactors began in the 1940s, but as of 2022, only one design, an inertial confinement laser-driven fusion machine at the US National Ignition Facility, has conclusively produced a positive fusion energy gain factor, i.e. more power output than input. Fusion processes require fuel and a confined environment with sufficient temperature, pressure, and confinement time to create a plasma in which fusion can occur. The combination of these figures that results in a power-producing system is known as the Lawson criterion. In stars, the most common fuel is hydrogen, and gravity provides extremely long confinement times that reach the conditions needed for fusion e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Mirror
A magnetic mirror, known as a magnetic trap (магнитный захват) in Russia and briefly as a pyrotron in the US, is a type of magnetic confinement device used in fusion power to trap high temperature plasma using magnetic fields. The mirror was one of the earliest major approaches to fusion power, along with the stellarator and z-pinch machines. In a classic magnetic mirror, a configuration of electromagnets is used to create an area with an increasing density of magnetic field lines at either end of the confinement area. Particles approaching the ends experience an increasing force that eventually causes them to reverse direction and return to the confinement area. This mirror effect will only occur for particles within a limited range of velocities and angles of approach, those outside the limits will escape, making mirrors inherently "leaky". An analysis of early fusion devices by Edward Teller pointed out that the basic mirror concept is inherently unstable. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biconic Cusp
The biconic cusp was one of the earliest suggestions for plasma confinement in a fusion reactor. It consists of two parallel electromagnets with the current running in opposite directions, creating oppositely directed magnetic fields. The two fields interact to form a "null area" between them where the fusion fuel can be trapped. Most early work on the cusp design was carried out at the Courant Institute in New York by Harold Grad in the late 1950s and early 1960s. Variations on the basic concept include the picket fence reactor built at Los Alamos in the 1950s and ring reactors. All of these devices leaked their fuel plasma at rates much greater than predicted and most work on the concept ended by the mid-1960s. Mikhail Ioffe later demonstrated why these problems arose. A later device that shares some design with the cusp is the polywell concept of the 1990s. This can be thought of as multiple cusps arranged in three dimensions. Description The magnetic fields in this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusor Mechanism
A fusor is a device that uses an electric field to heat ions to nuclear fusion conditions. The machine induces a voltage between two metal cages, inside a vacuum. Positive ions fall down this voltage drop, building up speed. If they collide in the center, they can fuse. This is one kind of an inertial electrostatic confinement device – a branch of fusion research. A Farnsworth–Hirsch fusor is the most common type of fusor. This design came from work by Philo T. Farnsworth in 1964 and Robert L. Hirsch in 1967.Robert L. Hirsch, "Inertial-Electrostatic Confinement of Ionized Fusion Gases", Journal of Applied Physics, v. 38, no. 7, October 1967 A variant type of fusor had been proposed previously by William Elmore, James L. Tuck, and Ken Watson at the Los Alamos National Laboratory"On the Inertial Electrostatic Confinement of a Plasma" William Elmore, James Tuck and Ken Watson, The Physics of Fluids, January 30, 1959 though they never built the machine. Fusors have been bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusor
A fusor is a device that uses an electric field to heat ions to nuclear fusion conditions. The machine induces a voltage between two metal cages, inside a vacuum. Positive ions fall down this voltage drop, building up speed. If they collide in the center, they can fuse. This is one kind of an inertial electrostatic confinement device – a branch of fusion research. A Farnsworth–Hirsch fusor is the most common type of fusor. This design came from work by Philo T. Farnsworth in 1964 and Robert L. Hirsch in 1967.Robert L. Hirsch, "Inertial-Electrostatic Confinement of Ionized Fusion Gases", Journal of Applied Physics, v. 38, no. 7, October 1967 A variant type of fusor had been proposed previously by William Elmore, James L. Tuck, and Ken Watson at the Los Alamos National Laboratory"On the Inertial Electrostatic Confinement of a Plasma" William Elmore, James Tuck and Ken Watson, The Physics of Fluids, January 30, 1959 though they never built the machine. Fusors have been b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Beta Fusion Reactor
The Lockheed Martin Compact Fusion Reactor (CFR) is a fusion power project at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works. Its high- beta configuration, which implies that the ratio of plasma pressure to magnetic pressure is greater than or equal to 1 (compared to tokamak designs' 0.05), allows a compact fusion reactor (CFR) design and expedited development. The CFR chief designer and technical team lead, Thomas McGuire studied fusion as a source of space propulsion in response to a NASA desire to improve travel times to Mars. History The project began in 2010, and was publicly presented at the Google Solve for X forum on February 7, 2013. In October 2014, Lockheed Martin announced a plan to "build and test a compact fusion reactor in less than a year with a prototype to follow within five years". In May 2016, Rob Weiss announced that Lockheed Martin continued to support the project and would increase its investment in it. Design CFR plans to achieve high beta (the ratio of plasma press ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Fusion
Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei are combined to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles (neutrons or protons). The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the release or absorption of energy. This difference in mass arises due to the difference in nuclear binding energy between the atomic nuclei before and after the reaction. Nuclear fusion is the process that powers active or main-sequence stars and other high-magnitude stars, where large amounts of energy are released. A nuclear fusion process that produces atomic nuclei lighter than iron-56 or nickel-62 will generally release energy. These elements have a relatively small mass and a relatively large binding energy per nucleon. Fusion of nuclei lighter than these releases energy (an exothermic process), while the fusion of heavier nuclei results in energy retained by the product nucleons, and the resulting reaction is end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Potential
The electric potential (also called the ''electric field potential'', potential drop, the electrostatic potential) is defined as the amount of work energy needed to move a unit of electric charge from a reference point to the specific point in an electric field. More precisely, it is the energy per unit charge for a test charge that is so small that the disturbance of the field under consideration is negligible. Furthermore, the motion across the field is supposed to proceed with negligible acceleration, so as to avoid the test charge acquiring kinetic energy or producing radiation. By definition, the electric potential at the reference point is zero units. Typically, the reference point is earth or a point at infinity, although any point can be used. In classical electrostatics, the electrostatic field is a vector quantity expressed as the gradient of the electrostatic potential, which is a scalar quantity denoted by or occasionally , equal to the electric potential ener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langmuir Probe
A Langmuir probe is a device used to determine the electron temperature, electron density, and electric potential of a plasma. It works by inserting one or more electrodes into a plasma, with a constant or time-varying electric potential between the various electrodes or between them and the surrounding vessel. The measured currents and potentials in this system allow the determination of the physical properties of the plasma. ''I-V'' characteristic of the Debye sheath The beginning of Langmuir probe theory is the ''I–V'' characteristic of the Debye sheath, that is, the current density flowing to a surface in a plasma as a function of the voltage drop across the sheath. The analysis presented here indicates how the electron temperature, electron density, and plasma potential can be derived from the ''I–V'' characteristic. In some situations a more detailed analysis can yield information on the ion density (n_i), the ion temperature T_i, or the electron energy distribution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |