|
Polymethine
Polymethines are compounds made up from an ''odd'' number of methine groups (CH) bound together by alternating single and double bonds.Kachovski and Dekhtyar, ''Dyes and Pigments'', 22 (1983) 83-97. Compounds made up from an ''even'' number of methine groups are known as polyenes. Polymethine dyes Cyanines are synthetic dyes belonging to polymethine group. Anthocyanidins are natural plant pigments belonging to the group of the polymethine dyes. Polymethines are fluorescent dyes that may be attached to nucleic acid probes for different uses, ''e.g.'', to accurately count reticulocyte Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells (RBCs). In the process of erythropoiesis (red blood cell formation), reticulocytes develop and mature in the bone marrow and then circulatory system, circulate for about a day in the blood stream before ...s. References Alkenes {{alkene-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanine
Cyanines, also referred to as tetramethylindo(di)-carbocyanines are a synthetic dye family belonging to the polymethine group. Although the name derives etymologically from terms for shades of blue, the cyanine family covers the electromagnetic spectrum from near IR to UV. Chemically, cyanines are a conjugated system between two nitrogen atoms; in each resonance structure, exactly one nitrogen atom is oxidized to an iminium. Typically, they form part of a nitrogenous heterocyclic system. The main application for cyanine dyes is in biological labeling. Nevertheless, there is a wide literature on both their synthesis and uses, and cyanines are common in some CD and DVD media. Structure Cyanines have been classified in many ways: * ''Streptocyanines'' or ''open chain cyanines'': : R2N+=CH H=CH'n''-NR2 (I) * ''Hemicyanines'': : Aryl=N+=CH H=CH'n''-NR2 (II) * ''Closed chain cyanines'': :Aryl=N+=CH H=CH'n''-N=Aryl (III) Additionally, these classes are recognized: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthocyanidin
Anthocyanidins are common plant pigments, the sugar-free counterparts of anthocyanins. They are based on the flavylium cation, an oxonium ion, with various groups substituted for its hydrogen atoms. They generally change color from red through purple, blue, and bluish green as a function of pH. Anthocyanidins are an important subclass of the polymethine dyes and flavonoids. The flavylium cation is a chromenylium cation with a phenyl group substituted in position 2; and chromenylium (also called benzopyrylium) is a bicyclic version of pyrylium. The positive charge can move around the molecule. At least 31 monomeric anthocyanidins have been properly identified in living organisms, mostly as the core components of anthocyanins. The latter are responsible for the red, purple, blue, or black color of many fruits (like grapes and blueberries), flowers (like roses), leaves (like purple cabbage), and even tubers (like radishes and purple yams). They are also found in some animals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
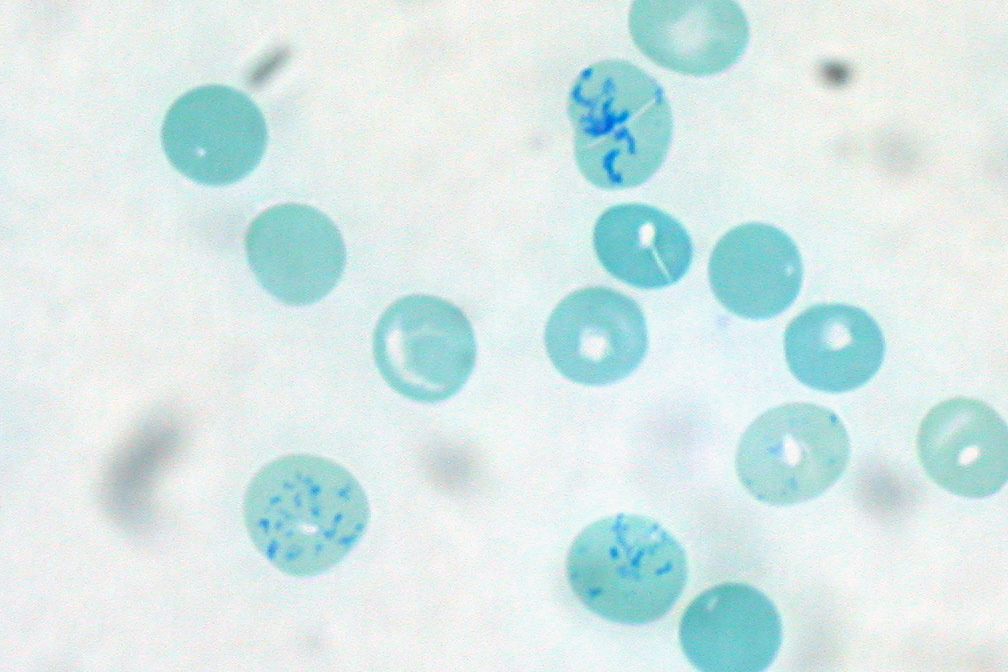
Reticulocyte
Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells (RBCs). In the process of erythropoiesis (red blood cell formation), reticulocytes develop and mature in the bone marrow and then circulatory system, circulate for about a day in the blood stream before developing into mature red blood cells. Like mature red blood cells, in mammals, reticulocytes do not have a cell nucleus. They are called reticulocytes because of a reticular (mesh-like) network of ribosome, ribosomal RNA that becomes visible under a microscope with certain staining, stains such as new methylene blue and Romanowsky stain. Clinical significance To accurately measure reticulocyte counts, automated flow cytometry, counters use a combination of laser excitation, detectors and a fluorophore, fluorescent dye that marks RNA and DNA (such as titan yellow or polymethine). Reticulocytes appear slightly bluer than other red cells when looked at with the normal Romanowsky stain. Reticulocytes are also relatively large, a character ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methine
In organic chemistry, a methine group or methine bridge is a trivalent functional group , derived formally from methane. It consists of a carbon atom bound by two single covalent bond, bonds and one double bond, where one of the single bonds is to a hydrogen. The group is also called methyne or methene; its International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, IUPAC systematic name is methylylidene or methanylylidene (2007''Methanylylidene group''in the Chemical Entities of Biological Interest (ChEBI) database. Accessed on 2015-03-05. This group is sometimes called "methylidyne", however that name belongs properly to either the methylidyne group (connected to the rest of the molecule by a triple bond) or to the methylidyne radical (the two atoms as a free molecule with dangling bonds). The name "methine" is also widely used in non-systematic nomenclature for the methanetriyl group (IUPAC): a carbon atom with four single bonds, where one bond is to a hydrogen (). (2007''Methan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Bond
In chemistry, a double bond is a covalent bond between two atoms involving four bonding electrons as opposed to two in a single bond. Double bonds occur most commonly between two carbon atoms, for example in alkenes. Many double bonds exist between two different elements: for example, in a carbonyl group between a carbon atom and an oxygen atom. Other common double bonds are found in azo compounds (N=N), imines (C=N), and sulfoxides (S=O). In a skeletal formula, a double bond is drawn as two parallel lines (=) between the two connected atoms; typographically, the equals sign is used for this. Double bonds were first introduced in chemical notation by Russian chemist Alexander Butlerov. Double bonds involving carbon are stronger and shorter than single bonds. The bond order is two. Double bonds are also electron-rich, which makes them potentially more reactive in the presence of a strong electron acceptor (as in addition reactions of the halogens). File:Ethene structural.svg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyenes
In organic chemistry, polyenes are poly- unsaturated, organic compounds that contain at least three alternating double () and single () carbon–carbon bonds. These carbon–carbon double bonds interact in a process known as conjugation, resulting in some unusual optical properties. Related to polyenes are dienes, where there are only two alternating double and single bonds. The following polyenes are used as antibiotics for humans: amphotericin B, nystatin, candicidin, pimaricin, methyl partricin, and trichomycin. Optical properties Some polyenes are brightly colored, an otherwise rare property for a hydrocarbon. Normally alkenes absorb in the ultraviolet region of a spectrum, but the absorption energy state of polyenes with numerous conjugated double bonds can be lowered such that they enter the visible region of the spectrum, resulting in compounds which are coloured (because they contain a chromophore). Thus many natural dyes contain linear polyenes. Chemical and electri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |