|
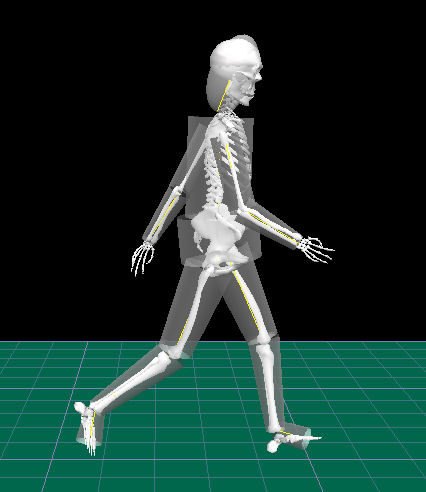
Polygon Mesh
In 3D computer graphics and solid modeling, a polygon mesh is a collection of , s and s that defines the shape of a polyhedron, polyhedral object's surface. It simplifies Rendering (computer graphics), rendering, as in a wire-frame model. The face (geometry), faces usually consist of triangles (triangle mesh), quadrilaterals (quads), or other simple convex polygon, convex polygons (n-gons). A polygonal mesh may also be more generally composed of concave polygon, concave polygons, or even Polygon with holes, polygons with holes. The study of Polygon (computer graphics), polygon meshes is a large sub-field of computer graphics (specifically 3D computer graphics) and geometric modeling. Different representations of polygon meshes are used for different applications and goals. The variety of operations performed on meshes includes Boolean logic (Constructive solid geometry), Subdivision surfaces, smoothing, and Level of detail (computer graphics), simplification. Algorithms also exist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolphin Triangle Mesh
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal in the cetacean clade Odontoceti (toothed whale). Dolphins belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (the brackish dolphins), and possibly extinct Lipotidae (baiji or Chinese river dolphin). There are 40 extant species named as dolphins. Dolphins range in size from the and Maui's dolphin to the and orca. Various species of dolphins exhibit sexual dimorphism where the males are larger than females. They have streamlined bodies and two limbs that are modified into flippers. Though not quite as flexible as Pinniped, seals, they are faster; some dolphins can briefly travel at speeds of or leap about . Dolphins use their conical teeth to capture fast-moving Predation, prey. They have well-developed hearing which is adapted for both air and water; it is so well developed that some can survive even if they are blind. Some species are w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Modeling
__NOTOC__ Geometric modeling is a branch of applied mathematics and computational geometry that studies methods and algorithms for the mathematical description of shapes. The shapes studied in geometric modeling are mostly two- or three-dimensional (''solid figures''), although many of its tools and principles can be applied to sets of any finite dimension. Today most geometric modeling is done with computers and for computer-based applications. Two-dimensional models are important in computer typography and technical drawing. Three-dimensional models are central to computer-aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM), and widely used in many applied technical fields such as civil and mechanical engineering, architecture, geology and medical image processing. Geometric models are usually distinguished from procedural and object-oriented models, which define the shape implicitly by an opaque algorithm that generates its appearance. They are also contrasted with digital imag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Triangulation
Triangulation of a surface means * a ''net'' of triangles, which covers a given surface partly or totally, ''or'' * the ''procedure'' of generating the points and triangles of such a net of triangles. Approaches This article describes the generation of a net of triangles. In literature there are contributions which deal with the optimization of a given net. Surface triangulations are important for * visualizing surfaces and * the application of finite element methods. The triangulation of a ''parametrically'' defined surface is simply achieved by triangulating the area of definition (see second figure, depicting the Monkey Saddle). However, the triangles may vary in shape and extension in object space, posing a potential drawback. This can be minimized through adaptive methods that consider step width while triangulating the parameter area. To triangulate an ''implicit surface'' (defined by one or more equations) is more difficult. There exist essentially two methods. * O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesh Overview
Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) is a comprehensive controlled vocabulary for the purpose of indexing journal articles and books in the life sciences. It serves as a thesaurus of index terms that facilitates searching. Created and updated by the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), it is used by the MEDLINE/PubMed article database and by NLM's catalog of book holdings. MeSH is also used by ClinicalTrials.gov registry to classify which diseases are studied by trials registered in ClinicalTrials. MeSH was introduced in the 1960s, with the NLM's own index catalogue and the subject headings of the Quarterly Cumulative Index Medicus (1940 edition) as precursors. The yearly printed version of MeSH was discontinued in 2007; MeSH is now available only online. It can be browsed and downloaded free of charge through PubMed. Originally in English, MeSH has been translated into numerous other languages and allows retrieval of documents from different origins. Structure MeSH v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volume Mesh
In 3D computer graphics and modeling, a volumetric mesh is a polyhedral representation of the interior region of an object. It is unlike polygon meshes, which represent only the surface as polygons. Applications One application of volumetric meshes is in finite element analysis, which may use regular or irregular volumetric meshes to compute internal stresses and forces in an object throughout the entire volume of the object. Volume meshes may also be used for portal rendering. See also * B-rep * Voxels * Hypergraph * Volume rendering In scientific visualization and computer graphics, volume rendering is a set of techniques used to display a 2D projection of a 3D discretely sampled data set, typically a 3D scalar field. A typical 3D data set is a group of 2D slice image ... References 3D computer graphics Computer graphics data structures Mesh generation {{mathapplied-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marching Cubes
Marching cubes is a computer graphics algorithm, published in the 1987 SIGGRAPH proceedings by Lorensen and Cline, for extracting a polygonal mesh of an isosurface from a three-dimensional discrete scalar field (the elements of which are sometimes called voxels). The applications of this algorithm are mainly concerned with medical visualizations such as CT and MRI scan data images, and special effects or 3-D modelling with what is usually called metaballs or other metasurfaces. The marching cubes algorithm is meant to be used for 3-D; the 2-D version of this algorithm is called the marching squares algorithm. History The algorithm was developed by William E. Lorensen (1946-2019) and Harvey E. Cline as a result of their research for General Electric General Electric Company (GE) was an American Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1892, incorporated in the New York (state), state of New York and headquartere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesh Generation
Mesh generation is the practice of creating a polygon mesh, mesh, a subdivision of a continuous geometric space into discrete geometric and topological cells. Often these cells form a simplicial complex. Usually the cells partition the geometric input domain. Mesh cells are used as discrete local approximations of the larger domain. Meshes are created by computer algorithms, often with human guidance through a GUI, depending on the complexity of the domain and the type of mesh desired. A typical goal is to create a mesh that accurately captures the input domain geometry, with high-quality (well-shaped) cells, and without so many cells as to make subsequent calculations intractable. The mesh should also be fine (have small elements) in areas that are important for the subsequent calculations. Meshes are used for rendering (computer graphics), rendering to a computer screen and for physical simulation such as finite element analysis or computational fluid dynamics. Meshes are compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wire-frame Model
In 3D computer graphics, a wire-frame model (also spelled wireframe model) is a visual representation of a three-dimensional (3D) physical object. It is based on a polygon mesh or a volumetric mesh, created by specifying each Edge (geometry), edge of the physical object where two mathematically continuous smooth surfaces meet, or by connecting an object's constituent Vertex (computer graphics), vertices using (straight) straight line, lines or Curve (geometry), curves. The object is projected into screen space and rendering (computer graphics), rendered by drawing lines at the location of each edge. The term "wire frame" comes from designers using metal wire to represent the three-dimensional shape of solid objects. 3D wireframe computer models allow for the construction and manipulation of solids and solid surfaces. 3D solid modeling efficiently draws higher quality representations of solids than conventional Line art, line drawing. Using a wire-frame model allows for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rigid-body Dynamics
In the physical science of dynamics, rigid-body dynamics studies the movement of systems of interconnected bodies under the action of external forces. The assumption that the bodies are '' rigid'' (i.e. they do not deform under the action of applied forces) simplifies analysis, by reducing the parameters that describe the configuration of the system to the translation and rotation of reference frames attached to each body. This excludes bodies that display fluid, highly elastic, and plastic behavior. The dynamics of a rigid body system is described by the laws of kinematics and by the application of Newton's second law ( kinetics) or their derivative form, Lagrangian mechanics. The solution of these equations of motion provides a description of the position, the motion and the acceleration of the individual components of the system, and overall the system itself, as a function of time. The formulation and solution of rigid body dynamics is an important tool in the compute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collision Detection
Collision detection is the computational problem of detecting an intersection of two or more objects in virtual space. More precisely, it deals with the questions of ''if'', ''when'' and ''where'' two or more objects intersect. Collision detection is a classic problem of computational geometry with applications in computer graphics, physical simulation, video games, robotics (including autonomous driving) and computational physics. Collision detection algorithms can be divided into operating on 2D or 3D spatial objects. Overview Collision detection is closely linked to calculating the distance between objects, as two objects (or more) intersect when the distance between them reaches zero or even becomes negative. Negative distance indicates that one object has penetrated another. Performing collision detection requires more context than just the distance between the objects. Accurately identifying the points of contact on both objects' surfaces is also essential for the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray Tracing (graphics)
In 3D computer graphics, ray tracing is a technique for modeling Light transport theory, light transport for use in a wide variety of Rendering (computer graphics), rendering algorithms for generating digital image, digital images. On a spectrum of Computation time, computational cost and visual fidelity, ray tracing-based rendering techniques, such as ray casting, #Recursive ray tracing algorithm, recursive ray tracing, Distributed ray tracing, distribution ray tracing, photon mapping and path tracing, are generally slower and higher fidelity than scanline rendering methods. Thus, ray tracing was first deployed in applications where taking a relatively long time to render could be tolerated, such as still computer-generated imagery, CGI images, and film and television visual effects (VFX), but was less suited to real-time computer graphics, real-time applications such as video games, where Frame rate, speed is critical in rendering each Film frame, frame. Since 2018, however, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Level Of Detail (computer Graphics)
In computer graphics, level of detail (LOD) refers to the complexity of a 3D model representation. LOD can be decreased as the model moves away from the viewer or according to other metrics such as object importance, viewpoint-relative speed or position. LOD techniques increase the efficiency of rendering (computer graphics), rendering by decreasing the workload on graphics pipeline stages, usually vertex transformations. The reduced visual quality of the model is often unnoticed because of the small effect on object appearance when distant or moving fast. Although most of the time LOD is applied to Geometry (computer graphics), geometry detail only, the basic concept can be generalized. Recently, LOD techniques also included shader management to keep control of pixel complexity. A form of level of detail management has been applied to texture maps for years, under the name of mipmapping, also providing higher rendering quality. It is commonplace to say that "an object has been '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |