|
Polyandry In Nature
In behavioral ecology, polyandry is a class of mating system where one female mates with several males in a breeding season. Polyandry is often compared to the polygyny system based on the cost and benefits incurred by members of each sex. Polygyny is where one male mates with several females in a breeding season (e.g., lions, deer, some primates, and many systems where there is an alpha male). A common example of polyandrous mating can be found in the field cricket (''Gryllus bimaculatus'') of the invertebrate order Orthoptera (containing crickets, grasshoppers, and groundhoppers). Polyandrous behavior is also prominent in many other insect species, including the red flour beetle and the species of spider ''Stegodyphus lineatus''. Polyandry also occurs in some primates such as marmosets, mammal groups, the marsupial genus' '' Antechinus'' and bandicoots, around 1% of all bird species, such as jacanas and dunnocks, insects such as honeybees, and fish such as pipefish. Predictors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacana Spinosa -Palo Verde National Park, Costa Rica-8
Jacana may refer to: * Jacana, a common name for the tropical bird family Jacanidae ** Jacana (genus), ''Jacana'' (genus), a genus of Jacanidae found in the Americas * Jácana or ''Pouteria multiflora'', a tree species in the family Sapotaceae of the order Ericales * USS Jacana (AMS-193), USS ''Jacana'' (AMS-193), a Falcon-class motor minesweeper Places * Jacana, Victoria, a suburb of Melbourne, Australia * Jaçanã (district of São Paulo) * Jaçanã, Rio Grande do Norte, a municipality in Brazil * Jácana, Yauco, Puerto Rico, a barrio in the municipality of Yauco, Puerto Rico * Jácanas, a barrio in the municipality of Yabucoa, Puerto Rico {{disambiguation, geo, plant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthoptera
Orthoptera () is an order of insects that comprises the grasshoppers, locusts, and crickets, including closely related insects, such as the bush crickets or katydids and wētā. The order is subdivided into two suborders: Caelifera – grasshoppers, locusts, and close relatives; and Ensifera – crickets and close relatives. More than 20,000 species are distributed worldwide. The insects in the order have incomplete metamorphosis, and produce sound (known as a "stridulation") by rubbing their wings against each other or their legs, the wings or legs containing rows of corrugated bumps. The tympanum, or ear, is located in the front tibia in crickets, mole crickets, and bush crickets or katydids, and on the first abdominal segment in the grasshoppers and locusts. These organisms use vibrations to locate other individuals. Grasshoppers and other orthopterans are able to fold their wings (i.e. they are members of Neoptera). Etymology The name is derived from the Greek ὀρθό� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
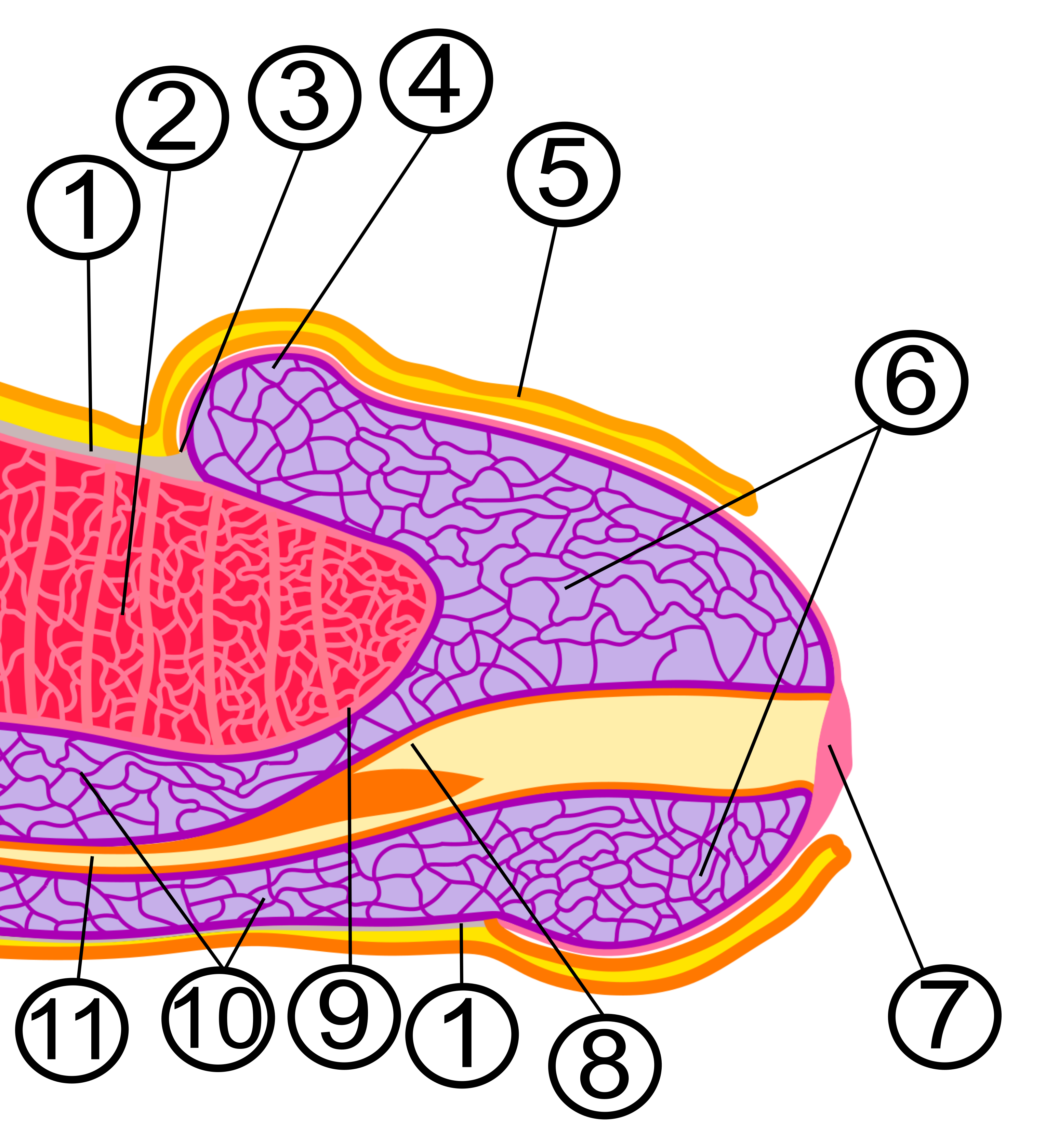
Cervix
The cervix or cervix uteri (Latin, 'neck of the uterus') is the lower part of the uterus (womb) in the human female reproductive system. The cervix is usually 2 to 3 cm long (~1 inch) and roughly cylindrical in shape, which changes during pregnancy. The narrow, central cervical canal runs along its entire length, connecting the uterine cavity and the lumen of the vagina. The opening into the uterus is called the internal os, and the opening into the vagina is called the external os. The lower part of the cervix, known as the vaginal portion of the cervix (or ectocervix), bulges into the top of the vagina. The cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time of Hippocrates, over 2,000 years ago. The cervical canal is a passage through which sperm must travel to fertilize an egg cell after sexual intercourse. Several methods of contraception, including cervical caps and cervical diaphragms, aim to block or prevent the passage of sperm through the cervical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvic Thrusting
The pelvic thrust is the thrusting motion of the pelvic region, which is used for a variety of activities, such as dance or sexual activity. Sexual activity The pelvic thrust is used during copulation by many species of mammals, including humans, or for other sexual activities (such as non-penetrative sex). In 2007, German scientists noted that female monkeys could increase the vigor and amount of pelvic thrusts made by the male by shouting during intercourse. In whitetail deer, copulation consists of a single pelvic thrust. Dance One of the first to perform this move on stage was Elvis Presley. It was quite controversial due to its obvious sexual connotations. Due to this controversy, he was sometimes shown (as seen on his third appearance on ''The Ed Sullivan Show'') from the waist up on TV. Later, the pelvic thrust also became one of the signature moves of Michael Jackson. Twerking, a reverse and sometimes passive form of pelvic thrust dance move, is also a very popular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glans Penis
In male human anatomy, the glans penis, commonly referred to as the glans, is the bulbous structure at the distal end of the human penis that is the human male's most sensitive erogenous zone and their primary anatomical source of sexual pleasure. It is anatomically homologous to the clitoral glans. The glans penis is part of the male reproductive organs in humans and other mammals where it may appear smooth, spiny, elongated or divided. It is externally lined with mucosal tissue, which creates a smooth texture and glossy appearance. In humans, the glans is a continuation of the corpus spongiosum of the penis. At the summit appears the urinary meatus and at the base forms the corona glandis. An elastic band of tissue, known as the frenulum, runs on its ventral surface. In men who are not circumcised, it is completely or partially covered by the foreskin. In adults, the foreskin can generally be retracted over and past the glans manually or sometimes automatically during an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordon G
Gordon may refer to: People * Gordon (given name), a masculine given name, including list of persons and fictional characters * Gordon (surname), the surname * Gordon (slave), escaped to a Union Army camp during the U.S. Civil War * Clan Gordon, aka the House of Gordon, a Scottish clan Education * Gordon State College, a public college in Barnesville, Georgia * Gordon College (Massachusetts), a Christian college in Wenham, Massachusetts * Gordon College (Pakistan), a Christian college in Rawalpindi, Pakistan * Gordon College (Philippines), a public university in Subic, Zambales * Gordon College of Education, a public college in Haifa, Israel Places Australia *Gordon, Australian Capital Territory *Gordon, New South Wales * Gordon, South Australia *Gordon, Victoria *Gordon River, Tasmania *Gordon River (Western Australia) Canada *Gordon Parish, New Brunswick *Gordon/Barrie Island, municipality in Ontario *Gordon River (Chochocouane River), a river in Quebec Scotland *Gordon ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acromyrmex Echinatior
''Acromyrmex echinatior'' is a species of New World ants of the subfamily Myrmicinae of the genus ''Acromyrmex''. It is found in the wild naturally from Mexico to Panama. In Costa Rica this species prefers open dry habitats such as urban areas around San Jose and seasonally dry habitats of Guanacaste Province. There is evidence to suggest that this species nests may occasionally be arboreal. Queens multiply mate, and colonies are facultatively polygynous. Nonreproductive workers of the colony 'police', that is, selectively destroy worker-laid eggs, but do not attack reproductive workers. Relatedness incentives are the most likely ultimate cause of the evolutionary maintenance of worker–egg policing in ''A. echinatior''. See also *List of leafcutter ants This is a list of leafcutter ants, comprising 42 species from two genera: ''Atta'' and ''Acromyrmex ''Acromyrmex'' is a genus of New World ants of the subfamily Myrmicinae. This genus is found in South America and par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redback Spider
The redback spider (''Latrodectus hasselti''), also known as the Australian black widow, is a species of highly venomous spider believed to originate in South Australia or adjacent Western Australian deserts, but now found throughout Australia, Southeast Asia and New Zealand, with colonies elsewhere outside Australia. It is a member of the cosmopolitan genus ''Latrodectus'', the widow spiders. The adult female is easily recognised by her spherical black body with a prominent red stripe on the upper side of her abdomen and an hourglass-shaped red/orange streak on the underside. Females usually have a body length of about , while the male is much smaller, being only long. Mainly nocturnal, the female redback lives in an untidy web in a warm sheltered location, commonly near or inside human residences. It preys on insects, spiders and small vertebrates that become ensnared in its web. It kills its prey by injecting a complex venom through its two fangs when it bites, before wrap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wattled Jacana
The wattled jacana (''Jacana jacana'') is a wader which is a resident breeder from western Panama and Trinidad south through most of South America east of the Andes. Breeding The wattled jacana lays four black-marked brown eggs in a floating nest. The male, as with other jacanas and some other wader families like the phalaropes, takes responsibility for incubation, with two eggs held between each wing and the breast. The females are polyandrous and will help to defend the nests of up to four mates. Description These are conspicuous and unmistakable birds. They are long, but the females are larger than the males. The adults have a chestnut back and wing coverts, with the rest of the body mainly black. In flight the greenish yellow flight feathers are obvious. Also visible are yellow bony spurs on the leading edge of the wings, which it can use to defend itself and its young. The yellow bill extends up as a red coot-like head shield and a reddish wattle, and the legs and very l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acorn Woodpecker
The acorn woodpecker (''Melanerpes formicivorus'') is a medium-sized woodpecker, long, with an average weight of . Taxonomy The acorn woodpecker was formally described in 1827 by the English naturalist William John Swainson under the binomial name ''Picus formicivorus'' from a specimen collected in Mexico. The specific epithet combines the Latin ''formica'' meaning "ant" with ''-vorus'' meaning "eating". The type locality is Temascaltepec in Mexico. The acorn woodpecker is one of 24 species now placed in the genus ''Melanerpes'' that was introduced by Swainson in 1832. Within ''Melanerpes'' the acorn woodpecker is sister to a clade containing two South American species: the white woodpecker (''Melanerpes candidus'') and the white-fronted woodpecker (''Melanerpes cactorum''). Seven subspecies are recognised: * ''M. f. bairdi'' Ridgway, 1881 – Oregon (USA) to north Baja California (Mexico) * ''M. f. angustifrons'' Baird, SF, 1870 – south Baja California (Mexico) * ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Female Sperm Storage
Female sperm storage is a biological process and often a type of sexual selection in which sperm cells transferred to a female during mating are temporarily retained within a specific part of the reproductive tract before the oocyte, or egg, is fertilized. The site of storage is variable among different animal taxa and ranges from structures that appear to function solely for sperm retention, such as insect spermatheca and bird sperm storage tubules (bird anatomy), to more general regions of the reproductive tract enriched with receptors to which sperm associate before fertilization, such as the caudal portion of the cow oviduct containing sperm-associating annexins. Female sperm storage is an integral stage in the reproductive process for many animals with internal fertilization. It has several documented biological functions including: * Supporting the sperm by: a.) enabling sperm to undergo biochemical transitions, called capacitation and motility hyperactivation, in which they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_mating_(31969339340).jpg)
.jpg)
