|
Platelet-rich Fibrin
Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) or leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF) is a second-generation PRP where autologous platelets and leukocytes are present in a complex fibrin matrix to accelerate the healing of soft and hard tissue and is used as a tissue-engineering scaffold for endodontics. To obtain PRF, required quantity of blood is drawn quickly into test tubes without an anticoagulant and centrifuged immediately. Blood can be centrifuged using a tabletop centrifuge from 3-8 minutes for 1300 revolutions per minute. The resultant product consists of the following three layers; topmost layer consisting of platelet poor plasma, PRF clot in the middle, and red blood cells (RBC) at the bottom. PRF is available as a fibrin clot. PRF clot can be removed from the test tube using a sterile tweezer-like instrument. After lifting, the RBC layer attached to the PRF clot can be carefully removed using a sterilized scissor. Platelet activation in response to tissue damage occurs during t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelet-rich Plasma
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP), also known as autologous conditioned plasma, is a concentrate of platelet-rich plasma protein derived from whole blood, centrifuged to remove red blood cells. Though promoted to treat an array of medical problems, evidence for benefit is mixed as of 2020, with some evidence for use in certain conditions and against use in other conditions. As a concentrated source of blood plasma and autologous conditioned plasma, PRP contains several different growth factors and other cytokines that can stimulate healing of soft tissue and joints. There are some indications for use in sports medicine and orthopedics (acute muscle strains, tendinopathy and muscle-fascial injuries and osteoarthritis), or dermatology (androgenic alopecia, wound healing, and skin rejuvenation) or even in proctology (fistula-in-ano). For preparation of PRP, various protocols are used, with an underlying principle of concentrating platelets to 3–5 times physiological levels, then injectin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meta Analysis
A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. Meta-analyses can be performed when there are multiple scientific studies addressing the same question, with each individual study reporting measurements that are expected to have some degree of error. The aim then is to use approaches from statistics to derive a pooled estimate closest to the unknown common truth based on how this error is perceived. Meta-analytic results are considered the most trustworthy source of evidence by the evidence-based medicine literature.Herrera Ortiz AF., Cadavid Camacho E, Cubillos Rojas J, Cadavid Camacho T, Zoe Guevara S, Tatiana Rincón Cuenca N, Vásquez Perdomo A, Del Castillo Herazo V, & Giraldo Malo R. A Practical Guide to Perform a Systematic Literature Review and Meta-analysis. Principles and Practice of Clinical Research. 2022;7(4):47–57. https://doi.org/10.21801/ppcrj.2021.74.6 Not only can meta-analyses provide an estimate of the unk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Products
A blood product is any therapeutic substance prepared from human blood. This includes whole blood; blood components; and plasma derivatives. Whole blood is not commonly used in transfusion medicine. Blood components include: red blood cell concentrates or suspensions; platelets produced from whole blood or via apheresis; plasma; and cryoprecipitate. Plasma derivatives are plasma proteins prepared under pharmaceutical manufacturing conditions, these include: albumin; coagulation factor concentrates; and immunoglobulins. __TOC__ Relation to other substances Blood products may also be called blood-based products to differ from blood substitutes, which generally refer to artificially produced products. Also, although many blood products have the effect of volume expansion, the group is usually distinguished from volume expanders, which generally refers to artificially produced substances and are thereby within the scope of ''blood substitutes''. See also * Cryoprecipitate * Cryosupe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelet Alpha-granule
Alpha granules, (α-granules) also known as platelet alpha-granules are a cellular component of platelets. Platelets contain different types of granules that perform different functions, and include alpha granules, dense granules, and lysosomes. Of these, alpha granules are the most common, making up between 50% to 80% of the secretory granules. Alpha granules contain several growth factors. Contents Contents include insulin-like growth factor 1, platelet-derived growth factors, TGF beta, platelet factor 4 (which is a heparin-binding chemokine) and other clotting proteins (such as thrombospondin, fibronectin, factor V, and von Willebrand factor). The alpha granules express the adhesion molecule P-selectin and CD63. These are transferred to the membrane after synthesis. The other type of granules within platelets are called dense granules. Clinical significance A deficiency of alpha granules is known as gray platelet syndrome Gray platelet syndrome (GPS), or platelet alpha-gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
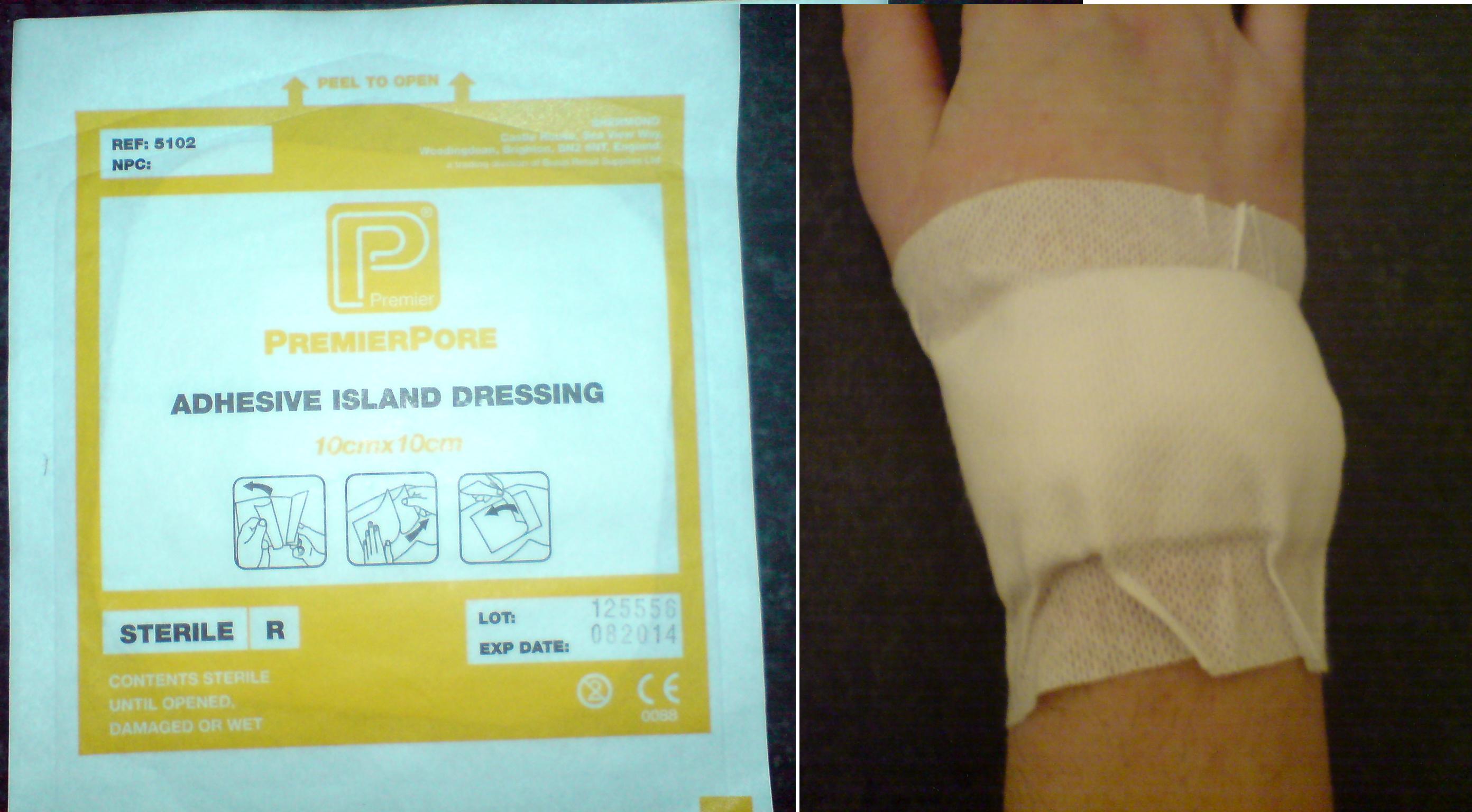
Dressing (medical)
A dressing is a sterile pad or compress applied to a wound to promote healing and protect the wound from further harm. A dressing is designed to be in direct contact with the wound, as distinguished from a bandage, which is most often used to hold a dressing in place. Many modern dressings are self-adhesive. Medical uses A dressing can have a number of purposes, depending on the type, severity and position of the wound, although all purposes are focused on promoting recovery and protecting from further harm. Key purposes of a dressing are: * Stop bleeding – to help to seal the wound to expedite the clotting process; * Protection from infection – to defend the wound against germs and mechanical damage; * Absorb exudate – to soak up blood, plasma, and other fluids exuded from the wound, containing it/them in one place and preventing maceration; * Ease pain – either by a medicated analgesic effect, compression or simply preventing pain from further trauma; * Debride the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regenerative Endodontics
Regenerative endodontic procedures is defined as biologically based procedures designed to replace damaged structures such as dentin, root structures, and cells of the pulp-dentin complex. This new treatment modality aims to promote normal function of the pulp. It has become an alternative to heal apical periodontitis. Regenerative endodontics is the extension of root canal therapy. Conventional root canal therapy cleans and fills the pulp chamber with biologically inert material after destruction of the pulp due to dental caries, congenital deformity or trauma. Regenerative endodontics instead seeks to replace live tissue in the pulp chamber. The ultimate goal of regenerative endodontic procedures is to regenerate the tissues and the normal function of the dentin-pulp complex. Before this treatment modality is introduced, apexification procedures using either immediate placement of mineral trioxide aggregate apical plug or long term-calcium hydroxide treatment were traditionally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apical Foramen
In dental anatomy, the apical foramen, literally translated "small opening of the apex," is the tooth's natural opening, found at the root's very tip—that is, the root's apex—whereby an artery, vein, and nerve enter the tooth and commingle with the tooth's internal soft tissue, called pulp. Additionally, the apical foramen is the point where the pulp meets the periodontal tissues, the connective tissues that surround and support the tooth. Characteristics The average size of the orifice is 0.3 to 0.4 mm in diameter. There can be two or more foramina separated by a portion of dentin and cementum or by cementum only. If more than one foramen is present on each root, the largest one is designated as the apical foramen and the rest are considered accessory foramina. Apical delta Apical delta refers to the branching pattern of small accessory canals and minor foramina seen at the tip or apex of some tooth roots. The pattern is said to be reminiscent of a river delta when se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Pulp
The pulp is the connective tissue, nerves, blood vessels, and odontoblasts that comprise the innermost layer of a tooth. The pulp's activity and signalling processes regulate its behaviour. Anatomy The pulp is the neurovascular bundle central to each tooth, permanent or primary. It is composed of a central pulp chamber, pulp horns, and radicular canals. The large mass of the pulp is contained within the pulp chamber, which is contained in and mimics the overall shape of the crown of the tooth.Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy, Bath-Balogh and Fehrenbach, Elsevier, 2011, page 164. Because of the continuous deposition of the dentine, the pulp chamber becomes smaller with the age. This is not uniform throughout the coronal pulp but progresses faster on the floor than on the roof or sidewalls. Radicular pulp canals extend down from the cervical region of the crown to the root apex. They are not always straight but vary in shape, size, and number. They are co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Grafting
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that replaces missing bone in order to repair bone fractures that are extremely complex, pose a significant health risk to the patient, or fail to heal properly. Some small or acute fractures can be cured without bone grafting, but the risk is greater for large fractures like compound fractures. Bone generally has the ability to regenerate completely but requires a very small fracture space or some sort of scaffold to do so. Bone grafts may be autologous (bone harvested from the patient's own body, often from the iliac crest), allograft (cadaveric bone usually obtained from a bone bank), or synthetic (often made of hydroxyapatite or other naturally occurring and biocompatible substances) with similar mechanical properties to bone. Most bone grafts are expected to be resorbed and replaced as the natural bone heals over a few months' time. The principles involved in successful bone grafts include osteoconduction (guiding the reparative growth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guided Bone And Tissue Regeneration
Guided bone regeneration (GBR) and guided tissue regeneration (GTR) are dental surgical procedures that use barrier membranes to direct the growth of new bone and gingival tissue at sites with insufficient volumes or dimensions of bone or gingiva for proper function, esthetics or prosthetic restoration. Guided bone regeneration typically refers to ridge augmentation or bone regenerative procedures; guided tissue regeneration typically refers to regeneration of periodontal attachment. Guided bone regeneration is similar to guided tissue regeneration, but is focused on development of hard tissues in addition to the soft tissues of the periodontal attachment. At present, guided bone regeneration is predominantly applied in the oral cavity to support new hard tissue growth on an alveolar ridge to allow stable placement of dental implants. When bone grafting is used in conjunction with sound surgical technique, guided bone regeneration is a reliable and validated procedure. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demineralized Freeze Dried Bone Allograft
Demineralized freeze dried bone allograft, referred to as DFDBA, is a bone graft material known for its '' de novo'' bone formation properties.Bowers, GM, ''et al.'' ''Histologic evaluation of new attachment apparatus formation in humans''. ''J Perio'' 1989;60:683-693 It is used extensively in bone grafting of alveolar bone in oral and periodontal Periodontology or periodontics (from Ancient Greek , – 'around'; and , – 'tooth', genitive , ) is the specialty of dentistry that studies supporting structures of teeth, as well as diseases and conditions that affect them. The supporting ... surgery. References Dentistry terminology Skeletal system {{Musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelet Derived Growth Factor
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) is one among numerous growth factors that regulate cell growth and division. In particular, PDGF plays a significant role in blood vessel formation, the growth of blood vessels from already-existing blood vessel tissue, mitogenesis, i.e. proliferation, of mesenchymal cells such as fibroblasts, osteoblasts, tenocytes, vascular smooth muscle cells and mesenchymal stem cells as well as chemotaxis, the directed migration, of mesenchymal cells. Platelet-derived growth factor is a dimeric glycoprotein that can be composed of two A subunits (PDGF-AA), two B subunits (PDGF-BB), or one of each (PDGF-AB). PDGF is a potent mitogen for cells of mesenchymal origin, including fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells and glial cells. In both mouse and human, the PDGF signalling network consists of five ligands, PDGF-AA through -DD (including -AB), and two receptors, PDGFRalpha and PDGFRbeta. All PDGFs function as secreted, disulphide-linked homodimers, but only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |