|
Plasmids
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; however, plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. In nature, plasmids often carry genes that benefit the survival of the organism and confer selective advantage such as antibiotic resistance. While chromosomes are large and contain all the essential genetic information for living under normal conditions, plasmids are usually very small and contain only additional genes that may be useful in certain situations or conditions. Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, serving to drive the replication of recombinant DNA sequences within host organisms. In the laboratory, plasmids may be introduced into a cell via transformation. Synthetic plasmids are available for procurement over the intern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmid (english)
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; however, plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. In nature, plasmids often carry genes that benefit the survival of the organism and confer selective advantage such as antibiotic resistance. While chromosomes are large and contain all the essential genetic information for living under normal conditions, plasmids are usually very small and contain only additional genes that may be useful in certain situations or conditions. Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, serving to drive the replication of recombinant DNA sequences within host organisms. In the laboratory, plasmids may be introduced into a cell via transformation. Synthetic plasmids are available for procurement over the intern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmid Replication (english)
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; however, plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. In nature, plasmids often carry genes that benefit the survival of the organism and confer selective advantage such as antibiotic resistance. While chromosomes are large and contain all the essential genetic information for living under normal conditions, plasmids are usually very small and contain only additional genes that may be useful in certain situations or conditions. Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, serving to drive the replication of recombinant DNA sequences within host organisms. In the laboratory, plasmids may be introduced into a cell via transformation. Synthetic plasmids are available for procurement over the intern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extrachromosomal DNA
Extrachromosomal DNA (abbreviated ecDNA) is any DNA that is found off the chromosomes, either inside or outside the nucleus of a cell. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes contained in the nucleus. Multiple forms of extrachromosomal DNA exist, and, while some of these serve important biological functions, they can also play a role in diseases, such as ecDNA in cancer. In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids, whereas, in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. The fact that this organelle contains its own DNA supports the hypothesis that mitochondria originated as bacterial cells engulfed by ancestral eukaryotic cells. Extrachromosomal DNA are often used in research of replication because they are easy to identify and isolate. Although extrachromosomal circular DNA (eccDNA) is found in normal eukaryotic cells, extrachrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector (molecular Biology)
In molecular cloning, a vector is any particle (e.g., plasmids, cosmids, Lambda phages) used as a vehicle to artificially carry a foreign nucleic sequence – usually DNA – into another cell, where it can be replicated and/or expressed. A vector containing foreign DNA is termed recombinant DNA. The four major types of vectors are plasmids, viral vectors, cosmids, and artificial chromosomes. Of these, the most commonly used vectors are plasmids. Common to all engineered vectors have an origin of replication, a multicloning site, and a selectable marker. The vector itself generally carries a DNA sequence that consists of an insert (in this case the transgene) and a larger sequence that serves as the "backbone" of the vector. The purpose of a vector which transfers genetic information to another cell is typically to isolate, multiply, or express the insert in the target cell. All vectors may be used for cloning and are therefore cloning vectors, but there are also vectors de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Conjugation
Bacterial conjugation is the transfer of genetic material between bacterial cells by direct cell-to-cell contact or by a bridge-like connection between two cells. This takes place through a pilus. It is a parasexual mode of reproduction in bacteria. It is a mechanism of horizontal gene transfer as are transformation and transduction although these two other mechanisms do not involve cell-to-cell contact. Classical ''E. coli'' bacterial conjugation is often regarded as the bacterial equivalent of sexual reproduction or mating since it involves the exchange of genetic material. However, it is not sexual reproduction, since no exchange of gamete occurs, and indeed no generation of a new organism: instead an existing organism is transformed. During classical ''E. coli'' conjugation the ''donor'' cell provides a conjugative or mobilizable genetic element that is most often a plasmid or transposon. Most conjugative plasmids have systems ensuring that the ''recipient'' cell does not al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between Unicellular organism, unicellular and/or multicellular organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the evolution of many organisms. HGT is influencing scientific understanding of higher order evolution while more significantly shifting perspectives on bacterial evolution. Horizontal gene transfer is the primary mechanism for the spread of antibiotic resistance in bacteria, and plays an important role in the evolution of bacteria that can degrade novel compounds such as human-created Bactericide, pesticides and in the evolution, maintenance, and transmission of virulence. It often involves Temperateness (virology), temperate bacteriophages and plasmids. Genes responsible for antibiotic resistance in one species of bacteria can be transferred to another species of bacteria through various m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word ''cloning'' refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine. In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformation (genetics)
In molecular biology and genetics, transformation is the genetic alteration of a cell resulting from the direct uptake and incorporation of exogenous genetic material from its surroundings through the cell membrane(s). For transformation to take place, the recipient bacterium must be in a state of competence, which might occur in nature as a time-limited response to environmental conditions such as starvation and cell density, and may also be induced in a laboratory. Transformation is one of three processes that lead to horizontal gene transfer, in which exogenous genetic material passes from one bacterium to another, the other two being conjugation (transfer of genetic material between two bacterial cells in direct contact) and transduction (injection of foreign DNA by a bacteriophage virus into the host bacterium). In transformation, the genetic material passes through the intervening medium, and uptake is completely dependent on the recipient bacterium. As of 2014 about 8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
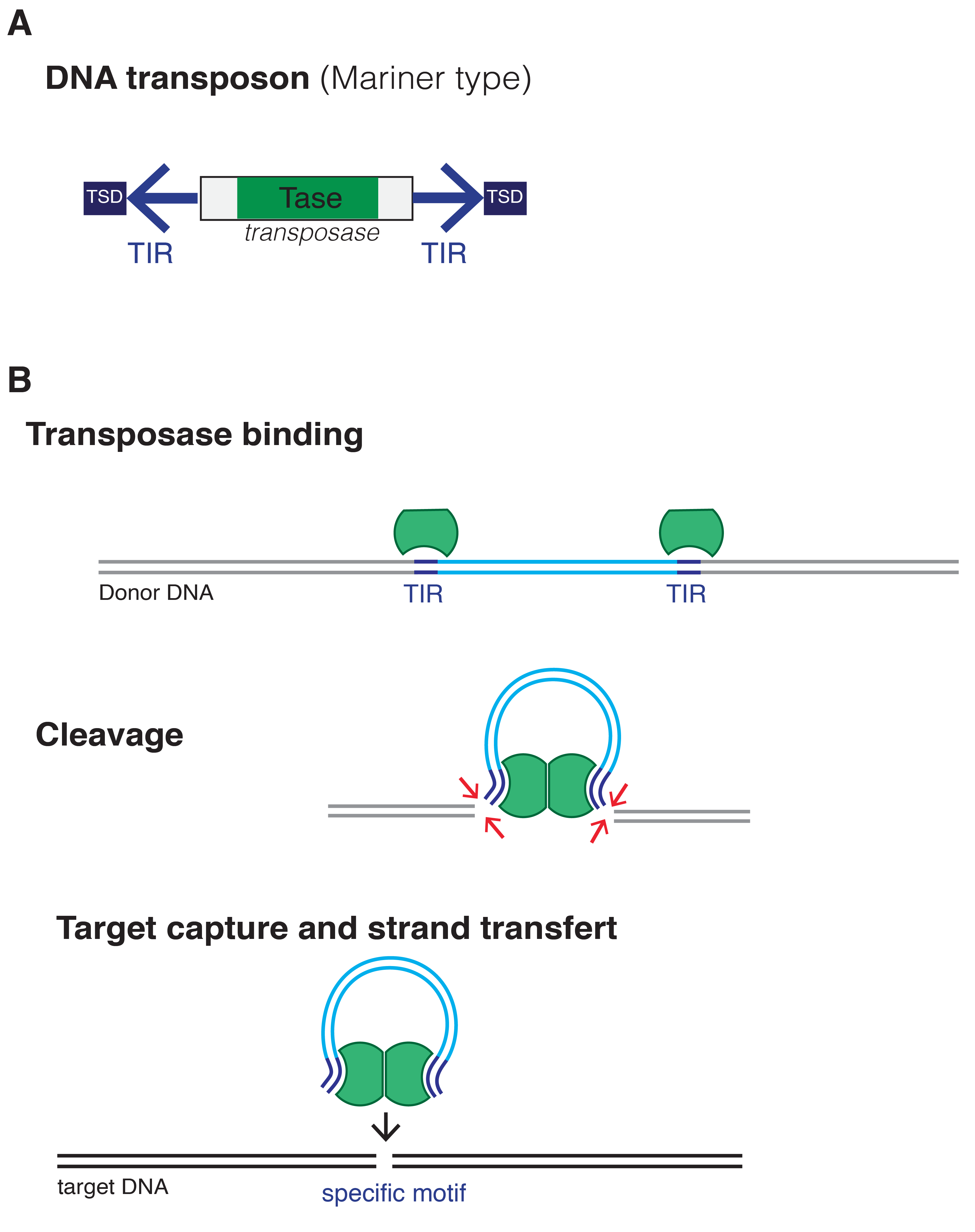
Mobilome
The mobilome is the entire set of mobile genetic elements in a genome. Mobilomes are found in eukaryotes, prokaryotes, and viruses. The compositions of mobilomes differ among lineages of life, with transposable elements being the major mobile elements in eukaryotes, and plasmids and prophages being the major types in prokaryotes. Virophages contribute to the viral mobilome. Mobilome in eukaryotes Transposable elements are elements that can move about or propagate within the genome, and are the major constituents of the eukaryotic mobilome. Transposable elements can be regarded as genetic parasites because they exploit the host cell's transcription and translation mechanisms to extract and insert themselves in different parts of the genome, regardless of the phenotypic effect on the host. Eukaryotic transposable elements were first discovered in maize (''Zea mays'') in which kernels showed a dotted color pattern. Barbara McClintock described the maize Ac/Ds system in which th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Plasmids
A DNA construct is an artificially-designed segment of DNA borne on a vector that can be used to incorporate genetic material into a target tissue or cell. A DNA construct contains a DNA insert, called a transgene, delivered via a transformation vector which allows the insert sequence to be replicated and/or expressed in the target cell. This gene can be cloned from a naturally occurring gene, or synthetically constructed. The vector can be delivered using physical, chemical or viral methods. Typically, the vectors used in DNA constructs contain an origin of replication, a multiple cloning site, and a selectable marker. Certain vectors can carry additional regulatory elements based on the expression system involved. DNA constructs can be as small as a few thousand base pairs (kbp) of DNA carrying a single gene, using vectors such as plasmids or bacteriophages, or as large as hundreds of kbp for large-scale genomic studies using an artificial chromosome. A DNA construct may express ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be found in the genome. Recombinant DNA is the general name for a piece of DNA that has been created by combining at least two fragments from two different sources. Recombinant DNA is possible because DNA molecules from all organisms share the same chemical structure, and differ only in the nucleotide sequence within that identical overall structure. Recombinant DNA molecules are sometimes called chimeric DNA, because they can be made of material from two different species, like the mythical chimera. R-DNA technology uses palindromic sequences and leads to the production of sticky and blunt ends. The DNA sequences used in the construction of recombinant DNA molecules can originate from any species. For example, plant DNA may be joined to bacter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iteron
Iterons are directly repeated DNA sequences which play an important role in regulation of plasmid copy number in bacterial cells. It is one among the three negative regulatory elements found in plasmids which control its copy number. The others include antisense RNAs and ctRNAs. Iterons complex with cognate replication (Rep) initiator proteins to achieve the required regulatory effect. Regulation of Replication Iterons have an important role in plasmid replication. An iteron-containing plasmid origin of replication can be found containing about five iterons about 20 base pairs in length total. These iterons provide a saturation site for initiator receptor proteins and promote replication thus increasing plasmid copy number in a given cell. Limiting Factors of Initiation There are 4 main limiting factors leading to no initiation of replication in iterons: *Transcriptional autorepression *Initiator dimerization *Initiator titration *Handcuffing Transcriptional auto-repress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |