|
Pinealoma
A pinealoma is a tumor of the pineal gland, a part of the brain that produces melatonin. If a pinealoma destroys the cells of the pineal gland in a child, it can cause precocious puberty. Signs and symptoms The pineal gland produces the hormone melatonin which plays a role in regulating circadian rhythms. A pinealoma may disrupt production of this hormone, and insomnia may result. Frequently, paralysis of upward gaze along with several ocular findings such as convergence retraction nystagmus and eyelid retraction also known as Collier's sign and Light Near Dissociation (pupil accommodates but doesn't react to light) are known collectively as Parinaud's syndrome or Dorsal Mid-brain syndrome, are the only physical symptoms seen. This is caused by the compression of the vertical gaze center in the midbrain tectum at the level of the superior colliculus and cranial nerve III. Work-up usually includes Neuro-imaging as seen on the right. A pinealoma may cause interruption of hypoth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the study, treatment, diagnosis and prevention of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an ''oncologist''. The name's etymological origin is the Greek word ὄγκος (''ónkos''), meaning "tumor", "volume" or "mass". Oncology is concerned with: * The diagnosis of any cancer in a person (pathology) * Therapy (e.g. surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and other modalities) * Follow-up of cancer patients after successful treatment * Palliative care of patients with terminal malignancies * Ethical questions surrounding cancer care * Screening efforts: ** of populations, or ** of the relatives of patients (in types of cancer that are thought to have a hereditary basis, such as breast cancer) Diagnosis Medical histories remain an important screening tool: the character of the complaints and nonspecific symptoms (such as fatigue, weight loss, unexplained anemia, fever of unknown origin, paraneoplastic phenome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
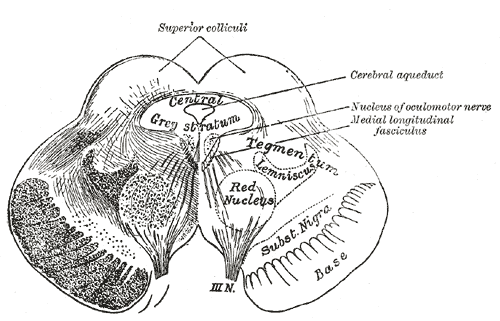
Cranial Nerve III
The oculomotor nerve, also known as the third cranial nerve, cranial nerve III, or simply CN III, is a cranial nerve that enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure and innervates extraocular muscles that enable most movements of the eye and that raise the eyelid. The nerve also contains fibers that innervate the intrinsic eye muscles that enable pupillary constriction and accommodation (ability to focus on near objects as in reading). The oculomotor nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic midbrain. Cranial nerves IV and VI also participate in control of eye movement. Structure The oculomotor nerve originates from the third nerve nucleus at the level of the superior colliculus in the midbrain. The third nerve nucleus is located ventral to the cerebral aqueduct, on the pre-aqueductal grey matter. The fibers from the two third nerve nuclei located laterally on either side of the cerebral aqueduct then pass through the red nucleus. From the red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pineocytoma
Pineocytoma, is a benign, slowly growing tumor of the pineal gland. Unlike the similar condition pineal gland cyst, it is uncommon. Diagnosis Pineocytomas are diagnosed from tissue, i.e. a brain biopsy.They consist of: * Cytopathology, cytologically benign cells (with nucleus (cell), nuclei of uniform size, regular nuclear membranes, and light chromatin) and, * have the characteristic Pineocytomatous/neurocytic pseudorosettes, pineocytomatous/neurocytic rosettes, which is an irregular circular/flower-like arrangement of cells with a large meshwork of fibers (neuropil) at the centre. Pineocytomatous/neurocytic rosettes are superficially similar to Homer Wright rosettes; however, they differ from Homer Wright rosettes as they have (1) more neuropil at centre of the rosette and, (2) the edge of neuropil meshwork irregular/undulating. Management See also * Pineal gland References External links {{Endocrine gland neoplasia Endocrine neoplasia Brain tumor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germinoma
A germinoma is a type of germ-cell tumor, which is not differentiated upon examination. It may be benign or malignant. Cause Germinomas are thought to originate from an error of development, when certain primordial germ cells fail to migrate properly. Germinomas lack histologic differentiation, whereas nongerminomatous germ-cell tumors display a variety of differentiation. Like other germ-cell tumors, germinomas can undergo malignant transformation. Histology The tumor is uniform in appearance, consisting of large, round cells with vesicular nuclei and clear or finely granular cytoplasm that is eosinophilic. On gross examination, the external surface is smooth and bosselated (knobby), and the interior is soft, fleshy, and either cream-coloured, gray, pink, or tan. Microscopic examination typically reveals uniform cells that resemble primordial germ cells. Typically, the stroma contains lymphocytes, and about 20% of patients have sarcoid-like granulomas. Diagnosis Metastasis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germ Cell
Germ or germs may refer to: Science * Germ (microorganism), an informal word for a pathogen * Germ cell, cell that gives rise to the gametes of an organism that reproduces sexually * Germ layer, a primary layer of cells that forms during embryonic development * Cereal germ, the reproductive part of a cereal grain * Tooth germ, an aggregation of cells that eventually forms a tooth * Germ theory of disease, which states that some diseases are caused by microorganisms * Germ (mathematics), an object in a topological space that captures local properties Art and media Music * Germs (band), an American punk rock band * Germ (musician), a stage name of Tim Wright * Germ (rapper), an American rapper affiliated with Suicideboys and Pouya * "Germs" (song), by "Weird Al" Yankovic * ''The Germ'' (album), by Victim's Family Others * "Germs" (''Invader Zim''), an episode of ''Invader Zim'' * ''The Germ'' (periodical), a British art magazine published in 1850 * The Germs (comics) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrocytoma
Astrocytomas are a type of brain tumor. They originate in a particular kind of glial cells, star-shaped brain cells in the cerebrum called astrocytes. This type of tumor does not usually spread outside the brain and spinal cord and it does not usually affect other organs. Astrocytomas are the most common glioma and can occur in most parts of the brain and occasionally in the spinal cord. Within the astrocytomas, two broad classes are recognized in literature, those with: * Narrow zones of infiltration (mostly noninvasive tumors; e.g., pilocytic astrocytoma, subependymal giant cell astrocytoma, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma), that often are clearly outlined on diagnostic images * Diffuse zones of infiltration (e.g., high-grade astrocytoma, anaplastic astrocytoma, glioblastoma), that share various features, including the ability to arise at any location in the central nervous system, but with a preference for the cerebral hemispheres; they occur usually in adults, and have an intrins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrocyte
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" + , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of endothelial cells that form the blood–brain barrier, provision of nutrients to the nervous tissue, maintenance of extracellular ion balance, regulation of cerebral blood flow, and a role in the repair and scarring process of the brain and spinal cord following infection and traumatic injuries. The proportion of astrocytes in the brain is not well defined; depending on the counting technique used, studies have found that the astrocyte proportion varies by region and ranges from 20% to 40% of all glia. Another study reports that astrocytes are the most numerous cell type in the brain. Astrocytes are the major source of cholesterol in the central nervous system. Apolipoprotein E transports cholesterol from astrocytes to neurons and other glial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pineocytomas
Pineocytoma, is a benign, slowly growing tumor of the pineal gland. Unlike the similar condition pineal gland cyst, it is uncommon. Diagnosis Pineocytomas are diagnosed from tissue, i.e. a brain biopsy.They consist of: * Cytopathology, cytologically benign cells (with nucleus (cell), nuclei of uniform size, regular nuclear membranes, and light chromatin) and, * have the characteristic Pineocytomatous/neurocytic pseudorosettes, pineocytomatous/neurocytic rosettes, which is an irregular circular/flower-like arrangement of cells with a large meshwork of fibers (neuropil) at the centre. Pineocytomatous/neurocytic rosettes are superficially similar to Homer Wright rosettes; however, they differ from Homer Wright rosettes as they have (1) more neuropil at centre of the rosette and, (2) the edge of neuropil meshwork irregular/undulating. Management See also * Pineal gland References External links {{Endocrine gland neoplasia Endocrine neoplasia Brain tumor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pineocyte
Pinealocytes are the main cells contained in the pineal gland, located behind the third ventricle and between the two hemispheres of the brain. The primary function of the pinealocytes is the secretion of the hormone melatonin, important in the regulation of circadian rhythms. In humans, the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus communicates the message of darkness to the pinealocytes, and as a result, controls the day and night cycle. It has been suggested that pinealocytes are derived from photoreceptor cells. Research has also shown the decline in the number of pinealocytes by way of apoptosis as the age of the organism increases. There are two different types of pinealocytes, type I and type II, which have been classified based on certain properties including shape, presence or absence of infolding of the nuclear envelope, and composition of the cytoplasm. Types of pinealocytes Type 1 pinealocytes Type 1 pinealocytes are also known as light pinealocytes because the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gait Disturbance
Gait deviations are nominally referred to as any variation of standard human gait, typically manifesting as a coping mechanism in response to an anatomical impairment. Lower-limb amputees are unable to maintain the characteristic walking patterns of an able-bodied individual due to the removal of some portion of the impaired leg. Without the anatomical structure and neuromechanical control of the removed leg segment, amputees must use alternative compensatory strategies to walk efficiently. Prosthetic limbs provide support to the user and more advanced models attempt to mimic the function of the missing anatomy, including biomechanically controlled ankle and knee joints. However, amputees still display quantifiable differences in many measures of ambulation when compared to able-bodied individuals. Several common observations are whole-body movements, slower and wider steps, shorter strides, and increased sway. Presentation and causes Lower-limb amputations Over 185,0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs within the brain. This typically causes increased intracranial pressure, pressure inside the skull. Older people may have headaches, double vision, poor balance, urinary incontinence, personality changes, or mental impairment. In babies, it may be seen as a rapid increase in head size. Other symptoms may include vomiting, sleepiness, seizures, and Parinaud's syndrome, downward pointing of the eyes. Hydrocephalus can occur due to birth defects or be acquired later in life. Associated birth defects include neural tube defects and those that result in aqueductal stenosis. Other causes include meningitis, brain tumors, traumatic brain injury, intraventricular hemorrhage, and subarachnoid hemorrhage. The four types of hydrocephalus are communicating, noncommunicating, ''ex vacuo'', and normal pressure hydrocephalus, normal pressure. Diagnosis is typically made by physical examination and medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Colliculus
In neuroanatomy, the superior colliculus () is a structure lying on the roof of the mammalian midbrain. In non-mammalian vertebrates, the homologous structure is known as the optic tectum, or optic lobe. The adjective form ''tectal'' is commonly used for both structures. In mammals, the superior colliculus forms a major component of the midbrain. It is a paired structure and together with the paired inferior colliculi forms the corpora quadrigemina. The superior colliculus is a layered structure, with a pattern that is similar to all mammals. The layers can be grouped into the superficial layers ( stratum opticum and above) and the deeper remaining layers. Neurons in the superficial layers receive direct input from the retina and respond almost exclusively to visual stimuli. Many neurons in the deeper layers also respond to other modalities, and some respond to stimuli in multiple modalities. The deeper layers also contain a population of motor-related neurons, capable of activat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |