|
Pinch (action)
A pinch is a grip of a flexible object in which a portion is taken between two fingers, until it hurts, or something of resemblance and squeezed so the gripped portion of the object is lifted from its normal level. By extension, that which is taken in the grip is referred to as a "pinch." When the fingers are used to perform a pinch, the action usually consists of the thumb and one other finger. The closer to the thumb the other finger is located, the stronger the pinch. Pinch of the skin The term "pinch" often refers to the action being taken on the skin. A pinch of the skin displaces the skin and blood beneath from its natural position, and may inflict a minor degree of pain, which may increase if the amount of skin being pinched is smaller, but is usually tolerable to most. Pinching the skin can result in pinch marks, a cutaneous condition, and when on the ears or in the genital region of male children may be suggestive of child abuse. Medical uses Pinching has the following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-touch
In computing, multi-touch is technology that enables a surface (a touchpad or touchscreen) to recognize the presence of more than one somatosensory system, point of contact with the surface at the same time. The origins of multitouch began at CERN, MIT, University of Toronto, Carnegie Mellon University and Bell Labs in the 1970s. CERN started using multi-touch screens as early as 1976 for the controls of the Super Proton Synchrotron. Capacitive multi-touch displays were popularized by Apple Inc., Apple's iPhone in 2007. Plural-point awareness may be used to implement additional functionality, such as pinch to zoom or to activate certain subroutines attached to Gesture recognition, predefined gestures. Several uses of the term multi-touch resulted from the quick developments in this field, and many companies using the term to market older technology which is called ''gesture-enhanced single-touch'' or several other terms by other companies and researchers. Several other similar or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Fat Percentage
The body fat percentage (BFP) of a human or other living being is the total mass of fat divided by total body mass, multiplied by 100; body fat includes essential body fat and storage body fat. Essential body fat is necessary to maintain life and reproductive functions. The percentage of essential body fat for women is greater than that for men, due to the demands of childbearing and other hormonal functions. Storage body fat consists of fat accumulation in adipose tissue, part of which protects internal organs in the chest and abdomen. A number of methods are available for determining body fat percentage, such as measurement with calipers or through the use of bioelectrical impedance analysis. The body fat percentage is a measure of fitness level, since it is the only body measurement which directly calculates a person's relative body composition without regard to height or weight. The widely used body mass index (BMI) provides a measure that allows the comparison of the adiposit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation. Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different cellular differentiation, developmental origin, structure and chemical composition. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'' 'skin'). In mammals, the skin is an organ (anatomy), organ of the integumentary system made up of multiple layers of ectodermal tissue (biology), tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments, and internal organs. Skin of a different nature exists in amphibians, reptiles, and birds. Skin (including cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues) plays crucial roles in formation, structure, and function of extraskeletal apparatus such as horns of bovids (e.g., cattle) and rhinos, cervids' antlers, giraffids' ossicones, armadillos' osteoderm, and os penis/os clitoris. All mammals have som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Street Drug
Recreational drug use indicates the use of one or more psychoactive drugs to induce an altered state of consciousness either for pleasure or for some other casual purpose or pastime by modifying the perceptions and emotions of the user. When a psychoactive drug enters the user's body, it induces an intoxicating effect. Generally, recreational drugs are divided into three categories: depressants (drugs that induce a feeling of relaxation and calmness); stimulants (drugs that induce a sense of energy and alertness); and hallucinogens (drugs that induce perceptual distortions such as hallucination). In popular practice, recreational drug use generally is a tolerated social behaviour, rather than perceived as the medical condition of self-medication. However, heavy use of some drugs is socially stigmatized. Many people also use prescribed and controlled depressants such as opioids, as well as opiates and benzodiazepines. Common recreational drugs include caffeine, commonly found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spice
A spice is a seed, fruit, root, bark, or other plant substance primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of plants used for flavoring or as a garnish. Spices are sometimes used in medicine, religious rituals, cosmetics or perfume production. For example, vanilla is commonly used as an ingredient in fragrance manufacturing. A spice may be available in several forms: fresh, whole dried, or pre-ground dried. Generally, spices are dried. Spices may be ground into a powder for convenience. A whole dried spice has the longest shelf life, so it can be purchased and stored in larger amounts, making it cheaper on a per-serving basis. A fresh spice, such as ginger, is usually more flavorful than its dried form, but fresh spices are more expensive and have a much shorter shelf life. Some spices are not always available either fresh or whole, for example turmeric, and often must be purchased in ground form. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Table Salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quantities in seawater. The open ocean has about of solids per liter of sea water, a salinity of 3.5%. Salt is essential for life in general, and saltiness is one of the basic human tastes. Salt is one of the oldest and most ubiquitous food seasonings, and is known to uniformly improve the taste perception of food, including otherwise unpalatable food. Salting, brining, and pickling are also ancient and important methods of food preservation. Some of the earliest evidence of salt processing dates to around 6,000 BC, when people living in the area of present-day Romania boiled spring water to extract salts; a salt-works in China dates to approximately the same period. Salt was also prized by the ancient Hebrews, Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinch (cooking)
A pinch is a small, indefinite amount of a substance, typically a powder like salt, sugar, spice, or snuff. It is the "amount that can be taken between the thumb and forefinger". Some manufacturers of measuring spoons and some U.S. cookbooks give more precise equivalents, typically , , or even teaspoon A teaspoon (tsp.) is an item of cutlery. It is a small spoon that can be used to stir a cup of tea or coffee, or as a tool for measuring volume. The size of teaspoons ranges from about . For cooking purposes and dosing of medicine, a teaspoonf ..., but there is no generally accepted standard. References Customary units of measurement Cooking weights and measures Units of volume {{Measurement-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Powder (substance)
A powder is a dry, bulk solid composed of many very fine particles that may flow freely when shaken or tilted. Powders are a special sub-class of granular materials, although the terms ''powder'' and ''granular'' are sometimes used to distinguish separate classes of material. In particular, ''powders'' refer to those granular materials that have the finer grain sizes, and that therefore have a greater tendency to form clumps when flowing. ''Granulars'' refers to the coarser granular materials that do not tend to form clumps except when wet. Types Many manufactured goods come in powder form, such as flour, sugar, ground coffee, powdered milk, copy machine toner, gunpowder, cosmetic powders, and some pharmaceuticals. In nature, dust, fine sand and snow, volcanic ash, and the top layer of the lunar regolith are also examples. Because of their importance to industry, medicine and earth science, powders have been studied in great detail by chemical engineers, mechanical engi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
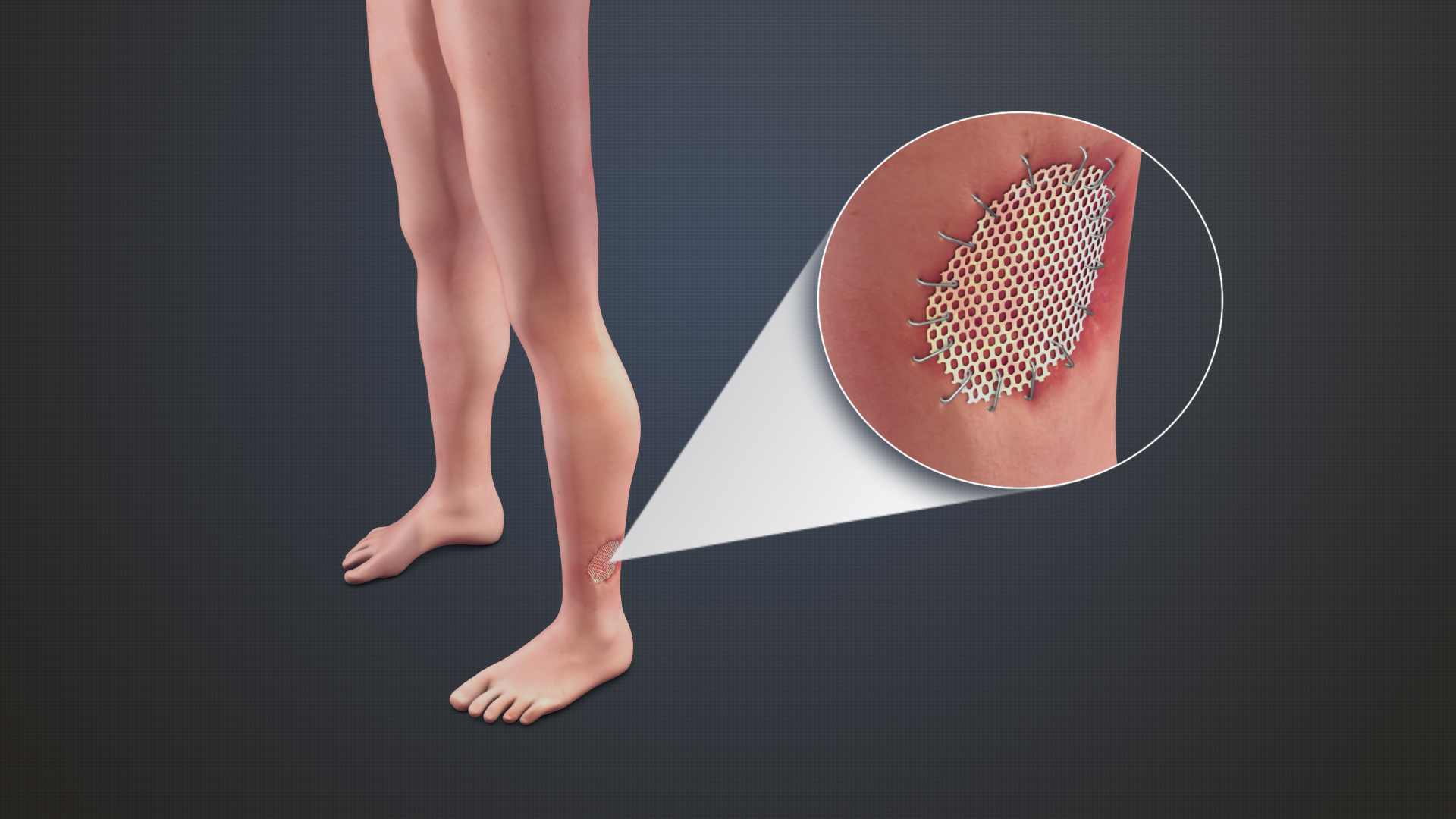
Medical Grafting
Grafting refers to a surgical procedure to move tissue from one site to another on the body, or from another creature, without bringing its own blood supply with it. Instead, a new blood supply grows in after it is placed. A similar technique where tissue is transferred with the blood supply intact is called a flap. In some instances, a graft can be an artificially manufactured device. Examples of this are a tube to carry blood flow across a defect or from an artery to a vein for use in hemodialysis. Classification Autografts and isografts are usually not considered as foreign and, therefore, do not elicit rejection. Allografts and xenografts may be recognized as foreign by the recipient and rejected. * Autograft: graft taken from one part of the body of an individual and transplanted onto another site in the same individual, e.g., skin graft. * Isograft: graft taken from one individual and placed on another individual of the same genetic constitution, e.g., grafts between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veterinary Medicine
Veterinary medicine is the branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, management, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, disorder, and injury in animals. Along with this, it deals with animal rearing, husbandry, breeding, research on nutrition, and product development. The scope of veterinary medicine is wide, covering all animal species, both domesticated and wild, with a wide range of conditions that can affect different species. Veterinary medicine is widely practiced, both with and without professional supervision. Professional care is most often led by a veterinary physician (also known as a veterinarian, veterinary surgeon, or "vet"), but also by paraveterinary workers, such as veterinary nurses or technicians. This can be augmented by other paraprofessionals with specific specialties, such as animal physiotherapy or dentistry, and species-relevant roles such as farriers. Veterinary science helps human health through the monitoring and control of zoonotic disease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schleroderma
Scleroderma is a group of autoimmune diseases that may result in changes to the skin, blood vessels, muscles, and internal organs. The disease can be either localized to the skin or involve other organs, as well. Symptoms may include areas of thickened skin, stiffness, feeling tired, and poor blood flow to the fingers or toes with cold exposure. One form of the condition, known as CREST syndrome, classically results in calcium deposits, Raynaud's syndrome, esophageal problems, thickening of the skin of the fingers and toes, and areas of small, dilated blood vessels. The cause is unknown, but it may be due to an abnormal immune response. Risk factors include family history, certain genetic factors, and exposure to silica. The underlying mechanism involves the abnormal growth of connective tissue, which is believed to be the result of the immune system attacking healthy tissues. Diagnosis is based on symptoms, supported by a skin biopsy or blood tests. While no cure is kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skinfold Test
The body fat percentage (BFP) of a human or other living being is the total mass of fat divided by total body mass, multiplied by 100; body fat includes essential body fat and storage body fat. Essential body fat is necessary to maintain life and reproductive functions. The percentage of essential body fat for women is greater than that for men, due to the demands of childbearing and other hormonal functions. Storage body fat consists of fat accumulation in adipose tissue, part of which protects internal organs in the chest and abdomen. A number of methods are available for determining body fat percentage, such as measurement with calipers or through the use of bioelectrical impedance analysis. The body fat percentage is a measure of fitness level, since it is the only body measurement which directly calculates a person's relative body composition without regard to height or weight. The widely used body mass index (BMI) provides a measure that allows the comparison of the adiposi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |