|
Pied-piping
In linguistics, pied-piping is a phenomenon of syntax whereby a given focused expression brings along an encompassing phrase with it when it is moved. The term was introduced by John Robert Ross in 1967. It references the legend of the Pied Piper of Hamelin, where a piper lures rats and children away from their town. In syntactic pied-piping, a focused expression (such as an interrogative word) pulls its host phrase with it when it moves to its new position in the sentence. Metaphorically, the focused expression is the piper, and the host phrase is the material being pied-piped. Pied-piping is an aspect of syntactic discontinuities and has to do with constituents that can or cannot be discontinuous. Pied-piping is most visible in cases of ''wh''-fronting of information questions and relative clauses, but it is not limited to ''wh''-fronting. It can also occur with almost any type of discontinuity, including extraposition, scrambling, and topicalization. Most, if not all, la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wh-fronting
In linguistics, wh-movement (also known as wh-fronting, wh-extraction, or wh-raising) is the formation of syntactic dependencies involving interrogative words. An example in English is the dependency formed between ''what'' and the object position of ''doing'' in "What are you doing?". Interrogative forms are sometimes known within English linguistics as ''interrogative word, wh-words'', such as ''what, when, where, who'', and ''why'', but also include other interrogative words, such as ''how''. This dependency has been used as a diagnostic tool in syntactic studies as it can be observed to interact with other grammatical constraints. In languages with wh-syntactic movement, movement, sentences or clauses with a wh-word show a non-canonical word order that places the wh-word (or phrase containing the wh-word) at or near the front of the sentence or clause ("''Whom'' are you thinking about?") instead of the canonical position later in the sentence ("I am thinking about ''you''"). Lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pied-piping With Inversion
Pied-piping with inversion is a special word order phenomenon found in some languages, such as those in the Mesoamerican linguistic area. Introduction The phenomenon was first named and identified as an areal characteristic of the Mesoamerican linguistic area in Smith Stark (1988). Some sources also refer to pied-piping with inversion as "secondary wh-movement". The phenomenon can be described as follows: *the language has wh-movement. *the language has pied-piping; that is, when certain words undergo wh-movement, the interrogative word and also the rest of the phrase moves. *the word order within the pied-piped phrase is different from the order of ordinary phrases. The following examples from San Dionisio Ocotepec Zapotec illustrate the phenomenon. As the following example shows, a possessor normally follows the noun that is possessed in the language (Broadwell 2001): If the possessor is questioned, the whole noun phrase must pied-pipe to the beginning of the sentence. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preposition Stranding
Preposition stranding or p-stranding is the syntax, syntactic construction in which a so-called ''stranded'', ''hanging'', or ''dangling'' preposition occurs somewhere other than immediately before its corresponding object (grammar), object; for example, at the end of a sentence. The term ''preposition stranding'' was coined in 1964, predated by stranded preposition in 1949. Linguists had previously identified such a construction as a sentence-terminal preposition or as a preposition at the end. Preposition stranding is found in English and other Germanic languages, as well as in Vata and Gbadi (languages in the Niger–Congo languages, Niger–Congo family), and certain dialects of French language, French spoken in North America. P-stranding occurs in various syntactic contexts, including passive voice, wh-movement, ''wh-''movement, and sluicing. ''Wh-''movement and P-stranding Wh-movement, ''Wh-''movement—which involves ''wh-''words like ''who'', ''what'', ''when'', ''where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages), phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language, and analogous systems of sign languages), and pragmatics (how the context of use contributes to meaning). Subdisciplines such as biolinguistics (the study of the biological variables and evolution of language) and psycholinguistics (the study of psychological factors in human language) bridge many of these divisions. Linguistics encompasses Outline of linguistics, many branches and subfields that span both theoretical and practical applications. Theoretical linguistics is concerned with understanding the universal grammar, universal and Philosophy of language#Nature of language, fundamental nature of language and developing a general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntactic Relationships
In linguistics, syntax ( ) is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics). Diverse approaches, such as generative grammar and functional grammar, offer unique perspectives on syntax, reflecting its complexity and centrality to understanding human language. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from the ancient Greek word , meaning an orderly or systematic arrangement, which consists of (''syn-'', "together" or "alike"), and (''táxis'', "arrangement"). In Hellenistic Greek, this also specifically developed a use referring to the grammatical order of words, with a slightly altered spelling: . The English term, which first appeared in 1548, is partly borrowed from Latin () and Greek, though the Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Syntax
Generative grammar is a research tradition in linguistics that aims to explain the cognitive basis of language by formulating and testing explicit models of humans' subconscious grammatical knowledge. Generative linguists, or generativists (), tend to share certain working assumptions such as the competence–performance distinction and the notion that some domain-specific aspects of grammar are partly innate in humans. These assumptions are rejected in non-generative approaches such as usage-based models of language. Generative linguistics includes work in core areas such as syntax, semantics, phonology, psycholinguistics, and language acquisition, with additional extensions to topics including biolinguistics and music cognition. Generative grammar began in the late 1950s with the work of Noam Chomsky, having roots in earlier approaches such as structural linguistics. The earliest version of Chomsky's model was called Transformational grammar, with subsequent iterati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Radford (linguist)
Andrew Radford (3 July 1945 – 16 December 2024) was a British linguist known for his work in syntax and child language acquisition. His first important contribution to the field was his 1977 book on Italian syntax, a revised version of his doctoral thesis. He achieved international recognition in 1981 for his book ''Transformational Syntax'', which sold over 30,000 copies and was the standard introduction to Chomsky's Government and Binding Theory for many years; and this was followed by an introduction to transformational grammar in 1988, which sold over 70,000. He has since published several books on syntax within the framework of generative grammar and the Minimalist Program of Noam Chomsky, a number of which have appeared in the series Cambridge University Press, Cambridge Textbooks in Linguistics. In the 1990s, Radford was a pioneer of the maturation-based #Structure building model, structure building model of child language, and the acquisition of functional categories i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
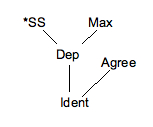
Word Grammar
Word Grammar is a theory of linguistics, developed by Richard Hudson since the 1980s. It started as a model of syntax, whose most distinctive characteristic is its use of dependency grammar, an approach to syntax in which the sentence's structure is almost entirely contained in the information about individual words, and syntax is seen as consisting primarily of principles for combining words. The central syntactic relation is that of dependency between words; constituent structure is not recognized except in the special case of coordinate structures. However an even more important claim of Word Grammar is that statements about words and their properties form a complex network of propositions. More recent work on Word Grammar cites neurocognitive linguistics as a source of inspiration for the idea that language is nothing but a network. One of the attractions of the network view is the possibility of analysing language in the same way as other kinds of knowledge, given that knowled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimalist Program
In linguistics, the minimalist program is a major line of inquiry that has been developing inside generative grammar since the early 1990s, starting with a 1993 paper by Noam Chomsky. Following Imre Lakatos's distinction, Chomsky presents minimalism as a research program, program, understood as a mode of inquiry that provides a conceptual framework which guides the development of linguistic theory. As such, it is characterized by a broad and diverse range of research directions. For Chomsky, there are two basic Minimalist grammar, minimalist questions—What is language? and Why does it have the properties it has?—but the answers to these two questions can be framed in any theory.Boeckx, Cedric ''Linguistic Minimalism. Origins, Concepts, Methods and Aims'', pp. 84 and 115. Conceptual framework Goals and assumptions Minimalism is an approach developed with the goal of understanding the nature of language. It models a speaker's knowledge of language as a computational syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optimality Theory
Optimality theory (frequently abbreviated OT) is a linguistic model proposing that the observed forms of language arise from the optimal satisfaction of conflicting constraints. OT differs from other approaches to phonological analysis, which typically use rules rather than constraints. However, phonological models of representation, such as autosegmental phonology, prosodic phonology, and linear phonology (SPE), are equally compatible with rule-based and constraint-based models. OT views grammars as systems that provide mappings from inputs to outputs; typically, the inputs are conceived of as underlying representations, and the outputs as their surface realizations. It is an approach within the larger framework of generative grammar. Optimality theory has its origin in a talk given by Alan Prince and Paul Smolensky in 1991 which was later developed in a book manuscript by the same authors in 1993. Overview There are three basic components of the theory: * Generator () t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head-driven Phrase Structure Grammar
Head-driven phrase structure grammar (HPSG) is a highly lexicalized, constraint-based grammar developed by Carl Pollard and Ivan Sag. It is a type of phrase structure grammar, as opposed to a dependency grammar, and it is the immediate successor to generalized phrase structure grammar. HPSG draws from other fields such as computer science (type system, data type theory and knowledge representation) and uses Ferdinand de Saussure's notion of the sign (linguistics), sign. It uses a uniform formalism and is organized in a modular way which makes it attractive for natural language processing. An HPSG includes principles and grammar rules and lexicon entries which are normally not considered to belong to a grammar. The formalism is based on lexicalism. This means that the lexicon is more than just a list of entries; it is in itself richly structured. Individual entries are marked with types. Types form a hierarchy. Early versions of the grammar were very lexicalized with few grammatica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |