|
Photoisomerization
In chemistry, photoisomerization is a form of isomerization induced by photoexcitation. Both reversible and irreversible photoisomerizations are known for photoswitchable compounds. The term "photoisomerization" usually, however, refers to a reversible process. Applications Photoisomerization of the compound retinal in the eye allows for vision. Photoisomerizable substrates have been put to practical use, for instance, in pigments for rewritable CDs, DVDs, and 3D optical data storage solutions. In addition, interest in photoisomerizable molecules has been aimed at molecular devices, such as molecular switches, molecular motors, and molecular electronics. Another class of device that uses the photoisomerization process is as an additive in liquid crystals to change their linear and nonlinear properties. Due to the photoisomerization is possible to induce a molecular reorientation in the liquid crystal bulk, which is used in holography, as spatial filter or optical switching. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoswitch
A photoswitch is a type of molecule that can change its structural geometry and chemical properties upon irradiation with electromagnetic radiation. Although often used interchangeably with the term molecular machine, a switch does not perform work upon a change in its shape whereas a machine does. However, photochromic compounds are the necessary building blocks for light driven molecular motors and machines. Upon irradiation with light, photoisomerization about double bonds in the molecule can lead to changes in the cis- or trans- configuration. These photochromic molecules are being considered for a range of applications. Chemical structures and properties A photochromic compound can change its configuration or structure upon irradiation with light. Several examples of photochromic compounds include: azobenzene, spiropyran, merocyanine, diarylethene, spirooxazine, fulgide, hydrazone, nobormadiene, thioindigo, acrylamide-azobenzene-quaternary ammonia, donor-acceptor Stenhouse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
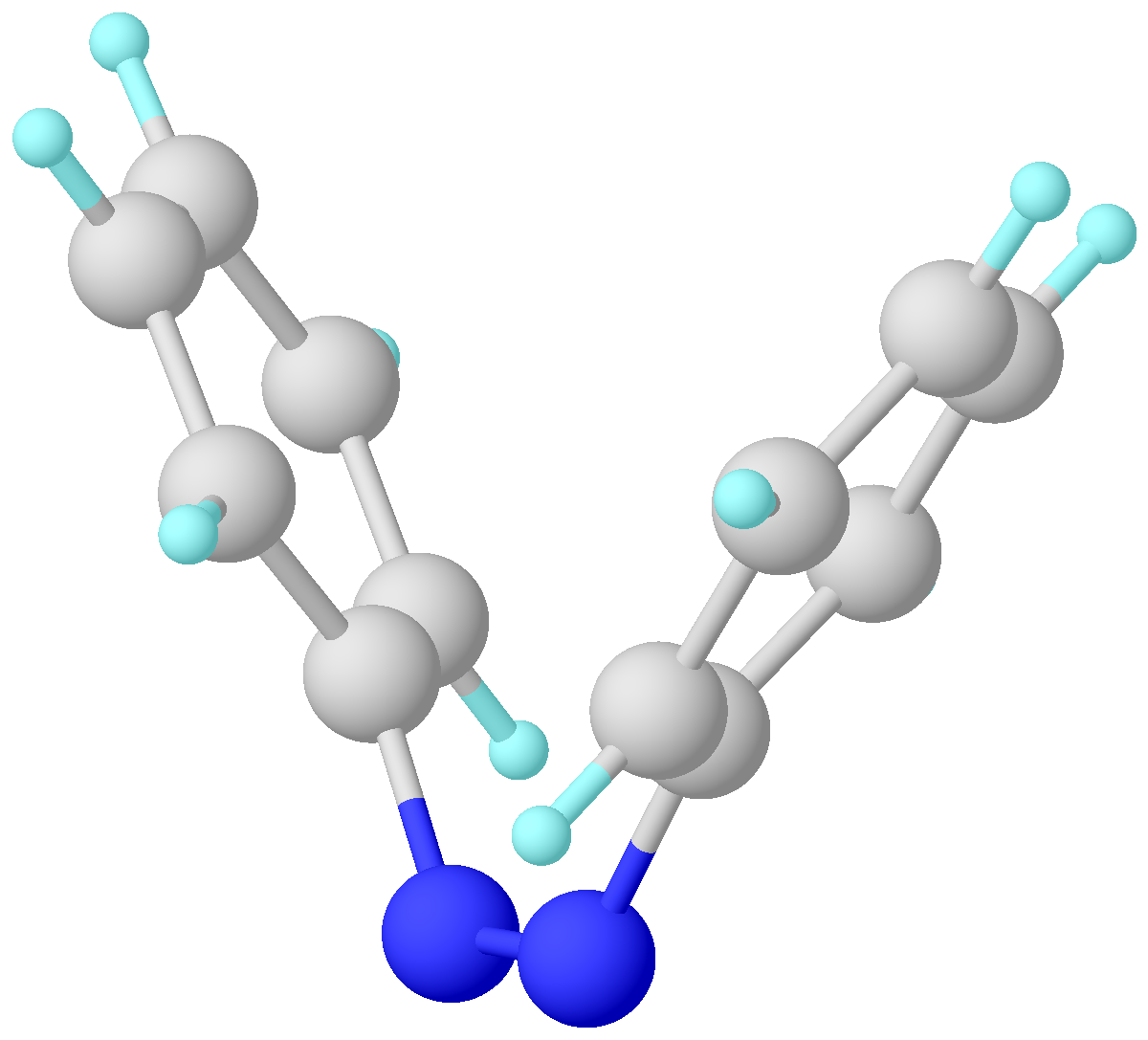
Azobenzene
Azobenzene is a photoswitchable chemical compound composed of two phenyl rings linked by a N=N double bond. It is the simplest example of an aryl azo compound. The term 'azobenzene' or simply 'azo' is often used to refer to a wide class of similar compounds. These azo compounds are considered as derivatives of diazene (diimide), and are sometimes referred to as 'diazenes'. The diazenes absorb light strongly and are common dyes. Structure and synthesis ''trans''-Azobenzene is planar. The N-N distance is 1.189 Å. ''cis''-Azobenzene is nonplanar with a C-N=N-C dihedral angle of 173.5°. The N-N distance is 1.251 Å. Azobenzene was first described by Eilhard Mitscherlich in 1834. Yellowish-red crystalline flakes of azobenzene were obtained in 1856. Its original preparation is similar to the modern one. According to the 1856 method, nitrobenzene is reduced by iron filings in the presence of acetic acid. In the modern synthesis, zinc is the reductant in the presence of a base. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fulgide
In organic chemistry, a fulgide is any of a class of photochromic compounds consisting of a bis methylene-succinic anhydride core that has an aromatic group as a substituent. The highly conjugated system is a good chromophore. It can undergo reversible photoisomerization induced by ultraviolet light, converting between the ''E'' and ''Z'' isomers, both of which are typically colorless compounds. Unlike the more-stable ''Z'' isomer, the ''E'' isomer can also undergo a photochemically-induced electrocyclic reaction, forming a new ring and becoming a distinctly colored product called the ''C'' form. It is thus the two-step ''Z''–''C'' isomerization that is the photochromic change starting from the stable uncyclized form. : History The first compound of this class was synthesized in 1905, with the name based on the Latin word "fulgere", meaning shiny, for the shiny and large variety of colors of the crystal. The photochromic mechanism of fulgide was reported in 1968. Not until 1981 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Optical Data Storage
3D optical data storage is any form of optical data storage in which information can be recorded or read with three-dimensional resolution (as opposed to the two-dimensional resolution afforded, for example, by CD). This innovation has the potential to provide petabyte-level mass storage on DVD-sized discs (120mm). Data recording and readback are achieved by focusing lasers within the medium. However, because of the volumetric nature of the data structure, the laser light must travel through other data points before it reaches the point where reading or recording is desired. Therefore, some kind of nonlinearity is required to ensure that these other data points do not interfere with the addressing of the desired point. No commercial product based on 3Doptical data storage has yet arrived on the mass market, although several companies are actively developing the technology and claim that it may become available 'soon'. Overview Current optical data storage media, such as the CD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bis(triphenylphosphine)platinum Chloride
Bis(triphenylphosphine)platinum chloride is a metal phosphine complex with the formula PtCl2 (C6H5)3sub>2. Cis- and trans isomers are known. The cis isomer is a white crystalline powder, while the trans isomer is yellow. Both isomers are square planar about the central platinum atom. The cis isomer is used primarily as a reagent for the synthesis of other platinum compounds. Preparation The cis isomer is the prepared by heating solutions of platinum(II) chlorides with triphenylphosphine. For example, starting from potassium tetrachloroplatinate: :K2PtCl4 + 2 PPh3 → ''cis''-Pt(PPh3)2Cl2 + 2 KCl The trans isomer is the prepared by treating potassium trichloro(ethylene)platinate(II) (Zeise's salt) with triphenylphosphine: :KPt(C2H4)Cl3 + 2 PPh3 → ''trans''-Pt(PPh3)2Cl2 + KCl + C2H4 With heating or in the presence of excess PPh3, the trans isomer converts to the cis complex. The latter complex is the thermodynamic product due to triphenylphosphine being a strong trans effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinal
Retinal (also known as retinaldehyde) is a polyene chromophore. Retinal, bound to proteins called opsins, is the chemical basis of visual phototransduction, the light-detection stage of visual perception (vision). Some microorganisms use retinal to convert light into metabolic energy. In fact, a recent study suggests most living organisms on our planet ~3 billion years ago used retinal to convert sunlight into energy rather than chlorophyll. Since retinal absorbs mostly green light and transmits purple light, this gave rise to the Purple Earth Hypothesis. There are many forms of vitamin A — all of which are converted to retinal, which cannot be made without them. Retinal itself is considered to be a form of vitamin A when eaten by an animal. The number of different molecules that can be converted to retinal varies from species to species. Retinal was originally called retinene, and was renamed after it was discovered to be vitamin A aldehyde. Vertebrate animals ingest reti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthesis Of Quadricyclane From Norbornadiene
Synthesis or synthesize may refer to: Science Chemistry and biochemistry *Chemical synthesis, the execution of chemical reactions to form a more complex molecule from chemical precursors **Organic synthesis, the chemical synthesis of organic compounds ***Total synthesis, the complete organic synthesis of complex organic compounds, usually without the aid of biological processes ***Convergent synthesis or linear synthesis, a strategy to improve the efficiency of multi-step chemical syntheses **Dehydration synthesis, a chemical synthesis resulting in the loss of a water molecule *Biosynthesis, the creation of an organic compound in a living organism, usually aided by enzymes **Photosynthesis, a biochemical reaction using a carbon molecule to produce an organic molecule, using sunlight as a catalyst **Chemosynthesis, the synthesis of biological compounds into organic waste, using methane or an oxidized molecule as a catalyst **Amino acid synthesis, the synthesis of an amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norbornadiene
Norbornadiene is an organic compound In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The ... and a bicyclic hydrocarbon. Norbornadiene is of interest as a metal-binding ligand, whose complexes are useful for homogeneous catalysis. It has been intensively studied owing to its high reactivity and distinctive structural property of being a diene that cannot isomerization, isomerize (isomers would be anti-Bredt alkenes). Norbornadiene is also a useful Diels–Alder_reaction#The_dienophile, dienophile in Diels-Alder reactions. Synthesis Norbornadiene can be formed by a Diels-Alder reaction between cyclopentadiene and acetylene : Reactions Quadricyclane, a valence isomer, can be obtained from norbornadiene by a photochemical reaction when assisted by a photochemical sensitizer, sensiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadricyclane
Quadricyclane is a strained, multi-cyclic hydrocarbon with the formula CH2(CH)6. A white volatile colorless liquid, it is highly strained molecule (78.7 kcal/mol). Isomerization of quadricyclane proceeds slowly at low temperatures.Petrov, V. A; Vasil’ev, N. V. “Synthetic Chemistry of Quadricyclane.” ''Current Organic Synthesis'' 3 (2006): 215–259 Because of quadricyclane’s strained structure and thermal stability, it has been studied extensively. Preparation Quadricyclane is produced by the irradiation of norbornadiene (bicyclo .2.1epta-2,5-diene) in the presence of Michler's ketone or ethyl Michler's ketone. Other sensitizers, such as acetone, benzophenone, acetophenone, etc., may be used but with a lesser yield. The yield is higher for freshly distilled norbornadiene, but commercial reagents will suffice. : Proposed applications to solar energy The conversion of norbornadiene into quadricyclane is achievd with ~300nm UV radiation. . When converted back to norbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UV Radiation
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack the energy to ionize atoms, it can cause chemical reactions and causes many substances to glow or fluoresce. Consequently, the chemical and biological effects of UV are greater than simple heating effects, and many practical applications of UV radiation derive from its interactions with organic molecules. Short-wave ultraviolet light damages DNA and sterilizes surfaces with which it comes into contact. For h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Energy
Solar energy is radiant light and heat from the Sun that is harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar power to generate electricity, solar thermal energy (including solar water heating), and solar architecture. It is an essential source of renewable energy, and its technologies are broadly characterized as either passive solar or active solar depending on how they capture and distribute solar energy or convert it into solar power. Active solar techniques include the use of photovoltaic systems, concentrated solar power, and solar water heating to harness the energy. Passive solar techniques include orienting a building to the Sun, selecting materials with favorable thermal mass or light-dispersing properties, and designing spaces that naturally circulate air. The large magnitude of solar energy available makes it a highly appealing source of electricity. In 2020 solar energy has been the cheapest source of Electricity. In Saudi Arabia a power purchase agreemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |