|
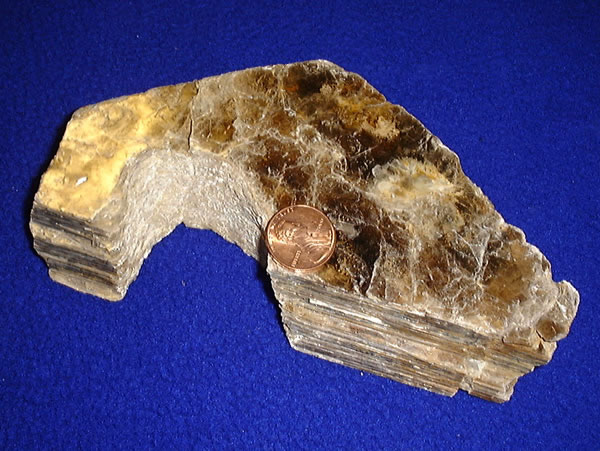
Phlogopite
Phlogopite is a yellow, greenish, or reddish-brown member of the mica family of phyllosilicates. It is also known as magnesium mica. Phlogopite is the magnesium endmember of the biotite solid solution series, with the chemical formula KMg3AlSi3O10(F,OH)2. Iron substitutes for magnesium in variable amounts leading to the more common biotite with higher iron content. For physical and optical identification, it shares most of the characteristic properties of biotite. Paragenesis Phlogopite is an important and relatively common end-member composition of biotite. Phlogopite micas are found primarily in igneous rocks, although it is also common in contact metamorphic aureoles of intrusive igneous rocks with magnesian country rocks and in marble formed from impure dolomite (dolomite with some siliclastic sediment). The occurrence of phlogopite mica within igneous rocks is difficult to constrain precisely because the primary control is rock composition as expected, but phlogopite is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mica
Micas ( ) are a group of silicate minerals whose outstanding physical characteristic is that individual mica crystals can easily be split into extremely thin elastic plates. This characteristic is described as perfect basal cleavage. Mica is common in igneous and metamorphic rock and is occasionally found as small flakes in sedimentary rock. It is particularly prominent in many granites, pegmatites, and schists, and "books" (large individual crystals) of mica several feet across have been found in some pegmatites. Micas are used in products such as drywalls, paints, fillers, especially in parts for automobiles, roofing and shingles, as well as in electronics. The mineral is used in cosmetics and food to add "shimmer" or "frost." Properties and structure The mica group is composed of 37 phyllosilicate minerals. All crystallize in the monoclinic system, with a tendency towards pseudohexagonal crystals, and are similar in structure but vary in chemical composition. Micas are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mica
Micas ( ) are a group of silicate minerals whose outstanding physical characteristic is that individual mica crystals can easily be split into extremely thin elastic plates. This characteristic is described as perfect basal cleavage. Mica is common in igneous and metamorphic rock and is occasionally found as small flakes in sedimentary rock. It is particularly prominent in many granites, pegmatites, and schists, and "books" (large individual crystals) of mica several feet across have been found in some pegmatites. Micas are used in products such as drywalls, paints, fillers, especially in parts for automobiles, roofing and shingles, as well as in electronics. The mineral is used in cosmetics and food to add "shimmer" or "frost." Properties and structure The mica group is composed of 37 phyllosilicate minerals. All crystallize in the monoclinic system, with a tendency towards pseudohexagonal crystals, and are similar in structure but vary in chemical composition. Micas are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
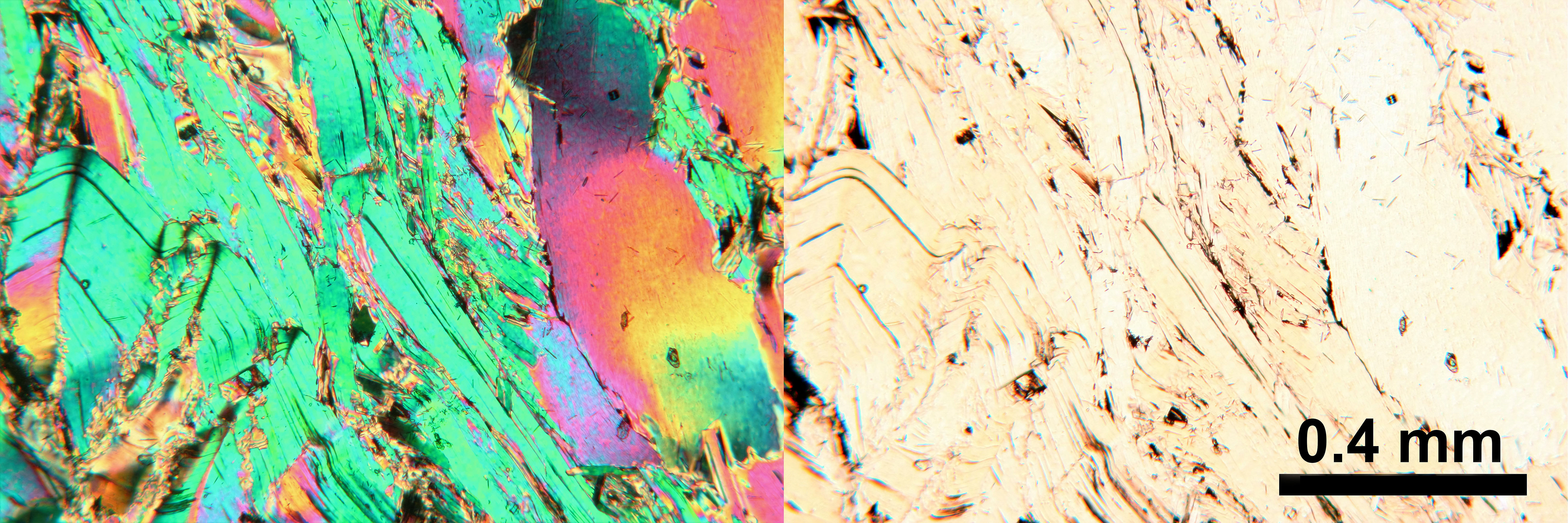
Phlogopite Peridotite
Phlogopite is a yellow, greenish, or reddish-brown member of the mica family of phyllosilicates. It is also known as magnesium mica. Phlogopite is the magnesium endmember of the biotite solid solution series, with the chemical formula KMg3AlSi3O10(F,OH)2. Iron substitutes for magnesium in variable amounts leading to the more common biotite with higher iron content. For physical and optical identification, it shares most of the characteristic properties of biotite. Paragenesis Phlogopite is an important and relatively common end-member composition of biotite. Phlogopite micas are found primarily in igneous rocks, although it is also common in contact metamorphic aureoles of intrusive igneous rocks with magnesian country rocks and in marble formed from impure dolomite (dolomite with some siliclastic sediment). The occurrence of phlogopite mica within igneous rocks is difficult to constrain precisely because the primary control is rock composition as expected, but phlogopite is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamproite
Lamproite is an ultrapotassic mantle-derived volcanic or subvolcanic rock. It has low CaO, Al2O3, Na2O, high K2O/Al2O3, a relatively high MgO content and extreme enrichment in incompatible elements. Lamproites are geographically widespread yet are volumetrically insignificant. Unlike kimberlites, which are found exclusively in Archaean cratons, lamproites are found in terrains of varying age, ranging from Archaean in Western Australia, to Palaeozoic and Mesozoic in southern Spain. They also vary widely in age, from Proterozoic to Pleistocene, the youngest known example from Gaussberg in Antarctica being 56,000 ± 5,000 years old. Lamproite volcanology is varied, with both diatreme styles and cinder cone or cone edifices known. Petrology Lamproites form from partially melted mantle at depths exceeding 150 km. The molten material is forced to the surface in volcanic pipes, bringing with it xenoliths and diamonds from the harzburgitic peridotite or eclogite mantle regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kimberlite
Kimberlite is an igneous rock and a rare variant of peridotite. It is most commonly known to be the main host matrix for diamonds. It is named after the town of Kimberley in South Africa, where the discovery of an diamond called the Star of South Africa in 1869 spawned a diamond rush and the digging of the open-pit mine called the Big Hole. Previously, the term kimberlite has been applied to olivine lamproites as Kimberlite II, however this has been in error. Kimberlite occurs in the Earth's crust in vertical structures known as kimberlite pipes, as well as igneous dykes. Kimberlite also occurs as horizontal sills. Kimberlite pipes are the most important source of mined diamonds today. The consensus on kimberlites is that they are formed deep within the mantle. Formation occurs at depths between , potentially from anomalously enriched exotic mantle compositions, and they are erupted rapidly and violently, often with considerable carbon dioxide and other volatile componen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamprophyres
Lamprophyres () are uncommon, small-volume ultrapotassic igneous rocks primarily occurring as dikes, lopoliths, laccoliths, stocks, and small intrusions. They are alkaline silica-undersaturated mafic or ultramafic rocks with high magnesium oxide, >3% potassium oxide, high sodium oxide, and high nickel and chromium. Lamprophyres occur throughout all geologic era (geology), eras. Archean, Archaean examples are commonly associated with lode gold deposits. Cenozoic examples include magnesian rocks in Mexico and South America, and young ultramafic lamprophyres from Gympie in Australia with 18.5% MgO at ~250 Ma. Petrology Modern science treats lamprophyres as a catch-all term for ultrapotassic mafic A mafic mineral or rock is a silicate mineral or igneous rock rich in magnesium and iron. Most mafic minerals are dark in color, and common rock-forming mafic minerals include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Common mafic rocks include ... igneous rocks which have primary m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamprophyre
Lamprophyres () are uncommon, small-volume ultrapotassic igneous rocks primarily occurring as dikes, lopoliths, laccoliths, stocks, and small intrusions. They are alkaline silica-undersaturated mafic or ultramafic rocks with high magnesium oxide, >3% potassium oxide, high sodium oxide, and high nickel and chromium. Lamprophyres occur throughout all geologic eras. Archaean examples are commonly associated with lode gold deposits. Cenozoic examples include magnesian rocks in Mexico and South America, and young ultramafic lamprophyres from Gympie in Australia with 18.5% MgO at ~250 Ma. Petrology Modern science treats lamprophyres as a catch-all term for ultrapotassic mafic igneous rocks which have primary mineralogy consisting of amphibole or biotite, and with feldspar in the groundmass. Lamprophyres are not amenable to classification according to modal proportions, such as the system QAPF due to peculiar mineralogy, nor compositional discrimination diagrams, such as TAS be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial planet, rocky planet or natural satellite, moon. More than 90% of all volcanic rock on Earth is basalt. Rapid-cooling, fine-grained basalt is chemically equivalent to slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro. The eruption of basalt lava is observed by geologists at about 20 volcanoes per year. Basalt is also an important rock type on other planetary bodies in the Solar System. For example, the bulk of the plains of volcanism on Venus, Venus, which cover ~80% of the surface, are basaltic; the lunar mare, lunar maria are plains of flood-basaltic lava flows; and basalt is a common rock on the surface of Mars. Molten basalt lava has a low viscosity due to its relatively low silica content (between 45% and 52%), resulting in rapidly moving lava flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotite
Biotite is a common group of phyllosilicate minerals within the mica group, with the approximate chemical formula . It is primarily a solid-solution series between the iron-endmember annite, and the magnesium-endmember phlogopite; more aluminous end-members include siderophyllite and eastonite. Biotite was regarded as a mineral ''species'' by the International Mineralogical Association until 1998, when its status was changed to a mineral ''group''. The term ''biotite'' is still used to describe unanalysed dark micas in the field. Biotite was named by J.F.L. Hausmann in 1847 in honor of the French physicist Jean-Baptiste Biot, who performed early research into the many optical properties of mica. Members of the biotite group are sheet silicates. Iron, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, oxygen, and hydrogen form sheets that are weakly bound together by potassium ions. The term "iron mica" is sometimes used for iron-rich biotite, but the term also refers to a flaky micaceous form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metasomatism
Metasomatism (from the Greek μετά ''metá'' "change" and σῶμα ''sôma'' "body") is the chemical alteration of a rock by hydrothermal and other fluids. It is the replacement of one rock by another of different mineralogical and chemical composition. The minerals which compose the rocks are dissolved and new mineral formations are deposited in their place. Dissolution and deposition occur simultaneously and the rock remains solid. Synonyms to the word metasomatism are metasomatose and metasomatic process. The word metasomatose can also be used as a name for specific varieties of metasomatism (for example '' Mg-metasomatose'' and '' Na-metasomatose''). Metasomatism can occur via the action of hydrothermal fluids from an igneous or metamorphic source. In the igneous environment, metasomatism creates skarns, greisen, and may affect hornfels in the contact metamorphic aureole adjacent to an intrusive rock mass. In the metamorphic environment, metasomatism is created by mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metasomatic
Metasomatism (from the Greek μετά ''metá'' "change" and σῶμα ''sôma'' "body") is the chemical alteration of a rock by hydrothermal and other fluids. It is the replacement of one rock by another of different mineralogical and chemical composition. The minerals which compose the rocks are dissolved and new mineral formations are deposited in their place. Dissolution and deposition occur simultaneously and the rock remains solid. Synonyms to the word metasomatism are metasomatose and metasomatic process. The word metasomatose can also be used as a name for specific varieties of metasomatism (for example '' Mg-metasomatose'' and '' Na-metasomatose''). Metasomatism can occur via the action of hydrothermal fluids from an igneous or metamorphic source. In the igneous environment, metasomatism creates skarns, greisen, and may affect hornfels in the contact metamorphic aureole adjacent to an intrusive rock mass. In the metamorphic environment, metasomatism is created by mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrapotassic Igneous Rocks
Ultrapotassic igneous rocks are a class of rare, volumetrically minor and generally ultramafic or mafic silica-depleted igneous rocks. Ultrapotassic rocks are defined by molar K2 O/ Na2O >3 in much of the scientific literature. In other papers written as recently as 2005, they are defined as rocks with weight percents K2O/Na2O >2. Hence, caution is indicated in interpreting use of the term "ultrapotassic", and the nomenclature of these rocks continues to be debated. Genesis of these ultrapotassic rocks has been much discussed. The magmas probably are produced by a variety of mechanisms and from a variety of sources. The magma production may be favored by the following:*Stephen Foley and Angelo Peccerillo, ''Potassic and ultrapotassic magmas and their origin'', Lithos, v. 28, p. 181-185 (1992) * great depth of partial melting * low degrees of partial melting * lithophile element (K, Ba, Cs, Rb) enrichment in sources * peridotite (variety harzburgite) so enriched, especially in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |