|
Phenylphosphine
Phenylphosphine is an organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula C6H5PH2. It is the phosphorus analog of aniline. Like other primary phosphines, phenylphosphine has an intense penetrating odor and is highly oxidizable. It is mainly used as a precursor to other organophosphorus compounds. It can function as a ligand in coordination chemistry. Synthesis Phenylphosphine can be produced by reducing dichlorophenylphosphine with lithium aluminum hydride in ether: :LiAlH4 + 2C6H5PCl2 → 2C6H5PH2 + Li+ + Al3+ + 4Cl− This reaction is performed under a nitrogen atmosphere to prevent side reactions involving oxygen. Reactions Oxidation of phenylphosphine with air affords the oxide. :C6H5PH2 + O2 → C6H5P(OH)2 Bis(2-cyanoethylphenyl)phosphine, which is of interest as a synthetic intermediate, can be made from phenylphosphine by base-catalyzed allylic addition to acrylonitrile. :C6H5PH2 + 2CH2=CHCN → C6H5P(CH2CH2CN)2 Bis(2-cyanoethylphenyl)phosphine is a useful precursor to 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphinidene
Phosphinidenes (IUPAC: phosphanylidenes, formerly phosphinediyls) are low-valent phosphorus compounds analogous to carbenes and nitrenes, having the general structure RP. The "free" form of these compounds is conventionally described as having a singly-coordinated phosphorus atom containing only 6 electrons in its valence level. Most phosphinidenes are highly reactive and short-lived, thereby complicating empirical studies on their chemical properties. In the last few decades, several strategies have been employed to stabilize phosphinidenes (e.g. π-donation, steric protection, transition metal complexation), and researchers have developed a number of reagents and systems that can generate and transfer phosphinidenes as reactive intermediates in the synthesis of various organophosphorus compounds. Electronic Structure Like carbenes, phosphinidenes can exist in either a singlet state or triplet state, with the triplet state typically being more stable. The stability of these state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organophosphorus Compound
Organophosphorus compounds are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX nerve agents. Organophosphorus chemistry is the corresponding science of the properties and reactivity of organophosphorus compounds. Phosphorus, like nitrogen, is in group 15 of the periodic table, and thus phosphorus compounds and nitrogen compounds have many similar properties. The definition of organophosphorus compounds is variable, which can lead to confusion. In industrial and environmental chemistry, an organophosphorus compound need contain only an organic substituent, but need not have a direct phosphorus-carbon (P-C) bond. Thus a large proportion of pesticides (e.g., malathion), are often included in this class of compounds. Phosphorus can adopt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aniline
Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine In organic chemistry, an aromatic amine is an organic compound consisting of an aromatic ring attached to an amine. It is a broad class of compounds that encompasses aniline Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consi .... It is an industrially significant Commodity chemicals, commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starting material for fine chemical synthesis. Its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane, dyes, and other industrial chemicals. Like most volatile amines, it has the odor of rotten fish. It Combustion, ignites readily, burning with a smoky flame characteristic of aromatic compounds. It is toxic to humans. Relative to benzene, it is electron-rich. It thus participates more rapidly in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Likewise, it is also prone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Phosphine
Primary or primaries may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and labels * Primary (band), from Australia * Primary (musician), hip hop musician and record producer from South Korea * Primary Music, Israeli record label Works * ''Primary'' (album) by Rubicon (2002) * "Primary" (song) by The Cure * "Primary", song by Spoon from the album ''Telephono'' Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * Primaries or primary beams, in E. E. Smith's science-fiction series ''Lensman'' * ''Primary'' (film), American political documentary (1960) Computing * PRIMARY, an X Window selection * Primary data storage, computer technology used to retain digital data * Primary server, main server on the server farm Education * Primary education, the first stage of compulsory education * Primary FRCA, academic examination for anaesthetists in the U.K. * Primary school, school providing primary education Mathematics * ''p''-group of prime power order * Primary decomposition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent to ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acidic "ligands". Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in almost all circumstances, although gaseous "naked" metal ions can be generated in a high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection requires critical consideration in many practical areas, including bioinorganic and medicinal chemistry, homogeneous catalysis, and environmental chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Chemistry
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the Periodic Table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom are common. These compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichlorophenylphosphine
Dichlorophenylphosphine is an organophosphorus compound with the formula C6H5PCl2. This colourless viscous liquid is commonly used in the synthesis of organophosphines. Dichlorophenylphosphine is commercially available. It may be prepared by an electrophilic substitution of benzene by phosphorus trichloride, catalyzed by aluminium chloride. The compound is an intermediate for the synthesis of other chemicals for instance dimethylphenylphosphine: :C6H5PCl2 + 2 CH3MgI → C6H5P(CH3)2 + 2 MgICl Many tertiary phosphines can be prepared by this route. In the McCormack reaction dichlorophenylphosphine adds dienes to give the chlorophospholenium ring. : Reductive coupling of the dichlorophosphine gives the cyclophosphine (PhP)5.{{cite journal , author = Marianne Baudler, Klaus Glinka , title = Monocyclic and Polycyclic Phosphines , journal = Chem. Rev. ''Chemical Reviews'' is peer-reviewed scientific journal published twice per month by the American Chemical Society. It publishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air-free Technique
Air-free techniques refer to a range of manipulations in the chemistry laboratory for the handling of compounds that are air-sensitive. These techniques prevent the compounds from reacting with components of air, usually water and oxygen; less commonly carbon dioxide and nitrogen. A common theme among these techniques is the use of a fine (100–10−3 Torr) or high (10−3–10−6 Torr) vacuum to remove air, and the use of an inert gas: preferably argon, but often nitrogen. The two most common types of air-free technique involve the use of a glovebox and a Schlenk line, although some rigorous applications use a high-vacuum line. In both methods, glassware (often Schlenk tubes) are pre-dried in ovens prior to use. They may be flame-dried to remove adsorbed water. Prior to coming into an inert atmosphere, vessels are further dried by ''purge-and-refill'' — the vessel is subjected to a vacuum to remove gases and water, and then refilled with inert gas. This cycle is usually r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
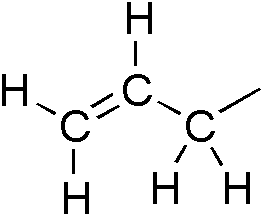
Allyl
In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula , where R is the rest of the molecule. It consists of a methylene bridge () attached to a vinyl group (). The name is derived from the scientific name for garlic, . In 1844, Theodor Wertheim isolated an allyl derivative from garlic oil and named it "". The term allyl applies to many compounds related to , some of which are of practical or of everyday importance, for example, allyl chloride. Allylation is any chemical reaction that adds an allyl group to a substrate. Nomenclature A site adjacent to the unsaturated carbon atom is called the allylic position or allylic site. A group attached at this site is sometimes described as allylic. Thus, "has an allylic hydroxyl group". Allylic C−H bonds are about 15% weaker than the C−H bonds in ordinary sp3 carbon centers and are thus more reactive. Benzylic and allylic are related in terms of structure, bond strength, and reactivity. Other re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grignard Reaction
The Grignard reaction () is an organometallic chemical reaction in which alkyl, allyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides ( Grignard reagent) is added to a carbonyl group in an aldehyde or ketone. This reaction is important for the formation of carbon–carbon bonds. The reaction of an organic halide with magnesium is ''not'' a Grignard reaction, but provides a Grignard reagent. : Grignard reactions and reagents were discovered by and are named after the French chemist François Auguste Victor Grignard (University of Nancy, France), who published it in 1900 and was awarded the 1912 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work. Reaction mechanism Because carbon is more electronegative than magnesium, the carbon attached to magnesium functions as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon atom that is present within the polar bond of a carbonyl group. The addition of the Grignard reagent to the carbonyl typically proceeds through a six-membered ring transition state. Based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reformatsky Reaction
The Reformatsky reaction (sometimes misspelled Reformatskii reaction) is an organic reaction which condenses aldehydes or ketones with α-halo esters using metallic zinc to form β-hydroxy-esters: The organozinc reagent, also called a 'Reformatsky enolate', is prepared by treating an alpha-halo ester with zinc dust. Reformatsky enolates are less reactive than lithium enolates or Grignard reagents and hence nucleophilic addition to the ester group does not occur. The reaction was discovered by Sergey Nikolaevich Reformatsky. Some reviews have been published. In addition to aldehydes and ketones, it has also been shown that the Reformatsky enolate is able to react with acid chlorides, imines, nitriles (see Blaise reaction), and nitrones. Moreover, metals other than zinc have also been used, including magnesium, iron, cobalt, nickel, germanium, cadmium, indium, barium, and cerium. Additionally, metal salts are also applicable in place of metals, notably samarium(II) iodide, chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemische Berichte
''Chemische Berichte'' (usually abbreviated as ''Ber.'' or ''Chem. Ber.'') was a German-language scientific journal of all disciplines of chemistry founded in 1868. It was one of the oldest scientific journals in chemistry, until it merged with ''Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas'' to form ''Chemische Berichte/Recueil'' in 1997. ''Chemische Berichte/Recueil'' was then merged with other European journals in 1998 to form ''European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry''. History Founded in 1868 as ''Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft'' (, CODEN BDCGAS), it operated under this title until 1928 (Vol. 61). The journal was then split into: * ''Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft, A: Vereins-Nachrichten'' (, CODEN BDCAAS), and * ''Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft, B: Abhandlungen'' (, CODEN BDCBAD). Vol. 78 and 79 (1945–1946) were omitted and not published due to World War II. The journal was renamed ''Chemische Berichte'' (, CODEN CHBEAM) in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


4-3D-balls.png)