|
Phenoxyethanol
Phenoxyethanol is the organic compound with the formula C6H5OC2H4OH. It is a colorless oily liquid. It can be classified as a glycol ether and a phenol ether. It is a common preservative in vaccine formulations. It has a faint rose-like aroma. Use Phenoxyethanol has germicidal and germistatic properties. It is often used together with quaternary ammonium compounds. Phenoxyethanol is used as a perfume fixative; an insect repellent; an antiseptic; a solvent for cellulose acetate, dyes, inks, and resins; a preservative for pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and lubricants; an anesthetic in fish aquaculture; and in organic synthesis. It is an alternative to formaldehyde-releasing preservatives. In Japan and the European Union, its concentration in cosmetics is restricted to 1%. History and synthesis Phenoxyethanol was first prepared by W. H. Perkin Jr. and his graduate student Edward Haworth in 1896. They reacted sodium, phenol and 2-chloroethanol in anhydrous ethanol. Starting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycol Ether
Glycol ethers are a class of chemical compounds consisting of alkyl ethers that are based on glycols such as ethylene glycol or propylene glycol. They are commonly used as solvents in paints and cleaners. They have good solvent properties while having higher boiling points than the lower-molecular-weight ethers and Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols. History The name "Cellosolve" was registered in 1924 as a United States trademark by Carbide & Carbon Chemicals Corporation (a division of Union_Carbide , Union Carbide Corporation) for "Solvents for Gums, Resins, Cellulose Esters, and the Like". "Ethyl Cellosolve" or simply "Cellosolve" consists mainly of ethylene glycol monoethyl ether and was introduced as a lower-cost solvent alternative to ethyl lactate. "Butyl Cellosolve" (ethylene glycol monobutyl ether) was introduced in 1928, and "Methyl Cellosolve" (ethylene glycol monomethyl ether) in 1929. Types Glycol ethers are designated "E-series" or "P-series" for those made from ethylene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroform
Chloroform, or trichloromethane (often abbreviated as TCM), is an organochloride with the formula and a common solvent. It is a volatile, colorless, sweet-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to refrigerants and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). Chloroform was once used as an inhalational anesthetic between the 19th century and the first half of the 20th century. It is miscible with many solvents but it is only very slightly soluble in water (only 8 g/L at 20°C). Structure and name The molecule adopts a tetrahedral molecular geometry with C3v symmetry. The chloroform molecule can be viewed as a methane molecule with three hydrogen atoms replaced with three chlorine atoms, leaving a single hydrogen atom. The name "chloroform" is a portmanteau of ''terchloride'' (tertiary chloride, a trichloride) and ''formyle'', an obsolete name for the methylylidene radical (CH) derived from formic acid. Natural occurrence Many kinds of seaweed produce chlor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formaldehyde Releaser
A formaldehyde releaser, formaldehyde donor or formaldehyde-releasing preservative is a chemical compound that slowly releases formaldehyde. Formaldehyde-releasers are added to prevent microbial growth and extend shelf life. The intent of these compounds is that they release formaldehyde at levels that suppress microbial growth but sufficiently low to not threaten humans. The use of these chemicals in cosmetics has elicited controversy. Examples Many compounds have been formulated a formaldehyde-releasers. * Quaternium-15 (Dowicil 200; Dowicil 75; Dowicil 100; Dowco 184; Dowicide Q). It was used in low concentrations in cosmetics but has been banned in the EU since 2017 and a bill is under consideration in the US. * DMDM hydantoin * (ethylenedioxy)dimethanol (EDDM) *(Benzyloxy)methanol (BHF, benzylhemiformal) * 2,2',2''-(Hexahydro-1,3-5-triazine-1,3,5-triyl-)triethanol (HHT) * Tetramethylolacetylenediurea (TMAD) * 1,3-Bis(hydroxymethyl)-5,5-dimethylimidazolidine-2,4-dione ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
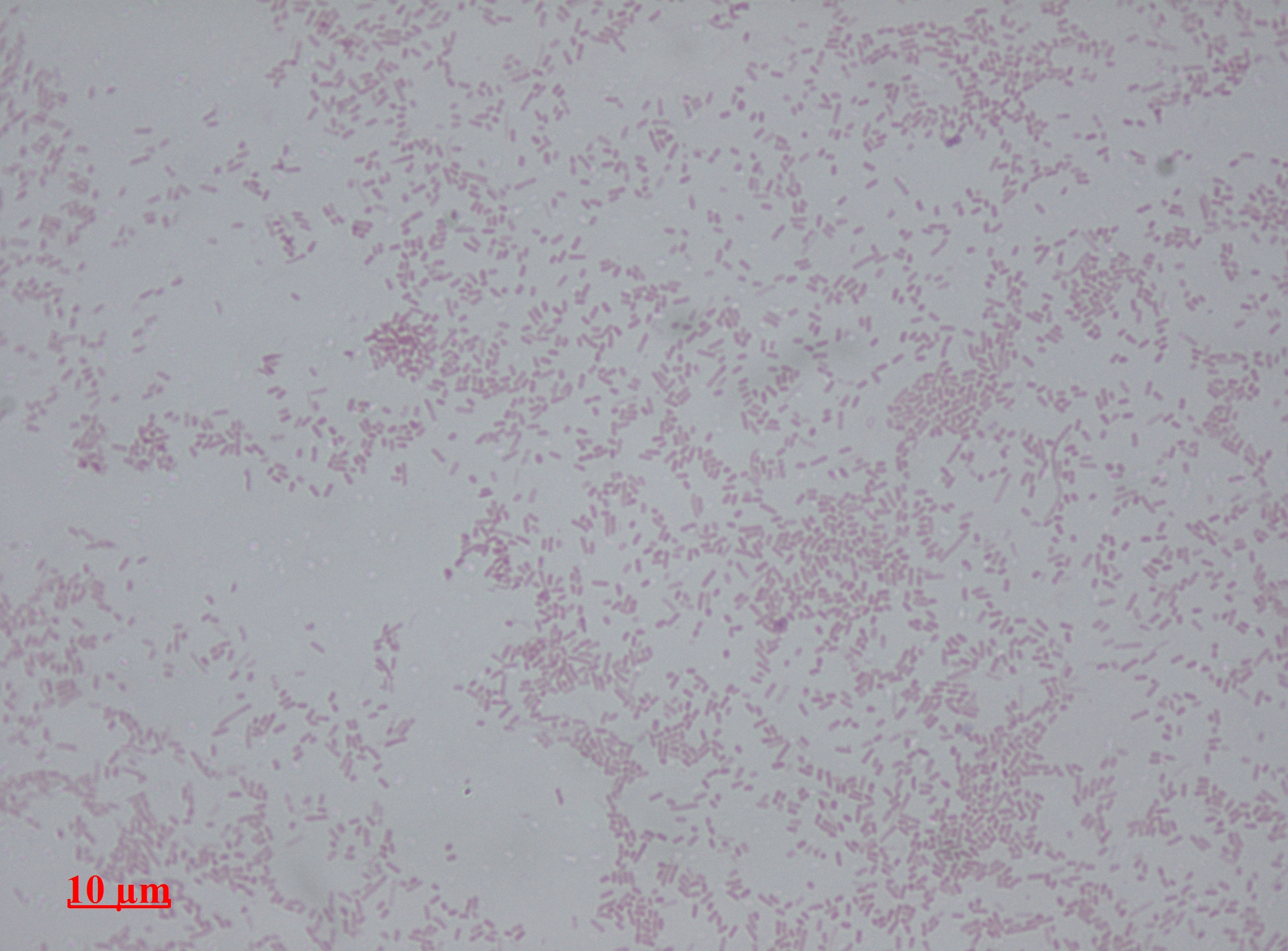
Proteus Mirabilis
''Proteus mirabilis'' is a Gram-negative, facultatively Anaerobic organism, anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium. It shows swarming motility and urease activity. ''P. mirabilis'' causes 90% of all ''Proteus (bacterium), Proteus'' infections in humans. It is widely distributed in soil and water. ''Proteus mirabilis'' can migrate across the surface of solid media or devices using a type of cooperative group motility called swarming. ''Proteus mirabilis'' is most frequently associated with Urinary tract infection, infections of the urinary tract, especially in complicated or catheter-associated urinary tract infections. Diagnosis An alkaline urine sample is a possible sign of ''P. mirabilis''. It can be diagnosed in the lab due to characteristic swarming motility, and inability to metabolize lactose (on a MacConkey agar plate, for example). Also ''P. mirabilis'' produces a very distinct fishy odor. Disease This rod-shaped bacterium has the ability to produce high levels of urease, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
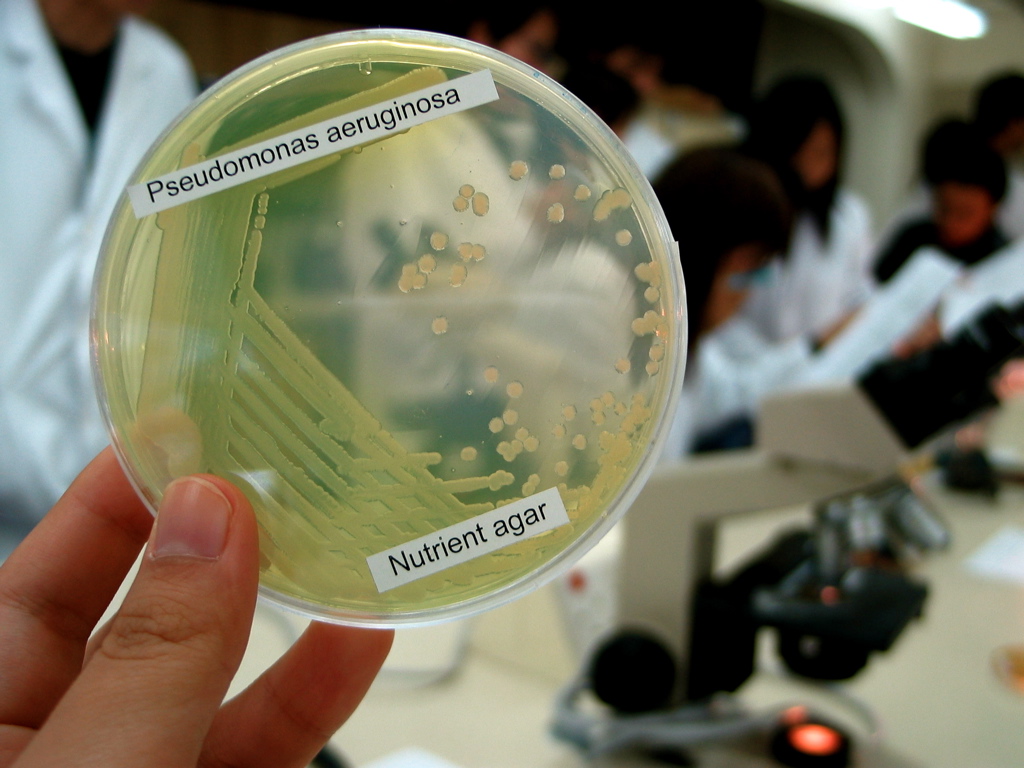
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common Bacterial capsule, encapsulated, Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative, Aerobic organism, aerobic–facultative anaerobe, facultatively anaerobic, Bacillus (shape), rod-shaped bacteria, bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aeruginosa'' is a multiple drug resistance, multidrug resistant pathogen recognized for its ubiquity, its Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsically advanced antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and its association with serious illnesses – hospital-acquired infections such as ventilator-associated pneumonia and various sepsis syndromes. ''P. aeruginosa'' is able to selectively inhibit various antibiotics from penetrating its outer membrane'' ''– and has high resistance to several antibiotics. According to the World Health Organization ''P. aeruginosa'' poses one of the greatest threats to humans in terms of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are part of the normal microbiota of the gut, where they constitute about 0.1%, along with other facultative anaerobes. These bacteria are mostly harmless or even beneficial to humans. For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by harmful pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. coli'' and humans are a type of mutualistic biological relationship—where both the humans and the ''E. coli'' are benefitting each other. ''E. coli'' is expelled into the environment within fecal matter. The bacterium grows massi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candida Albicans
''Candida albicans'' is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It can also survive outside the human body. It is detected in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth in 40–60% of healthy adults. It is usually a commensal organism, but it can become pathogenic in immunocompromised individuals under a variety of conditions. It is one of the few species of the genus '' Candida'' that cause the human infection candidiasis, which results from an overgrowth of the fungus. Candidiasis is, for example, often observed in HIV-infected patients. ''C. albicans'' is the most common fungal species isolated from biofilms either formed on (permanent) implanted medical devices or on human tissue. ''C. albicans'', ''C. tropicalis'', ''C. parapsilosis'', and ''C. glabrata'' are together responsible for 50–90% of all cases of candidiasis in humans. A mortality rate of 40% has been reported for patients with systemic candidiasis due to ''C. albicans''. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom (biology), kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species. Some yeast species have the ability to develop multicellular characteristics by forming strings of connected budding cells known as pseudohyphae or false hyphae, or quickly evolve into a Multicellular organism, multicellular cluster with specialised Organelle, cell organelles function. Yeast sizes vary greatly, depending on species and environment, typically measuring 3–4 micrometre, μm in diameter, although some yeasts can grow to 40 μm in size. Most yeasts reproduce asexual reproduction, asexually by mitosis, and many do so by the asymmetric division process known as budding. With their single-celled growth habit, yeasts can be contrasted with Mold (fungus), molds, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-positive Bacteria
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall. The Gram stain is used by microbiologists to place bacteria into two main categories, gram-positive (+) and gram-negative (−). Gram-positive bacteria have a thick layer of peptidoglycan within the cell wall, and gram-negative bacteria have a thin layer of peptidoglycan. Gram-positive bacteria retain the crystal violet stain used in the test, resulting in a purple color when observed through an optical microscope. The thick layer of peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall retains the stain after it has been fixed in place by iodine. During the decolorization step, the decolorizer removes crystal violet from all other cells. Conversely, gram-negative bacteria cannot retain the violet stain after the decolorization step; alcohol used in this stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative Bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the Crystal violet, crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelope consists of a thin peptidoglycan gram-negative cell wall, cell wall sandwiched between an inner (Cytoplasm, cytoplasmic) Cell membrane, membrane and an Bacterial outer membrane, outer membrane. These bacteria are found in all environments that support life on Earth. Within this category, notable species include the model organism ''Escherichia coli'', along with various pathogenic bacteria, such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', ''Chlamydia trachomatis'', and ''Yersinia pestis''. They pose significant challenges in the medical field due to their outer membrane, which acts as a protective barrier against numerous Antibiotic, antibiotics (including penicillin), Detergent, detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkali Metal Hydroxide
The alkali hydroxides are a class of chemical compounds which are composed of an alkali metal cation and the hydroxide anion (). The alkali hydroxides are: *Lithium hydroxide (LiOH) *Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) *Potassium hydroxide (KOH) * Rubidium hydroxide (RbOH) * Caesium hydroxide (CsOH) * Francium hydroxide (FrOH) Production Alkali hydroxides are formed in the reaction between alkali metals and water. A typical school demonstration demonstrates what happens when a piece of an alkali metal is introduced to a bowl of water. A vigorous reaction occurs, producing hydrogen gas and the specific alkali hydroxide. For example, if sodium is the alkali metal: : Sodium hydroxide is an important industrial chemical, where it is produced by the chloralkali process. Properties and uses The alkali metal hydroxides form white crystals that are hygroscopic and readily soluble in water, generating large amounts of heat upon dissolution. The solubility increases down the column as the alkali m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Williamson Synthesis
The Williamson ether synthesis is an organic reaction, forming an ether from an organohalide and a deprotonated alcohol (alkoxide). This reaction was developed by Alexander Williamson in 1850. Typically it involves the reaction of an alkoxide ion with a primary alkyl halide via an SN2 reaction. This reaction is important in the history of organic chemistry because it helped prove the structure of ethers. The general reaction mechanism is as follows: An example is the reaction of sodium ethoxide with chloroethane to form diethyl ether and sodium chloride: : Mechanism The Williamson ether reaction follows an SN2 (bimolecular nucleophilic substitution) mechanism. In an SN2 reaction mechanism there is a backside attack of an electrophile by a nucleophile and it occurs in a concerted mechanism (happens all at once). In order for the SN2 reaction to take place there must be a good leaving group which is strongly electronegative, commonly a halide. In the Williamson ether reactio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |