|
Pfennig
The 'pfennig' (; . 'pfennigs' or ; symbol pf or ₰) or penny is a former German coin or note, which was the official currency from the 9th century until the introduction of the euro in 2002. While a valuable coin during the Middle Ages, it lost its value through the years and was the minor coin of the Mark currencies in the German Reich, West and East Germany, and the reunified Germany until the introduction of the euro. Pfennig was also the name of the subunit of the Danzig mark (1922–1923) and the Danzig gulden (1923–1939) in the Free City of Danzig (modern Gdańsk, Poland). Overview Name The word ''Pfennig'' (replacing the ''denarius'' or ''denarius'' as a low-denomination silver coin) can be traced back to the 8th century and also became known as the ''Penning'', ''Panni(n)g '', ''Pfenni(n)c'', ''Pfending'' and by other names, e.g. in Prussia until 1873, ''Pfenning''. The ''-ing''- or ''-inc'' suffix was used, in addition to ''-ung'', the formation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danzig Gulden
The ''Gulden'' was the currency of the Free City of Danzig between 1923 and 1939. It was divided into 100 ''Pfennige''. History Until 1923, Danzig used the German '' Papiermark'' and issued several local 'emergency notes'. Inflation during 1922–23 averaged roughly 2,440% per month. In July 1923 it was announced that a new and independent currency (the gulden) was being established with the approval of the League of Nations finance committee to replace the German mark. The gulden was introduced at a value of 25 gulden = 1 pound sterling. Incorporation into Nazi Germany Danzig, separated from Germany after World War I, was annexed by Nazi Germany on 1 September 1939, the day the invasion of Poland had begun On the same day reichsmark coins and notes were declared legal tender alongside the Danzig gulden, with 1 gulden being equal to 0.70 reichsmark. This was a favourable exchange rate for inhabitants of Danzig, since the actual exchange rate was around 0.47 reichsmark per gulden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danzig Mark
The Papiermark (; 'paper mark', officially just ''Mark'', sign: ℳ) was the German currency from 4 August 1914 when the link between the Goldmark and gold was abandoned, due to the outbreak of World War I. In particular, the Papiermark was the currency issued during the hyperinflation in Germany of 1922 and 1923. History From 1914, the value of the mark fell. The rate of inflation rose following the end of World War I and reached its highest point in October 1923. The currency stabilized in November 1923 after the announcement of the creation of the Rentenmark, although the Rentenmark did not come into circulation until 1924. When it did, it replaced the Papiermark at the rate of 1 trillion (1012)-ℳ to RM1. On 30 August 1924 the Rentenmark was replaced by the Reichsmark. In addition to the issues of the government, emergency issues of both tokens and paper money, known as ''Kriegsgeld'' (war money) and ''Notgeld'' (emergency money), were produced by local authorities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penny
A penny is a coin ( pennies) or a unit of currency (pl. pence) in various countries. Borrowed from the Carolingian denarius (hence its former abbreviation d.), it is usually the smallest denomination within a currency system. Presently, it is the formal name of the British penny ( p) and the ''de facto'' name of the American one-cent coin (abbr. ¢) as well as the informal Irish designation of the 1 cent euro coin (abbr. c). It is the informal name of the cent unit of account in Canada, although one-cent coins are no longer minted there. The name is used in reference to various historical currencies, also derived from the Carolingian system, such as the French denier and the German pfennig. It may also be informally used to refer to any similar smallest-denomination coin, such as the euro cent or Chinese fen. The Carolingian penny was originally a 0.940-fine silver coin, weighing pound. It was adopted by Offa of Mercia and other English kings and rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Witte (coin)
The ''Witte'', also called a ''Witten, Wittenpfennig'', or ''Veerling'', was the name of an historical north German coin stamped on both sides with a value of four pfennigs.Niemann (1830), pp. 373–374. The coin received this colloquial name because of its white appearance, which was caused by the oxidation of the copper. In documents the ''Witte'' was called the ''penningh van veer penninghen'' ("pfennig of four pfennigs"). In Denmark-Norway the coin was called the ''Hvide''. ''Witten'' were minted from 1330, starting in Lübeck and in the northern German cities of Hamburg and Wismar. The cities of Lüneburg, Rostock and Stralsund followed, the coins having different compositions, but a common appearance, weight and fineness based on the agreements of the Wendish Coinage Treaty. Outside of the Wendish Minting Union, ''Witten'' emerged in towns in Pomerania and in Holstein. In the course of the 15th century, the ''Witte'' was replaced by other denominations, the '' Dreiling, Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bosnia And Herzegovina Pfenig
The convertible mark ( Bosanski: , sign: KM; code: BAM) is the currency of Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is divided into 100 or (/) and locally abbreviated ''KM''. While the currency and its subunits are uniform for both constituent polities of Bosnia and Herzegovina, namely the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (FBiH) and Republika Srpska (RS), the designs of the KM 10, KM 20, KM 50, and KM 100 banknotes are differentiated for each polity. History The convertible mark was established by the 1995 Dayton Agreement. It replaced the Bosnia and Herzegovina dinar, Croatian kuna and Yugoslav novi dinar as the single currency of Bosnia and Herzegovina in 1998. ''Mark'' refers to the Deutsche Mark, the currency to which it was pegged at par. Etymology The names derive from German. The three official languages of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnian, Serbian and Croatian, have adopted the German nouns and as loanwords ''marka'' and ''pfenig''. The Official Gaz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bracteates
A bracteate (from the Latin ''bractea'', a thin piece of metal) is a flat, thin, single-sided gold medal worn as jewelry that was produced in Northern Europe predominantly during the Migration Period of the Germanic Iron Age (including the Vendel era in Sweden). Bracteate coins are also known from the medieval kingdoms around the Bay of Bengal such as Harikela and Mon city-states. The term is also used for thin discs, especially in gold, to be sewn onto clothing in the ancient world, as found for example in the ancient Persian Oxus treasure, and also later silver coins produced in central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. Gold bracteates from the Migration Period Gold bracteates commonly denote a certain type of jewelry, made mainly in the 5th to 7th century AD, represented by numerous gold specimens. Bead-rimmed and fitted with a loop, most were intended to be worn suspended by a string around the neck, supposedly as an amulet. The gold for the bracteates came from coins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rappen
A Rappen (pl. Rappen) originally was a variant of the medieval Pfennig ("penny") coin common to the Alemannic German regions Alsace, Sundgau, northern Switzerland and south-western Germany. As with other German pennies, its half-piece was a Haller, the smallest piece which was struck. Today, one-hundredth of a Swiss franc is still officially called a ''Rappen'' in German and Swiss German and a ''rap'' in Romansh. In French-speaking Switzerland, the modern Swiss currency-unit is called a ''centime'' (pl. ''centimes'') and in Italian-speaking Switzerland, a ''centesimo'' (pl. ''centesimi''), respectively. ''Centime(s)'' is also used internationally or in other languages than the Swiss national languages. Name The origin of the term can be traced back to the ''Rappenpfennig'', a form of the penny minted in Freiburg im Breisgau in the 13th century featuring an eagle, which later on was interpreted to depict a raven (German ''Rabe''; the word is thus a cognate of its German hom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Currency Symbol
A currency symbol or currency sign is a graphic symbol used to denote a currency unit. Usually it is defined by the monetary authority, like the national central bank for the currency concerned. In formatting, the symbol can use various formattings: before, between or after the numeric amounts: , and , for example; this positioning is determined by national convention. The symbol is not defined or listed by ISO 4217: that only assigns three-letter codes to currencies (like for Azerbaijani manat) and special cases like gold and silver ( and respectively) that are used as financial instruments. Usage When writing currency amounts, the location of the symbol varies by language. Many currencies in English-speaking countries and Latin America (except Haiti) place it before the amount (e.g., R$50,00). The Cape Verdean escudo (like the Portuguese escudo, to which it was formerly pegged) places its symbol in the decimal separator position (e.g. 20$00). Banco de Cabo Verde.Moed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albus (coin)
From the Late Middle Ages the ''albus'' was a common currency in parts of the Holy Roman Empire, especially in the Rhineland. The name ''albus'' is Latin and means "white". Because of its higher silver content, this lighter coin differed in colour from the other inferior coins. This resulted in the names ''denarius albus'' (white ''pfennig''), ''Weißpfennig'' or Rhenish ''groschen''. History The ''albus'' was a silver ''groschen'' coin of the Late Middle Ages that was distributed in the Lower Rhine region from the second half of the 14th century. The four Rhenish electors, who united in 1385/86 to form the Rhenish Minting Union (''Rheinischer Münzverein''), together had the ''Weißpfennig'' minted as a silver coin alongside the Rhenish gold gulden.Heinz Fengler, Gerhard Gierow, Willy Unger: ''Transpress Lexikon Numismatik.'' Berlin 1976, p. 19 Arthur Suhle: ''Die Groschen- und Goldmünzenprägung im 14.und 15. Jahrhundert'' in: „Deutsche Münz- und Geldgeschichte von den Anf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groschen
Groschen (; from la, grossus "thick", via Old Czech ') a (sometimes colloquial) name for various coins, especially a silver coin used in various states of the Holy Roman Empire and other parts of Europe. The word is borrowed from the late Latin description of a tornose, a ''grossus denarius Turnosus,'' in English the "thick denarius of Tours". Groschen was frequently abbreviated in old documents to ''gl'', whereby the second letter was not an '' l'' (12th letter of the alphabet), but an abbreviation symbol; later it was written as ''Gr'' or ''g''. Names and etymology The name was introduced in 13th-century France as ', lit. "thick penny", whence Old French ', Italian ', Middle High German ', Low German and Dutch ' and English '' groat''. In the 14th century, it appeared as Old Czech ', whence Modern German '. Names in other modern European languages include: * sq, grosh * Church Slavonic-derived languages: Bulgarian, Macedonian, Russian and Serbo-Croatian ('), Ukra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guter Groschen
The ''Guter Groschen'' ("good ''groschen''"), also ''Gutergroschen'' or ''Gutegroschen'', abbreviation ''Ggr.'', is name of the ''groschen'' coin that was valued at of a ''Reichsthaler'' from the end of the 16th century. It was called a "good ''groschen''" to distinguish it from the lighter ''Mariengroschen'' ("Mary's ''groschen''"), which was only valued at ''Reichsthaler''. The term ''Guter Groschen'' remained common until the middle of the 19th century. History According to the Imperial Circle decision of 1572 the ''groschen'', which depicted an orb on the reverse side, were initially valued at 21 to the ''Reichsthaler'', but later 24. These so-called ''Apfelgroschen'' were mainly minted in Northern Germany. During the time of counterfeiting, the ''Kipper'' and ''Wipper'' period, they were debased. After the ''Kipper'' mints were closed, they were minted as ''Gutegroschen'' with a higher value. The ''Groschen'' name was initially intended to express the return t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pound (currency)
Pound is the name for a unit of currency. It is used in some countries today and previously was used in many others. The English word ''pound'' derives from the Latin expression , in which lībra is a noun meaning "pound" and ''pondō'' is an adverb meaning "by weight". The currency's symbol is £, a stylised form of the blackletter L (\mathfrak) (from ''libra''), crossed to indicate abbreviation. The term was adopted in England from the weight of silver used to make to 240 pennies, and eventually spread to British colonies all over the world. While silver pennies were produced seven centuries earlier, the first pound coin was minted under Henry VII in 1489. Countries and territories currently using currency units named "pound" Historical currencies * Australian pound (until 1966, replaced by the Australian dollar). The Australian pound was also used in the Gilbert and Ellice Islands, Nauru, New Hebrides and Papua and New Guinea. It was replaced in the New Hebrides/V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

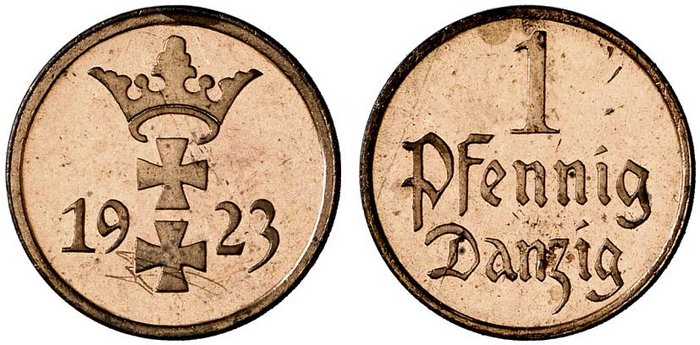
.jpg)
.jpg)



