|
Pertensive
Pertensive marking is to head-marking languages what possessive marking is to dependent-marking languages. For example, English, a dependent-marking language has ''a person's rodent'', where the head is ''rodent'' and the possessive marking is on the dependent ''person's''. In contrast, Shilluk has a pertensive affix on the head (e.g., ''dúup'' = "rodent", ''dû́uup'' = "rodent belonging to"). Other languages with pertensive marking are Nungon, Hungarian, Mansi, and Khanty. Some languages, such as Martuthunira employ both possessive and pertensive marking. The term was coined by Dixon Dixon may refer to: Places International * Dixon Entrance, part of the Inside Passage between Alaska and British Columbia Canada * Dixon, Ontario United States * Dixon, California * Dixon, Illinois * Dixon, Greene County, Indiana * Dixon, Indi ... in 2011. References Grammatical cases {{grammar-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shilluk Language
Shilluk (natively ''Dhøg Cøllø'' or ''d̪ɔ́cɔ̀llɔ̀'') is a language spoken by the Shilluk people of South Sudan and Sudan. It is closely related to other Luo languages. The term Shilluk is a pronunciation of Arabic origin. Phonology Vowels Each of these vowels also exists in a long form and an overlong form which are phonemic. Advanced and retracted tongue root Shilluk, like most Nilotic languages, differentiates vowels according to their place of articulation. They are either pronounced with advancement of the root of the tongue or with retraction of the root of the tongue. Gilley uses the terms "extended larynx" or "blown vowel". The vowels with advancement of the root of the tongue are , , , , and their corresponding long variants. The vowels with retraction of the root of the language are denoted by a macron below the letter: , , , , and and their corresponding long variants. Consonants Tone Shilluk has a rich inventory of tones, with at le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
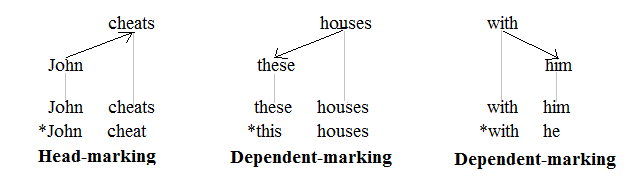
Head-marking
A language is head-marking if the grammatical marks showing agreement between different words of a phrase tend to be placed on the heads (or nuclei) of phrases, rather than on the modifiers or dependents. Many languages employ both head-marking and dependent-marking, and some languages double up and are thus double-marking. The concept of head/dependent-marking was proposed by Johanna Nichols in 1986 and has come to be widely used as a basic category in linguistic typology. In English The concepts of head-marking and dependent-marking are commonly applied to languages that have richer inflectional morphology than English. There are, however, a few types of agreement in English that can be used to illustrate these notions. The following graphic representations of a clause, a noun phrase, and a prepositional phrase involve agreement. The three tree structures shown are those of a dependency grammar (as opposed to those of a phrase structure grammar): :: Heads and dependents are id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genitive Case
In grammar, the genitive case ( abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive can also serve purposes indicating other relationships. For example, some verbs may feature arguments in the genitive case; and the genitive case may also have adverbial uses (see adverbial genitive). Genitive construction includes the genitive case, but is a broader category. Placing a modifying noun in the genitive case is one way of indicating that it is related to a head noun, in a genitive construction. However, there are other ways to indicate a genitive construction. For example, many Afroasiatic languages place the head noun (rather than the modifying noun) in the construct state. Possessive grammatical constructions, including the possessive case, may be regarded as a subset of genitive construction. For example, the genitive co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dependent-marking Language
A dependent-marking language has grammatical markers of agreement and case government between the words of phrases that tend to appear more on dependents than on heads. The distinction between head-marking and dependent-marking was first explored by Johanna Nichols in 1986, and has since become a central criterion in language typology in which languages are classified according to whether they are more head-marking or dependent-marking. Many languages employ both head and dependent-marking, but some employ double-marking, and yet others employ zero-marking. However, it is not clear that the head of a clause has anything to do with the head of a noun phrase, or even what the head of a clause is. In English English has few inflectional markers of agreement and so can be construed as zero-marking much of the time. Dependent-marking, however, occurs when a singular or plural noun demands the singular or plural form of the demonstrative determiner ''this/these'' or ''that/those'' and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain. Existing on a dialect continuum with Scots, and then closest related to the Low Saxon and Frisian languages, English is genealogically West Germanic. However, its vocabulary is also distinctively influenced by dialects of France (about 29% of Modern English words) and Latin (also about 29%), plus some grammar and a small amount of core vocabulary influenced by Old Norse (a North Germanic language). Speakers of English are called Anglophones. The earliest forms of English, collectively known as Old English, evolved from a group of West Germanic ( Ingvaeonic) dialects brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the 5th century and further mutated by Norse-speaking Viking settlers starting in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Language
Hungarian () is an Uralic language spoken in Hungary and parts of several neighbouring countries. It is the official language of Hungary and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Outside Hungary, it is also spoken by Hungarian communities in southern Slovakia, western Ukraine (Subcarpathia), central and western Romania ( Transylvania), northern Serbia ( Vojvodina), northern Croatia, northeastern Slovenia ( Prekmurje), and eastern Austria. It is also spoken by Hungarian diaspora communities worldwide, especially in North America (particularly the United States and Canada) and Israel. With 17 million speakers, it is the Uralic family's largest member by number of speakers. Classification Hungarian is a member of the Uralic language family. Linguistic connections between Hungarian and other Uralic languages were noticed in the 1670s, and the family itself (then called Finno-Ugric) was established in 1717. Hungarian has traditionally been assigned to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mansi Language
The Mansi languages are spoken by the Mansi people in Russia along the Ob River and its tributaries, in the Khanty–Mansi Autonomous Okrug, and Sverdlovsk Oblast. Traditionally considered a single language, they constitute a branch of the Uralic languages, often considered most closely related to neighbouring Khanty and then to Hungarian. The base dialect of the Mansi literary language is the Sosva dialect, a representative of the northern language. The discussion below is based on the standard language. Fixed word order is typical in Mansi. Adverbials and participles play an important role in sentence construction. A written language was first published in 1868, and the current Cyrillic alphabet was devised in 1937. Varieties Mansi is subdivided into four main dialect groups which are to a large degree mutually unintelligible, and therefore best considered four languages. A primary split can be set up between the Southern variety and the remainder. A number of features ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khanty Language
Khanty (also spelled Khanti or Hanti), previously known as Ostyak (), is a Uralic language spoken by the Khanty people, primarily in the Khanty–Mansi and Yamalo-Nenets autonomous okrugs and the Aleksandrovsky and Kargosoksky districts of Tomsk Oblast in Russia. The closest living relatives of Khanty are Hungarian and Mansi. According to the 2010 Russian census, there were around 9,600 Khanty-speaking people in Russia. The Khanty people are rapidly experiencing a language shift to Russian. The Khanty language has many dialects. The western group includes the Obdorian, Ob, and Irtysh dialects. The eastern group includes the Surgut and Vakh- Vasyugan dialects, which, in turn, are subdivided into thirteen other dialects. All these dialects differ significantly from each other by phonetic, morphological, and lexical features to the extent that the three main "dialects" (northern, southern and eastern) are mutually unintelligible. Thus, based on their significant mult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martuthunira Language
Martuthunira is an extinct Australian Aboriginal language, that was the traditional language of the Martuthunira people of Western Australia. The last fluent speaker of Martuthunira, Algy Paterson, died on 6 August 1995. From 1980 he worked with the linguist Alan Dench to preserve Martuthunira in writing, and it is from their work that most of our knowledge of Martuthunira today comes. Name The name ''Martuthunira'', pronounced by native speakers, means "those who live around the Fortescue River". It has many spelling variants, including: Maratunia, Mardadhunira, Mardathon, Mardathoni, Mardathoonera, Mardatuna, Mardatunera, Mardudhoonera, Mardudhunera, Mardudhunira, Mardudjungara, Marduduna, Mardudunera, Marduthunira, Mardutunera, Mardutunira, Marduyunira, Martuthinya, and Martuyhunira. Classification Martuthunira is classified as a member of the Ngayarta branch of the Pama–Nyungan languages. Under Carl Georg von Brandenstein's 1967 classification, Martuthunira was clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert M
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown" and '' berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe it entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including English, German, Dutch, Norwegian, Swedish, Scots, Danish, and Icelandic. It can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |