|
Personal Epistemology
Epistemic cognition, sometimes known as epistemological beliefs, or personal epistemology, is "cognition about knowledge and knowing", an area of research in the learning sciences and educational psychology. Research into epistemic cognition investigates people's beliefs regarding the characteristics of knowledge and knowing—as distinct from thinking or believing in general—and the impact of this on learning. Scope of research Research on epistemic cognition has drawn on research in epistemology, the area of philosophy concerned with the nature of knowledge. The seminal work in the area is characterised as research on student development and as an area of developmental psychology. More recent work has sought to situate epistemic cognition in a broad non-developmental model of learning. This work has linked epistemic cognition at an individual level to models of (1) metacognition, the construct characterising how people think about thinking, and (2) self-regulated learning, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognition
Cognition is the "mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, imagination, intelligence, the formation of knowledge, memory and working memory, judgment and evaluation, reasoning and computation, problem-solving and decision-making, comprehension and production of language. Cognitive processes use existing knowledge to discover new knowledge. Cognitive processes are analyzed from very different perspectives within different contexts, notably in the fields of linguistics, musicology, anesthesia, neuroscience, psychiatry, psychology, education, philosophy, anthropology, biology, systemics, logic, and computer science. These and other approaches to the analysis of cognition (such as embodied cognition) are synthesized in the developing field of cognitive science, a progressively autonomou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Educational Assessment
Educational assessment or educational evaluation is the systematic process of documenting and using empirical data on the knowledge, skill, Attitude (psychology), attitudes, aptitude and beliefs to refine programs and improve student learning. Assessment data can be obtained by examining student work directly to assess the achievement of learning outcomes or it is based on data from which one can make inferences about learning. Assessment is often used interchangeably with test but is not limited to tests. Assessment can focus on the individual learner, the learning community (class, workshop, or other organized group of learners), a course, an academic program, the institution, or the educational system as a whole (also known as granularity). The word "assessment" came into use in an educational context after the World War II, Second World War. As a continuous process, assessment establishes measurable student learning outcomes, provides a sufficient amount of learning opportuniti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Society Of The Learning Sciences
The International Society of the Learning Sciences is a professional society dedicated to the interdisciplinary empirical investigation of learning as it exists in real-world settings and how learning may be facilitated both with and without technology. Learning sciences research explores the nature and conditions of learning as it occurs in educational environments, broadly construed. The field draws upon multiple theoretical perspectives and research paradigms to understand the complexities associated with human learning, cognition, and development. Researchers in the interdisciplinary field of learning sciences, born during the 1990s, study learning as it happens in real-life situations and how to better facilitate learning in designed environments – in school, online, in the workplace, at home, and in informal environments. Learning sciences research is guided by constructivist, social-constructivist, socio-cognitive, and socio-cultural theories of learning. The society is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Development (journal)
''Human Development'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Karger Publishers. Established in 1958 as ''Vita Humana'' by Hans Thomae, the journal was published under the name ''Human Development'' from 1965. Scope ''Human Development'' covers all aspects of human development, particularly developmental psychology. Its scope includes disparate disciplines such as anthropology, biology, education, psychology, and sociology, among others. ''Human Development'' publishes theoretical and metatheoretical contributions and integrative reviews of lines of research in psychological development within conceptual, historical, and methodological frameworks. Contributions serve to raise theoretical issues, flesh out interesting and potentially powerful ideas, and differentiate key constructs. Contributions come primarily from developmental psychology but are welcome from other relevant disciplines. Abstracting and indexing The journal is indexed in, but not limited to,: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Educational Psychologist (journal)
The ''Educational Psychologist'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal published by Routledge on behalf of Division 15 (Educational Psychology) of the American Psychological Association. It was established in 1963 and the current co-editors are Jeffrey A. Greene (University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill) and Lisa Linnenbrink-Garcia (Michigan State University). The journal publishes conceptual, theoretical, and review articles (including meta-analyses), rather than empirical studies, on all aspects of educational psychology and learning in formal and informal educational environments. It is considered one of the "big five" educational psychology journals (along with ''Cognition and Instruction'', '' Journal of Educational Psychology'', '' Educational Psychology Review'', and ''Contemporary Educational Psychology''). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports ''Journal Citation Reports'' (''JCR'') is an annual publication by Clarivate. It has been integrated with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Situated Cognition
Situated cognition is a theory that posits that knowing is inseparable from doing by arguing that all knowledge is situated in activity bound to social, cultural and physical contexts. Situativity theorists suggest a model of knowledge and learning that requires thinking on the fly rather than the storage and retrieval of conceptual knowledge. In essence, cognition cannot be separated from the context. Instead, knowing exists ''in situ'', inseparable from context, activity, people, culture, and language. Therefore, learning is seen in terms of an individual's increasingly effective performance across situations rather than in terms of an accumulation of knowledge, since what is known is co-determined by the agent and the context. History While situated cognition gained recognition in the field of educational psychology in the late twentieth century,Brown, Collins, & Duguid, 1989 it shares many principles with older fields such as critical theory, anthropology ( Jean Lave & Etie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtue Epistemology
Virtue epistemology is a current philosophical approach to epistemology that stresses the importance of intellectual and specifically epistemic virtues. Virtue epistemology evaluates knowledge according to the properties of the persons, or other knowers, who hold beliefs in addition to or instead of the properties of the propositions and beliefs. Some advocates of virtue epistemology also adhere to theories of virtue ethics, while others see only loose analogy between virtue in ethics and virtue in epistemology. Intellectual virtue has been a subject of philosophy since the work of Aristotle, but virtue epistemology is a development in the modern analytic tradition. It is characterized by efforts to solve problems of special concern to modern epistemology, such as justification and reliabilism, by focusing on the knower as agent in a manner similar to how virtue ethics focuses on moral agents rather than moral acts. The area has a parallel in the theory of unity of knowledg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naturalized Epistemology
Naturalized epistemology (a term coined by W. V. O. Quine) is a collection of philosophic views about the theory of knowledge that emphasize the role of natural scientific methods. This shared emphasis on scientific methods of studying knowledge shifts the focus of epistemology away from many traditional philosophical questions, and towards the empirical processes of knowledge acquisition. There are noteworthy distinctions within naturalized epistemology. Replacement naturalism maintains that we should abandon traditional epistemology Epistemology is the branch of philosophy that examines the nature, origin, and limits of knowledge. Also called "the theory of knowledge", it explores different types of knowledge, such as propositional knowledge about facts, practical knowle ... and replace it with the methodologies of the natural sciences. The general thesis of cooperative naturalism is that traditional epistemology can benefit in its inquiry by using the knowledge we hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Epistemology
Genetic epistemology or 'developmental theory of knowledge' is a study of the origins (genesis) of knowledge (epistemology) established by Swiss psychologist Jean Piaget. This theory opposes traditional epistemology and unites constructivism and structuralism. Piaget took epistemology as the starting point and adopted the method of genetics, arguing that all knowledge of the child is generated through interaction with the environment. Aims The goal of genetic epistemology is to link the knowledge to the model of its construction – i.e., the context in which knowledge is gained affects its perception, quality, and degree of retention. Further, genetic epistemology seeks to explain the process of cognitive development (from birth) in four primary stages: sensorimotor (birth to age 2), pre-operational (2–7), concrete operational (7–11), and formal operational (11 years onward). As an example, consider that for children in the sensorimotor stage, teachers should try to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Piaget
Jean William Fritz Piaget (, ; ; 9 August 1896 – 16 September 1980) was a Swiss psychologist known for his work on child development. Piaget's theory of cognitive development and epistemological view are together called genetic epistemology. Piaget placed great importance on the education of children. As the Director of the International Bureau of Education, he declared in 1934 that "only education is capable of saving our societies from possible collapse, whether violent, or gradual". His theory of child development has been studied in pre-service education programs. Nowadays, educators and theorists working in the area of early childhood education persist in incorporating constructivist-based strategies. Piaget created the International Center for Genetic Epistemology in Geneva in 1955 while on the faculty of the University of Geneva, and directed the center until his death in 1980. The number of collaborations that its founding made possible, and their impact, ultimately le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deanna Kuhn
Deanna Zipse Kuhn (born 1944) is an American psychologist. She is Professor of Psychology and Education at Columbia University. She is known for contributions to the psychology of science – the scientific study of scientific thought and behavior. Her research program has focused on the development of scientific reasoning skills, critical thinking, metacognition, informal reasoning, and constructivist teaching methods, such as problem-based learning and collaborative learning. Kuhn is the author of ''The Skills of Argument –'' a book examining the development of informal reasoning, which often takes the form of argument or debate. Kuhn's emphasis on argumentation skills as the foundation for critical thinking and analysis is further developed in her book ''Argue with Me: Argument as a Path to Developing Students' Thinking and Writing,'' co-authored with Laura Hemberger and Valerie Khait. Other books authored by Kuhn include ''The Development of Scientific Thinking Skills,' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
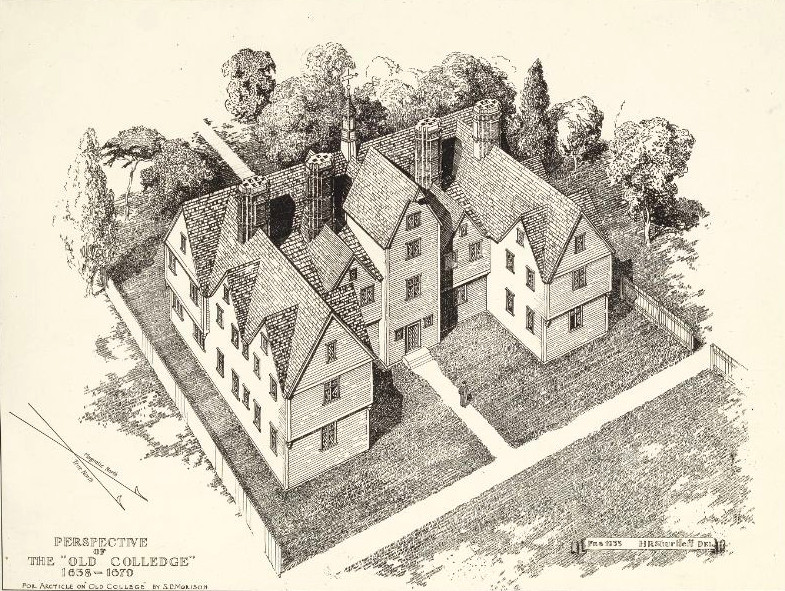
Harvard College
Harvard College is the undergraduate education, undergraduate college of Harvard University, a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Part of the Harvard Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Harvard College is Harvard University's traditional undergraduate program, offering BA (Bachelor of Arts) and BS (Bachelor of Science) degrees. It is highly selective, with fewer than four percent of applicants being offered admission as of 2022. Harvard College students participate in over 450 extracurricular organizations and nearly all live on campus. First-year students reside in or near Harvard Yard while upperclass students reside in other on-campus housing. History Harvard College was founded in 1636 by vote of the Massachusetts General Court, Great and General Court of the Massachusetts Bay Colony. Two years later, the college became home to North America's first known printing press, carri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |