|
Peroneus
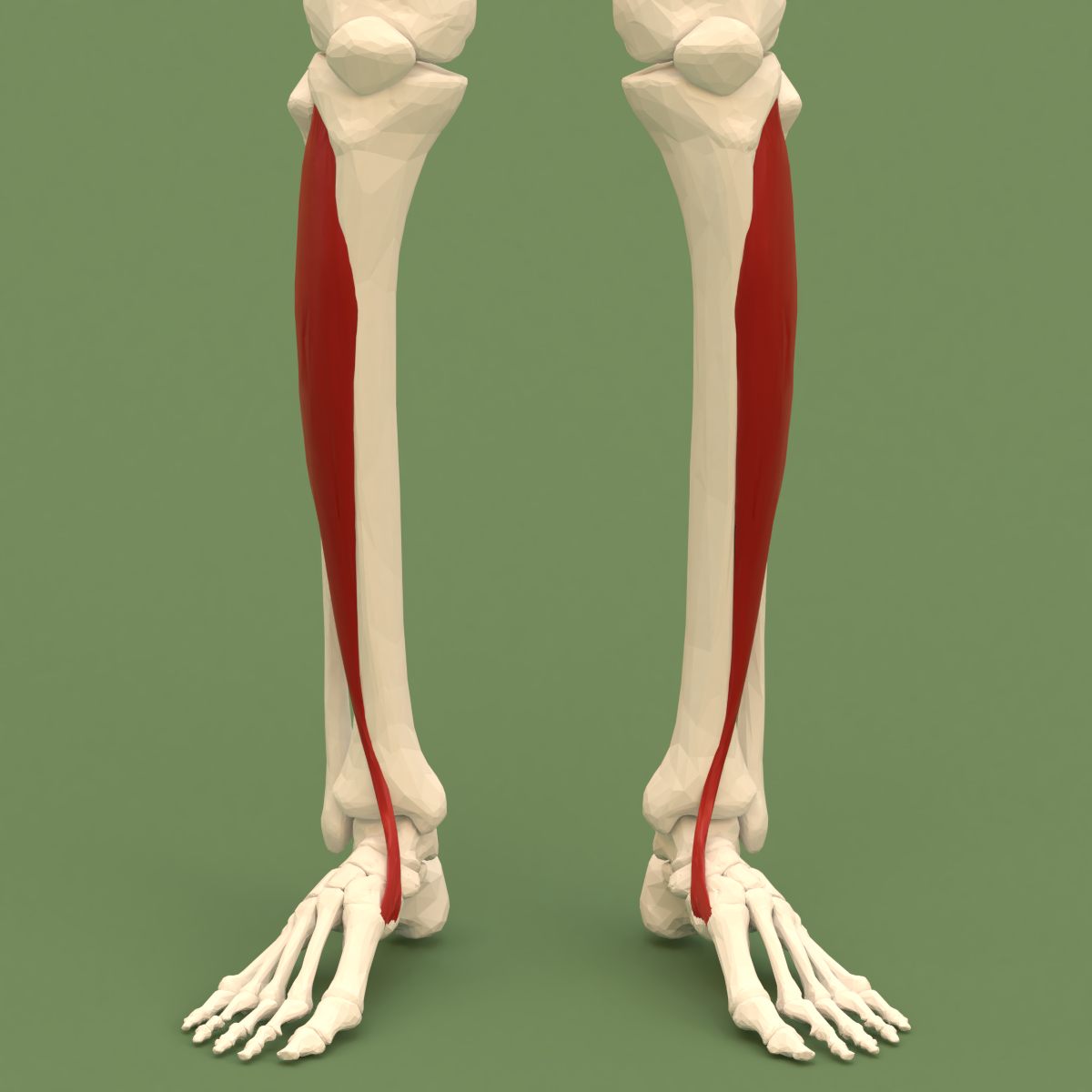
The fibularis muscles (also called peroneus muscles or peroneals) are a group of muscles in the lower leg. Description The muscle group is normally composed of three muscles: fibularis longus, fibularis brevis, and fibularis tertius. The fibularis longus and fibularis brevis are located in the lateral compartment of the leg and are supplied by the fibular artery and the superficial fibular nerve. The fibularis tertius is located in the anterior compartment of the leg and is supplied by the anterior tibial artery and the deep fibular nerve. While all three muscles move the sole of the foot outward, away from the midline of the body ( eversion), the longus and brevis extend the foot downward away from the body (plantar flexion), whereas the tertius muscle pulls the foot upward toward the body (dorsiflexion). The fibularis muscles are highly variable. Several variants are occasionally present, including the peroneus digiti minimi and the peroneus quartus. The quartus is more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Leg
The human leg, in the general word sense, is the entire lower limb (anatomy), limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or Gluteal muscles, gluteal region. However, the definition in human anatomy refers only to the section of the lower limb extending from the knee to the ankle, also known as the crus or, especially in non-technical use, the shank. Legs are used for standing, and all forms of locomotion including recreational such as dancing, and constitute a significant portion of a person's mass. Female legs generally have greater hip anteversion and tibiofemoral angles, but shorter femur and tibial lengths than those in males. Structure In human anatomy, the lower leg is the part of the lower limb that lies between the knee and the ankle. Anatomists restrict the term ''leg'' to this use, rather than to the entire lower limb. The thigh is between the hip and knee and makes up the rest of the lower limb. The term ''lower limb'' or ''lower extre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibularis Longus
In human anatomy, the fibularis longus (also known as peroneus longus) is a superficial muscle in the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body ( eversion) and to extend the foot downward away from the body (plantar flexion) at the ankle. The fibularis longus is the longest and most superficial of the three fibularis (peroneus) muscles. At its upper end, it is attached to the head of the fibula, and its "belly" runs down along most of this bone. The muscle becomes a tendon that wraps around and behind the lateral malleolus of the ankle, then continues under the foot to attach to the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal. It is supplied by the superficial fibular nerve. Structure The fibularis longus arises from the head and upper two-thirds of the lateral, or outward, surface of the fibula, from the deep surface of the fascia, and from the connective tissue between it and the muscles on the front and back of the leg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibularis Brevis
In human anatomy, the fibularis brevis (or peroneus brevis) is a muscle that lies underneath the fibularis longus within the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to extend the foot downward away from the body at the ankle (plantar flexion). Structure The fibularis brevis arises from the lower two-thirds of the lateral, or outward, surface of the fibula (inward in relation to the fibularis longus) and from the connective tissue between it and the muscles on the front and back of the leg. The muscle passes downward and ends in a tendon that runs behind the lateral malleolus of the ankle in a groove that it shares with the tendon of the fibularis longus; the groove is converted into a canal by the superior fibular retinaculum, and the tendons in it are contained in a common mucous sheath. The tendon then runs forward along the lateral side of the calcaneus, above the calcaneal tubercle and the tendon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibularis Tertius
In human anatomy, the fibularis tertius (also known as the peroneus tertius) is a muscle in the anterior compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body ( eversion) and to pull the foot upward toward the body (dorsiflexion). Structure The fibularis tertius arises from the lower third of the front surface of the fibula, the lower part of the interosseous membrane, and septum, or connective tissue, between it and the fibularis brevis. The septum is sometimes called the intermuscular septum of Otto. The muscle passes downward and ends in a tendon that passes under the superior extensor retinaculum and the inferior extensor retinaculum of the foot in the same canal as the extensor digitorum longus muscle. It may be mistaken as a fifth tendon of the extensor digitorum longus. The tendon inserts into the medial part of the posterior surface of the shaft of the fifth metatarsal bone. The fibularis tertius is supplied by the deep fibula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibularis Tertius
In human anatomy, the fibularis tertius (also known as the peroneus tertius) is a muscle in the anterior compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body ( eversion) and to pull the foot upward toward the body (dorsiflexion). Structure The fibularis tertius arises from the lower third of the front surface of the fibula, the lower part of the interosseous membrane, and septum, or connective tissue, between it and the fibularis brevis. The septum is sometimes called the intermuscular septum of Otto. The muscle passes downward and ends in a tendon that passes under the superior extensor retinaculum and the inferior extensor retinaculum of the foot in the same canal as the extensor digitorum longus muscle. It may be mistaken as a fifth tendon of the extensor digitorum longus. The tendon inserts into the medial part of the posterior surface of the shaft of the fifth metatarsal bone. The fibularis tertius is supplied by the deep fibula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibularis Brevis
In human anatomy, the fibularis brevis (or peroneus brevis) is a muscle that lies underneath the fibularis longus within the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to extend the foot downward away from the body at the ankle (plantar flexion). Structure The fibularis brevis arises from the lower two-thirds of the lateral, or outward, surface of the fibula (inward in relation to the fibularis longus) and from the connective tissue between it and the muscles on the front and back of the leg. The muscle passes downward and ends in a tendon that runs behind the lateral malleolus of the ankle in a groove that it shares with the tendon of the fibularis longus; the groove is converted into a canal by the superior fibular retinaculum, and the tendons in it are contained in a common mucous sheath. The tendon then runs forward along the lateral side of the calcaneus, above the calcaneal tubercle and the tendon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibularis Longus
In human anatomy, the fibularis longus (also known as peroneus longus) is a superficial muscle in the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body ( eversion) and to extend the foot downward away from the body (plantar flexion) at the ankle. The fibularis longus is the longest and most superficial of the three fibularis (peroneus) muscles. At its upper end, it is attached to the head of the fibula, and its "belly" runs down along most of this bone. The muscle becomes a tendon that wraps around and behind the lateral malleolus of the ankle, then continues under the foot to attach to the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal. It is supplied by the superficial fibular nerve. Structure The fibularis longus arises from the head and upper two-thirds of the lateral, or outward, surface of the fibula, from the deep surface of the fascia, and from the connective tissue between it and the muscles on the front and back of the leg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibula
The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint. Structure The bone has the following components: * Lateral malleolus * Interosseous membrane connecting the fibula to the tibia, forming a syndesmosis joint * The superior tibiofibular articulation is an arthrodial joint between the lateral condyle of the tibia and the head of the fibula. * The inferior tibiofibular articulation (tibiofibular syndesmosis) is formed by the rough, convex surface of the medial side of the lower end of the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Fibular Nerve
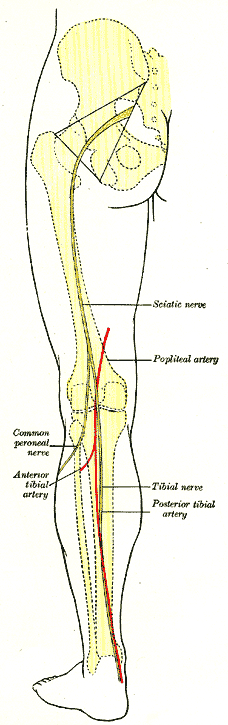
The deep fibular nerve (also known as deep peroneal nerve) begins at the bifurcation of the common fibular nerve between the fibula and upper part of the fibularis longus, passes infero-medially, deep to the extensor digitorum longus, to the anterior surface of the interosseous membrane, and comes into relation with the anterior tibial artery above the middle of the leg; it then descends with the artery to the front of the ankle-joint, where it divides into a ''lateral'' and a '' medial terminal branch''. Structure Lateral side of the leg The deep fibular nerve is the nerve of the anterior compartment of the leg and the dorsum of the foot. It is one of the terminal branches of the common fibular nerve. It corresponds to the posterior interosseus nerve of the forearm. It begins at the lateral side of the fibula bone, and then enters the anterior compartment by piercing the anterior intermuscular septum. It then pierces the extensor digitorum longus and lies next to the anterior tib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Compartment Of Leg
The anterior compartment of the leg is a fascial compartments of leg, fascial compartment of the lower leg. It contains muscles that produce Anatomical terms of motion#Flexion and extension of the foot, dorsiflexion and participate in Anatomical terms of motion#Inversion and eversion, inversion and eversion of the foot, as well as vascular and nervous elements, including the anterior tibial artery and anterior tibial vein, veins and the deep fibular nerve. Muscles The muscles of the compartment are: * tibialis anterior muscle, tibialis anterior * extensor hallucis longus muscle, extensor hallucis longus * extensor digitorum longus muscle, extensor digitorum longus * Fibularis tertius, fibularis (peroneus) tertius Function The compartment contains muscles that are Anatomical terms of motion#Flexion and extension of the foot, dorsiflexors and participate in Anatomical terms of motion#Inversion and eversion, inversion and eversion of the foot. Innervation and blood supply The an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superficial Fibular Nerve
The superficial fibular nerve (also known as superficial peroneal nerve) innervates the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis muscles and the skin over the antero-lateral aspect of the leg along with the greater part of the dorsum of the foot (with the exception of the first web space, which is innervated by the deep fibular nerve). Structure Lateral side of the leg The superficial fibular nerve is the main nerve of the lateral compartment of the leg. It begins at the lateral side of the neck of fibula, and runs through the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis muscles. In the middle third of the leg, it descends between the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis, and then reaches the anterior border of the fibularis brevis to enter the groove between the fibularis brevis and the extensor digitorum longus under the deep fascia of leg. It becomes superficial at the junction of upper two-thirds and lower one-thirds of the leg by piercing the deep fascia. The superficial fibular nerve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Tibial Artery
The anterior tibial artery is an artery of the leg. It carries blood to the anterior compartment of the leg and dorsum (biology), dorsal surface of the foot, from the popliteal artery. Structure Course The anterior tibial artery is a branch of the popliteal artery. It originates at the distal end of the popliteus muscle posterior to the tibia. The artery typically passes anterior to the popliteus muscle prior to passing between the tibia and fibula through an oval opening at the superior aspect of the interosseus membrane. The artery then descends between the tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus muscles. It is accompanied by the anterior tibial vein, and the deep peroneal nerve, along its course. It crosses the anterior aspect of the ankle joint, at which point it becomes the dorsalis pedis artery. Branches The branches of the anterior tibial artery are: *posterior tibial recurrent artery *anterior tibial recurrent artery *muscular branches *anterior medial malleo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |