|
Perceptron
In machine learning, the perceptron is an algorithm for supervised classification, supervised learning of binary classification, binary classifiers. A binary classifier is a function that can decide whether or not an input, represented by a vector of numbers, belongs to some specific class. It is a type of linear classifier, i.e. a classification algorithm that makes its predictions based on a linear predictor function combining a set of Weighting, weights with the feature vector. History The artificial neuron network was invented in 1943 by Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts in ''A Logical Calculus of the Ideas Immanent in Nervous Activity, A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity''. In 1957, Frank Rosenblatt was at the Cornell Aeronautical Laboratory. He simulated the perceptron on an IBM 704. Later, he obtained funding by the Information Systems Branch of the United States Office of Naval Research and the Rome Air Development Center, to build a custom- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Frank Rosenblatt
Frank Rosenblatt (July 11, 1928July 11, 1971) was an American psychologist notable in the field of artificial intelligence. He is sometimes called the father of deep learning for his pioneering work on artificial neural networks. Life and career Rosenblatt was born into a Jewish family in New Rochelle, New York as the son of Dr. Frank and Katherine Rosenblatt. After graduating from The Bronx High School of Science in 1946, he attended Cornell University, where he obtained his Bachelor of Arts, A.B. in 1950 and his Doctor of Philosophy, Ph.D. in 1956. For his PhD thesis he built a custom-made computer, the Electronic Profile Analyzing Computer (EPAC), to perform multidimensional analysis for psychometrics. He used it between 1951 and 1953 to analyze psychometric data collected for his PhD thesis. The data were collected from a paid, 600 item survey of more than 200 Cornell undergraduates. The total computational cost was 2.5 million arithmetic operations, necessitating the use of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of research in computer science that develops and studies methods and software that enable machines to machine perception, perceive their environment and use machine learning, learning and intelligence to take actions that maximize their chances of achieving defined goals. High-profile applications of AI include advanced web search engines (e.g., Google Search); recommendation systems (used by YouTube, Amazon (company), Amazon, and Netflix); virtual assistants (e.g., Google Assistant, Siri, and Amazon Alexa, Alexa); autonomous vehicles (e.g., Waymo); Generative artificial intelligence, generative and Computational creativity, creative tools (e.g., ChatGPT and AI art); and Superintelligence, superhuman play and analysis in strategy games (e.g., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Linear Classifier
In machine learning, a linear classifier makes a classification decision for each object based on a linear combination of its features. Such classifiers work well for practical problems such as document classification, and more generally for problems with many variables ( features), reaching accuracy levels comparable to non-linear classifiers while taking less time to train and use. Definition If the input feature vector to the classifier is a real vector \vec x, then the output score is :y = f(\vec\cdot\vec) = f\left(\sum_j w_j x_j\right), where \vec w is a real vector of weights and ''f'' is a function that converts the dot product of the two vectors into the desired output. (In other words, \vec is a one-form or linear functional mapping \vec x onto R.) The weight vector \vec w is learned from a set of labeled training samples. Often ''f'' is a threshold function, which maps all values of \vec\cdot\vec above a certain threshold to the first class and all other value ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
A Logical Calculus Of The Ideas Immanent In Nervous Activity
"A Logical Calculus of the Ideas Immanent to Nervous Activity" is a 1943 article written by Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts. The paper, published in the journal '' The Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics,'' proposed a mathematical model of the nervous system as a network of simple logical elements, later known as artificial neurons, or McCulloch-Pitts neurons. These neurons receive inputs, perform a weighted sum, and fire an output signal based on a threshold function. By connecting these units in various configurations, McCulloch and Pitts demonstrated that their model could perform all logical functions. It is a seminal work in cognitive science, computational neuroscience, computer science, and artificial intelligence. It was a foundational result in automata theory. John von Neumann cited it as a significant result.von Neumann, J. (1951). The general and logical theory of automata'. In L. A. Jeffress (Ed.), ''Cerebral mechanisms in behavior; the Hixon Symposium'' (pp. 1– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Linear Predictor Function
In statistics and in machine learning, a linear predictor function is a linear function (linear combination) of a set of coefficients and explanatory variables (independent variables), whose value is used to predict the outcome of a dependent variable. This sort of function usually comes in linear regression, where the coefficients are called regression coefficients. However, they also occur in various types of linear classifiers (e.g. logistic regression, perceptrons, support vector machines, and linear discriminant analysis), as well as in various other models, such as principal component analysisJolliffe I.T. ''Principal Component Analysis'', Series: Springer Series in Statistics, 2nd ed., Springer, NY, 2002, XXIX, 487 p. 28 illus. and factor analysis. In many of these models, the coefficients are referred to as "weights". Definition The basic form of a linear predictor function f(i) for data point ''i'' (consisting of ''p'' explanatory variables), for ''i'' = 1, ..., ''n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
IBM 704
The IBM 704 is the model name of a large digital computer, digital mainframe computer introduced by IBM in 1954. Designed by John Backus and Gene Amdahl, it was the first mass-produced computer with hardware for floating-point arithmetic. The IBM 704 ''Manual of operation'' states: The type 704 Electronic Data-Processing Machine is a large-scale, high-speed electronic calculator controlled by an internally stored program of the single address type. The 704 at that time was thus regarded as "pretty much the only computer that could handle complex math". The 704 was a significant improvement over the earlier IBM 701 in terms of architecture and implementation. Like the 701, the 704 used vacuum-tube logic circuitry, but increased the instruction size from 18-bit computing, 18 bits to 36-bit computing, 36 bits, the same as the memory's word size. Changes from the 701 include the use of magnetic-core memory instead of Williams tubes, floating-point arithmetic instructions, 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task (computing), tasks without explicit Machine code, instructions. Within a subdiscipline in machine learning, advances in the field of deep learning have allowed Neural network (machine learning), neural networks, a class of statistical algorithms, to surpass many previous machine learning approaches in performance. ML finds application in many fields, including natural language processing, computer vision, speech recognition, email filtering, agriculture, and medicine. The application of ML to business problems is known as predictive analytics. Statistics and mathematical optimisation (mathematical programming) methods comprise the foundations of machine learning. Data mining is a related field of study, focusing on exploratory data analysi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Information Processing Techniques Office
The Information Processing Techniques Office (IPTO), originally "Command and Control Research",Lyon, Matthew; Hafner, Katie (1999-08-19). ''Where Wizards Stay Up Late: The Origins Of The Internet'' (p. 39). Simon & Schuster. Kindle Edition. was part of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency of the United States Department of Defense. Origin According to an ARPA-sponsored history of the organization, IPTO grew from a distinctly unpromising beginning: the Air Force had a large, expensive computer ( AN/FSQ 321A) which was intended as a backup for the SAGE air defense program, but no longer needed; and it also had too few required tasks to maintain the desired staffing level at its main software contractor, the System Development Corporation (SDC). Accordingly, the Under Secretary of Defense for Research and Engineering decided to capitalize on these "sunk costs" and SDC expertise by standing up an ARPA program in Command & Control Research. It was accordingly begun in June 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Herbert A
Herbert may refer to: People * Herbert (musician), a pseudonym of Matthew Herbert * Herbert (given name) * Herbert (surname) Places Antarctica * Herbert Mountains, Coats Land * Herbert Sound, Graham Land Australia * Herbert, Northern Territory, a rural locality * Herbert, South Australia. former government town * Division of Herbert, an electoral district in Queensland * Herbert River, a river in Queensland * County of Herbert, a cadastral unit in South Australia Canada * Herbert, Saskatchewan, Canada, a town * Herbert Road, St. Albert, Canada New Zealand * Herbert, New Zealand, a town * Mount Herbert (New Zealand) United States * Herbert, Illinois, an unincorporated community * Herbert, Michigan, a former settlement * Herbert Creek, a stream in South Dakota * Herbert Island, Alaska Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * Herbert (Disney character) * Herbert Pocket, a character in the Charles Dickens novel ''Great Expectations'' * Herbert West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Allen Newell
Allen Newell (March 19, 1927 – July 19, 1992) was an American researcher in computer science and cognitive psychology at the RAND Corporation and at Carnegie Mellon University's School of Computer Science, Tepper School of Business, and Department of Psychology. He, Herbert A. Simon, and Cliff Shaw contributed to the Information Processing Language (1956) and two of the earliest AI programs, the Logic Theorist (1956) and the General Problem Solver (1957). He and Simon were awarded the ACM's A.M. Turing Award in 1975 for their contributions to artificial intelligence and the psychology of human cognition. Early studies Newell completed his bachelor's degree in physics from Stanford in 1949. He was a graduate student at Princeton University from 1949 to 1950, where he studied mathematics. Due to his early exposure to an unknown field known as game theory and the experiences from the study of mathematics, he was convinced that he would prefer a combination of experime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Image Recognition
Computer vision tasks include methods for acquiring, processing, analyzing, and understanding digital images, and extraction of high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical or symbolic information, e.g. in the form of decisions. "Understanding" in this context signifies the transformation of visual images (the input to the retina) into descriptions of the world that make sense to thought processes and can elicit appropriate action. This image understanding can be seen as the disentangling of symbolic information from image data using models constructed with the aid of geometry, physics, statistics, and learning theory. The scientific discipline of computer vision is concerned with the theory behind artificial systems that extract information from images. Image data can take many forms, such as video sequences, views from multiple cameras, multi-dimensional data from a 3D scanner, 3D point clouds from LiDaR sensors, or medical scanning devices. The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
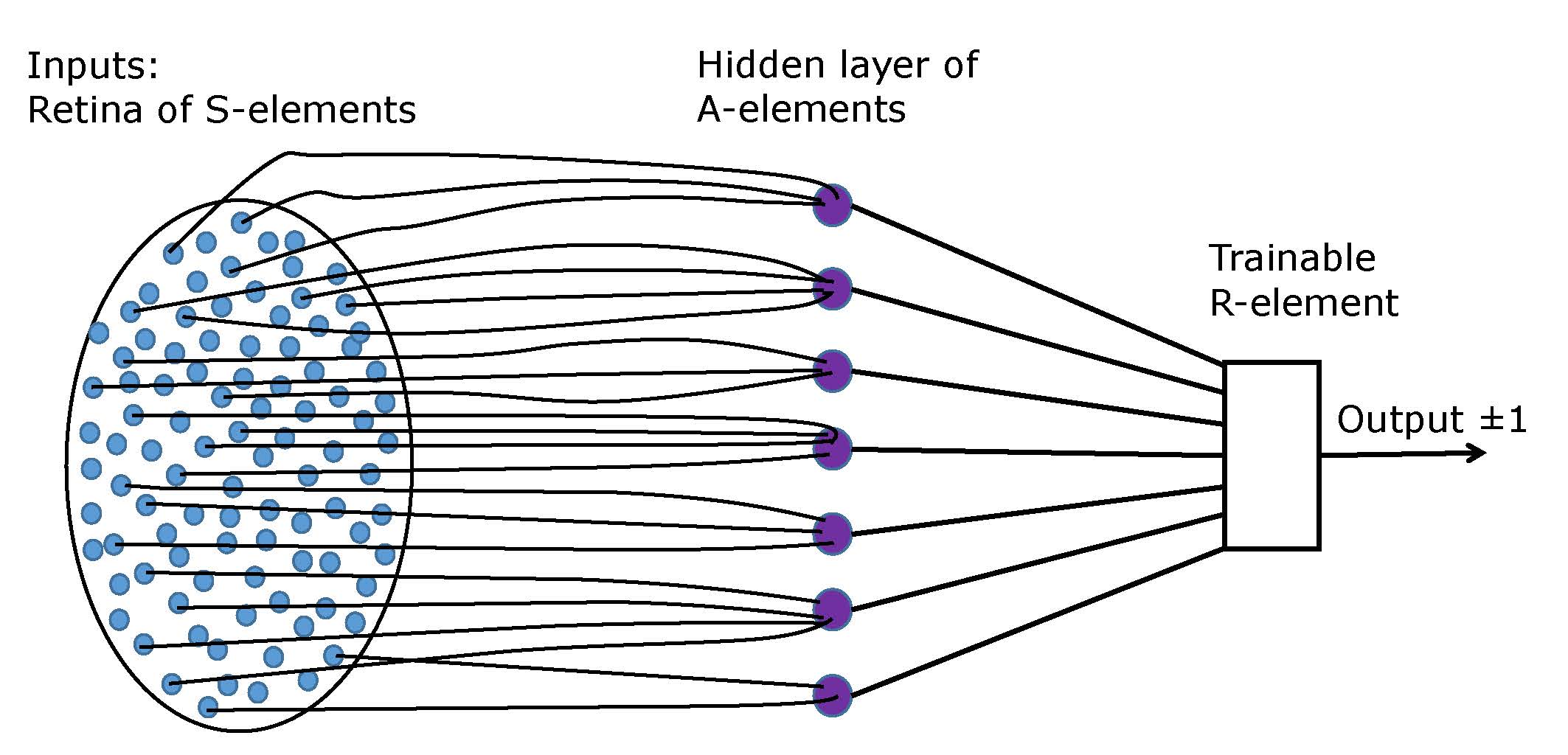
Organization Of A Biological Brain And A Perceptron
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is an entity—such as a company, or corporation or an institution (formal organization), or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose. Organizations may also operate secretly or illegally in the case of secret societies, criminal organizations, and resistance movements. And in some cases may have obstacles from other organizations (e.g.: MLK's organization). What makes an organization recognized by the government is either filling out incorporation or recognition in the form of either societal pressure (e.g.: Advocacy group), causing concerns (e.g.: Resistance movement) or being considered the spokesperson of a group of people subject to negotiation (e.g.: the Polisario Front being recognized as the sole representative of the Sahrawi people and forming a partially recognized state.) Compare the concept of social groups, which may include non-organiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |