|
Pen-based
Pen computing refers to any computer user-interface using a pen or stylus and tablet, over input devices such as a keyboard or a mouse. Pen computing is also used to refer to the usage of mobile devices such as tablet computers, PDAs and GPS receivers. The term has been used to refer to the usage of any product allowing for mobile communication. An indication of such a device is a stylus or digital pen, generally used to press upon a graphics tablet or touchscreen, as opposed to using a more traditional interface such as a keyboard, keypad, mouse or touchpad. Historically, pen computing (defined as a computer system employing a user-interface using a pointing device plus handwriting recognition as the primary means for interactive user input) predates the use of a mouse and graphical display by at least two decades, starting with the Stylator and RAND Tablet systems of the 1950s and early 1960s. General techniques User interfaces for pen computing can be implemented in sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newton OS
''Newton OS'' is a discontinued operating system for the Apple Newton PDAs produced by Apple Computer, Inc. between 1993 and 1997. It was written entirely in C++ and trimmed to be low power consuming and use the available memory efficiently. Many applications were pre-installed in the ROM of the Newton (making for quick start-up) to save on RAM and flash memory storage for user applications. Features Newton OS features many interface elements that the Macintosh system software didn't have at the time, such as drawers and the "poof" animation. An animation similar to this is found in Mac OS X, and parts of the Newton's handwriting recognition system have been implemented as Inkwell in Mac OS X. *Sound responsive — Clicking menus and icons makes a sound; this feature was later introduced in Mac OS 8. *Icons - Similar to the Macintosh Desktop metaphor, Newton OS uses icons to open applications. *Tabbed documents — Similar to tabbed browsing in today's browsers and Apple's At Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GO Corp
GO Corporation was founded in 1987 to create portable computers, an operating system, and software with a pen-based user interface. It was famous not only for its pioneering work in Pen-based computing but as well as being one of the most well-funded start-up companies of its time. Its founders were Jerry Kaplan, Robert Carr, and Kevin Doren. Mr. Kaplan subsequently chronicled the history of the company in his book ''Startup: A Silicon Valley Adventure''. Omid Kordestani, former Senior VP of Global Business at Google, began his startup career with GO Corporation. Other notable GO alumni include CEO Bill Campbell (who later became chairman of Intuit), VP Sales Stratton Sclavos (took VeriSign public as its CEO), CFO and VP of Business Operations Randy Komisar (became CEO of LucasArts), and VP Marketing Mike Homer (was VP Marketing at time of Netscape's IPO in 1995). History Though the company enjoyed high levels of public awareness and generally positive attention from industry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PenPoint OS
The PenPoint OS was a product of GO Corporation and was one of the earliest operating systems written specifically for graphical tablets and personal digital assistants. It ran on AT&T Corporation's EO Personal Communicator as well as a number of Intel x86 powered tablet PCs including IBM's ThinkPad 700T series, NCR's 3125, 3130 and some of GRiD Systems' pen-based portables. It was never widely adopted. Developers of the PenPoint OS included Robert Carr, who was involved with the Alto computer at Xerox PARC. He commissioned Dr. Tinker, the naming service company of Mark Beaulieu who generated the name 'PenPoint', using proprietary algorithms. Awards and innovation Byte magazine awarded PenPoint best Operating System in the 1992 Byte Awards. PenPoint won in the Standards and Operating Systems category in PC Magazine's 1991 Technical Excellence awards. The PenPoint operating system had novel early implementations of several computing advances, including: * a large set of ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stylus (computing)
In computing, a stylus (or stylus pen) is a small pen-shaped instrument whose tip position on a computer monitor can be detected. It is used to draw, or make selections by tapping. While devices with touchscreens such as newer computers, mobile devices (smartphones and personal digital assistants), game consoles, and graphics tablets can usually be operated with a fingertip, a stylus provides more accurate and controllable input. The stylus has the same function as a mouse or touchpad as a pointing device; its use is commonly called pen computing. History The earliest computer-related usage for a stylus was in 1643 with Pascal's calculator. The device had rotary dials that would rotate in accordance to the selected numbers, and with gears, drums, and clever engineering, it was capable of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division (using 9's constant). The user would use a stylus to turn the dials. Later devices of this type include the Arithmometer, in the 1860s; and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handwriting Recognition
Handwriting recognition (HWR), also known as handwritten text recognition (HTR), is the ability of a computer to receive and interpret intelligible handwritten input from sources such as paper documents, photographs, touch-screens and other devices. The image of the written text may be sensed "off line" from a piece of paper by optical scanning (optical character recognition) or intelligent word recognition. Alternatively, the movements of the pen tip may be sensed "on line", for example by a pen-based computer screen surface, a generally easier task as there are more clues available. A handwriting recognition system handles formatting, performs correct segmentation into characters, and finds the most plausible words. Offline recognition Offline handwriting recognition involves the automatic conversion of text in an image into letter codes that are usable within computer and text-processing applications. The data obtained by this form is regarded as a static representation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Touchpad
A touchpad or trackpad is a pointing device featuring a tactile sensor, a specialized surface that can translate the motion and position of a user's fingers to a relative position on the operating system that is made output to the screen. Touchpads are a common feature of laptop computers as opposed to using a mouse on a desktop, and are also used as a substitute for a mouse where desk space is scarce. Because they vary in size, they can also be found on personal digital assistants (PDAs) and some portable media players. Wireless touchpads are also available as detached accessories. Operation and function Touchpads operate in one of several ways, including capacitive sensing or resistive touchscreen. The most common technology used in the 2010s senses the change of capacitance where a finger touches the pad. Capacitance-based touchpads will not sense the tip of a pencil or other similar ungrounded or non-conducting implements. Fingers insulated by a glove may also be problemat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pencept
Pencept, Inc. was one of a small number of pioneering companies in the 1980s developing and marketing technology known as pen computing. Pencept was noted primarily for the robustness (for the time) of the handwriting and gesture recognition algorithms, and for an emphasis on developing novel user interface approaches for employing gesture recognition and handwriting recognition that would work with existing applications hardware and software. Pencept employed a proprietary technology for on-line character recognition, based on a functional attribute model of human reading. Thus, unlike many other recognition algorithms employed for handwriting recognition, the recognition was generally user-independent and did not involve training to a user's particular writing style. Early products included the PenPad 200 handwriting-only computer terminal that was a direct replacement for the VT-100 and other standard ANSI 3.62 terminals, but with a digitizing tablet and electronic pen and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
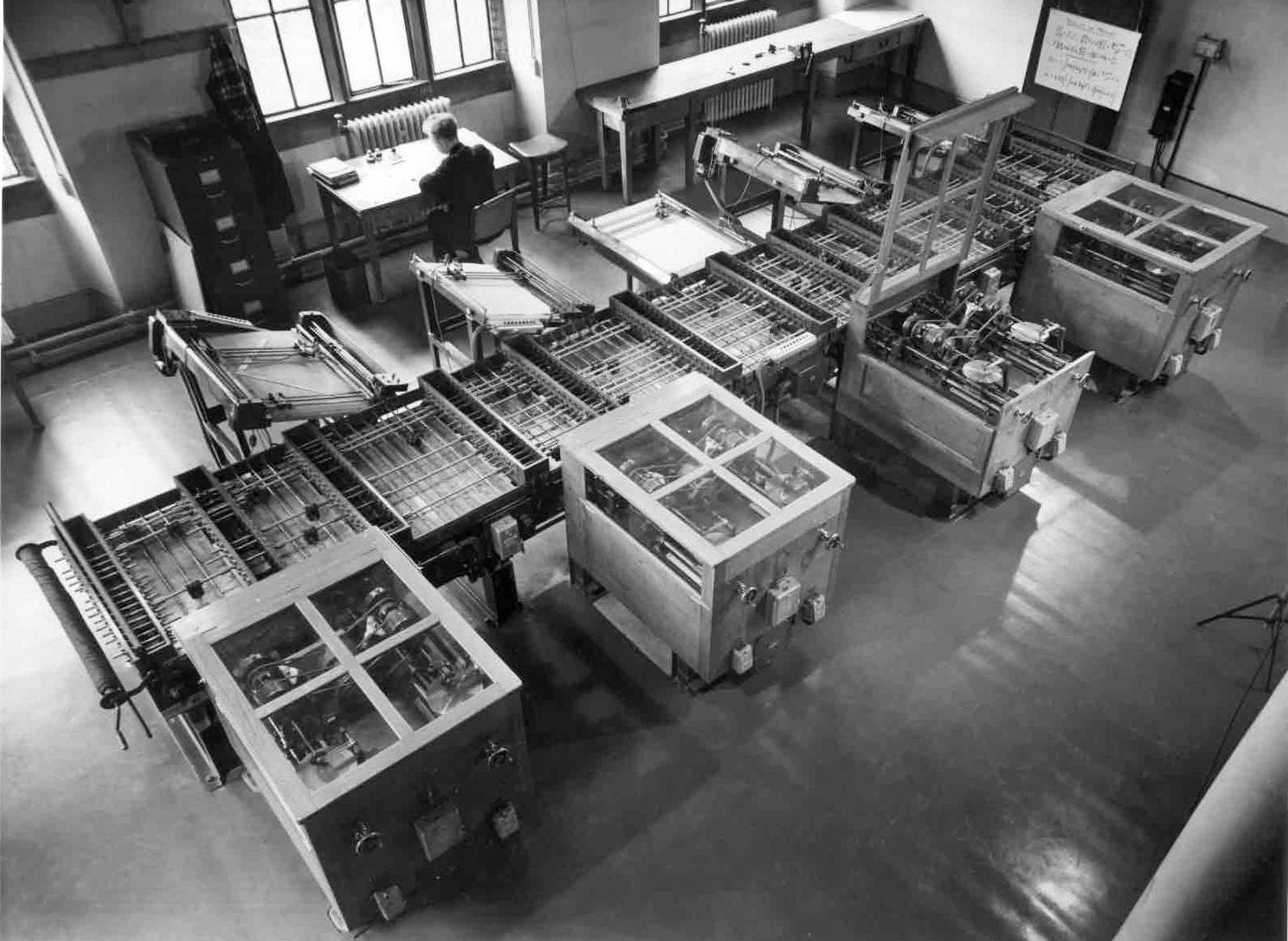
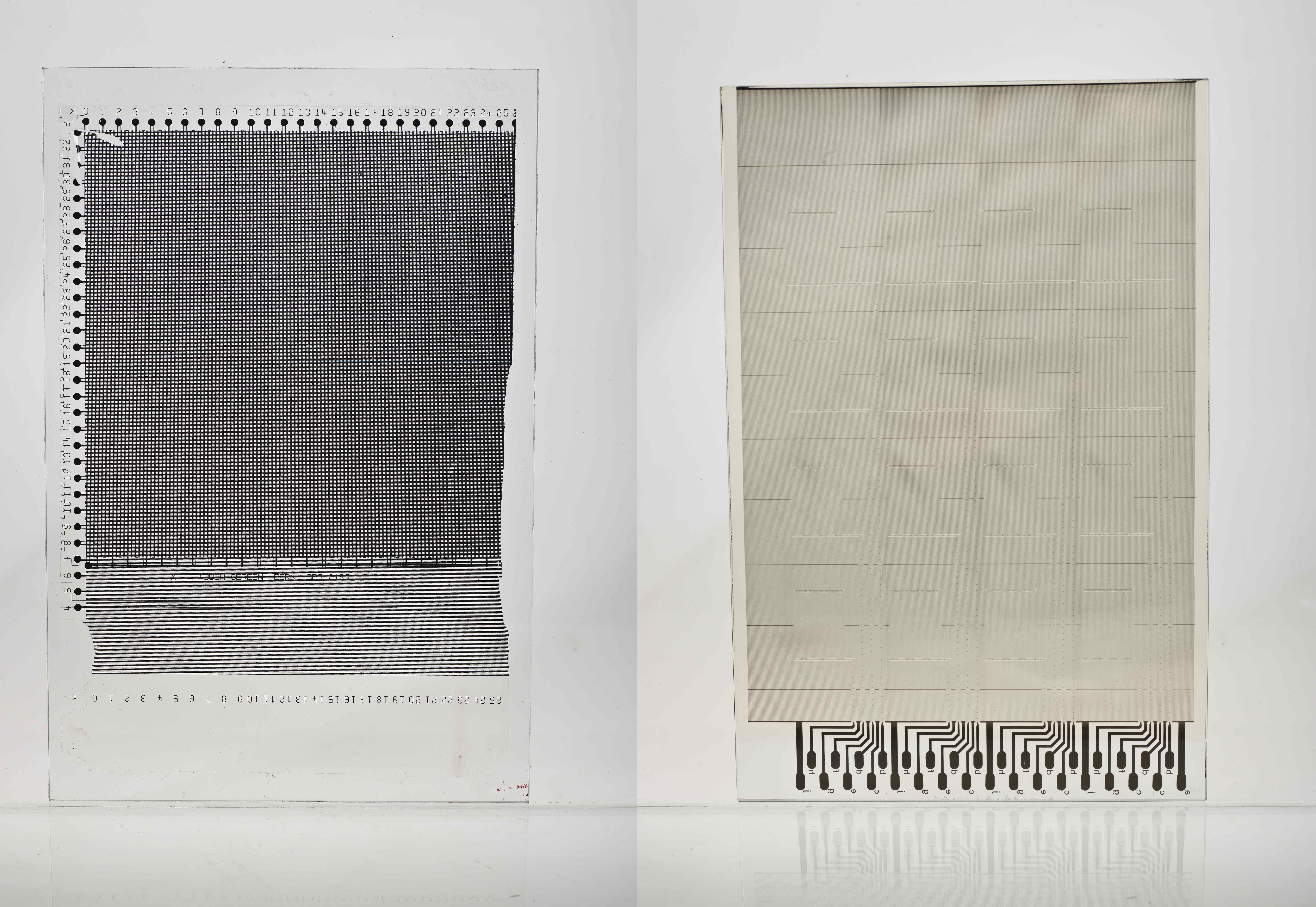
Multi-touch
In computing, multi-touch is technology that enables a surface (a touchpad or touchscreen) to recognize the presence of more than one somatosensory system, point of contact with the surface at the same time. The origins of multitouch began at CERN, MIT, University of Toronto, Carnegie Mellon University and Bell Labs in the 1970s. CERN started using multi-touch screens as early as 1976 for the controls of the Super Proton Synchrotron. Capacitive multi-touch displays were popularized by Apple Inc., Apple's iPhone in 2007. Plural-point awareness may be used to implement additional functionality, such as pinch to zoom or to activate certain subroutines attached to Gesture recognition, predefined gestures. Several uses of the term multi-touch resulted from the quick developments in this field, and many companies using the term to market older technology which is called ''gesture-enhanced single-touch'' or several other terms by other companies and researchers. Several other similar or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tablet Computer
A tablet computer, commonly shortened to tablet, is a mobile device, typically with a mobile operating system and touchscreen display processing circuitry, and a rechargeable battery in a single, thin and flat package. Tablets, being computers, do what other personal computers do, but lack some input/output (I/O) abilities that others have. Modern tablets largely resemble modern smartphones, the only differences being that tablets are relatively larger than smartphones, with screens or larger, measured diagonally, and may not support access to a cellular network. Unlike laptops which have traditionally run off operating systems usually designed for desktops, tablets usually run mobile operating systems, alongside smartphones. The touchscreen display is operated by Gesture recognition, gestures executed by finger or digital pen (stylus), instead of the Computer mouse, mouse, touchpad, and Keyboard (computing), keyboard of larger computers. Portable computers can be classifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elisha Gray
Elisha Gray (August 2, 1835 – January 21, 1901) was an American electrical engineer who co-founded the Western Electric Manufacturing Company. Gray is best known for his development of a telephone prototype in 1876 in Highland Park, Illinois. Some recent authors have argued that Gray should be considered the true inventor of the telephone because Alexander Graham Bell allegedly stole the idea of the liquid transmitter from him. Although Gray had been using liquid transmitters in his telephone experiments for more than two years previously, Bell's telephone patent was upheld in numerous court decisions. Gray is also considered to be the father of the modern music synthesizer, and was granted over 70 patents for his inventions. He was one of the founders of Graybar, purchasing a controlling interest in the company shortly after its inception. Biography and early inventions Gray was born in Barnesville, Ohio, the son of Christiana (Edgerton) and David Gray. His family were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vannevar Bush
Vannevar Bush ( ; March 11, 1890 – June 28, 1974) was an American engineer, inventor and science administrator, who during World War II headed the U.S. Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD), through which almost all wartime military R&D was carried out, including important developments in radar and the initiation and early administration of the Manhattan Project. He emphasized the importance of scientific research to national security and economic well-being, and was chiefly responsible for the movement that led to the creation of the National Science Foundation. Bush joined the Department of Electrical Engineering at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1919, and founded the company that became the Raytheon Company in 1922. Bush became vice president of MIT and dean of the MIT School of Engineering in 1932, and president of the Carnegie Institution of Washington in 1938. During his career, Bush patented a string of his own inventions. He is known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communications Intelligence Corporation
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inquiry studying them. There are many disagreements about its precise definition. John Peters argues that the difficulty of defining communication emerges from the fact that communication is both a universal phenomenon and a specific discipline of institutional academic study. One definitional strategy involves limiting what can be included in the category of communication (for example, requiring a "conscious intent" to persuade). By this logic, one possible definition of communication is the act of developing meaning among entities or groups through the use of sufficiently mutually understood signs, symbols, and semiotic conventions. An important distinction is between verbal communication, which happens through the use of a language, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)