|
Parahippocampus
The parahippocampal gyrus (or hippocampal gyrus') is a grey matter cortical region of the brain that surrounds the hippocampus and is part of the limbic system. The region plays an important role in memory encoding and retrieval. It has been involved in some cases of hippocampal sclerosis. Asymmetry has been observed in schizophrenia. Structure The anterior part of the gyrus includes the perirhinal and entorhinal cortices. The term parahippocampal cortex is used to refer to an area that encompasses both the posterior parahippocampal gyrus and the medial portion of the fusiform gyrus. Function Scene recognition The parahippocampal place area (PPA) is a sub-region of the parahippocampal cortex that lies medially in the inferior temporo-occipital cortex. PPA plays an important role in the encoding and recognition of environmental scenes (rather than faces). fMRI studies indicate that this region of the brain becomes highly active when human subjects view topographical scene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
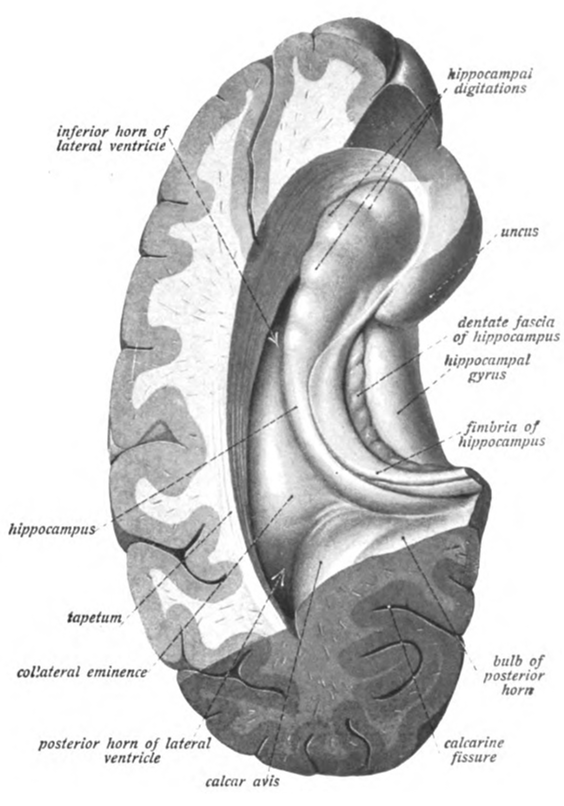
Hippocampus (brain)
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , 'seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic system, and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory, and in spatial memory that enables navigation. The hippocampus is located in the allocortex, with neural projections into the neocortex in humans, as well as primates. The hippocampus, as the medial pallium, is a structure found in all vertebrates. In humans, it contains two main interlocking parts: the hippocampus proper (also called ''Ammon's horn''), and the dentate gyrus. In Alzheimer's disease (and other forms of dementia), the hippocampus is one of the first regions of the brain to suffer damage; short-term memory loss and disorientation are included among the early symptoms. Damage to the hippocampus can also result from o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocampus
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , ' seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic system, and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory, and in spatial memory that enables navigation. The hippocampus is located in the allocortex, with neural projections into the neocortex in humans, as well as primates. The hippocampus, as the medial pallium, is a structure found in all vertebrates. In humans, it contains two main interlocking parts: the hippocampus proper (also called ''Ammon's horn''), and the dentate gyrus. In Alzheimer's disease (and other forms of dementia), the hippocampus is one of the first regions of the brain to suffer damage; short-term memory loss and disorientation are included among the early symptoms. Damage to the hippocampus can also result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Parahippocampal Gyrus
The posterior parahippocampal gyrus is a portion of the parahippocampal gyrus The parahippocampal gyrus (or hippocampal gyrus') is a grey matter cortical region of the brain that surrounds the hippocampus and is part of the limbic system. The region plays an important role in memory encoding and retrieval. It has been inv .... It can show deterioration in Alzheimer's disease. References Gyri {{neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusiform Face Area
The fusiform face area (FFA, meaning spindle-shaped face area) is a part of the human visual system (while also activated in people blind from birth) that is specialized for facial recognition. It is located in the inferior temporal cortex (IT), in the fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37). Structure The FFA is located in the ventral stream on the ventral surface of the temporal lobe on the lateral side of the fusiform gyrus. It is lateral to the parahippocampal place area. It displays some lateralization, usually being larger in the right hemisphere. The FFA was discovered and continues to be investigated in humans using positron emission tomography (PET) and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies. Usually, a participant views images of faces, objects, places, bodies, scrambled faces, scrambled objects, scrambled places, and scrambled bodies. This is called a functional localizer. Comparing the neural response between faces and scrambled faces will reveal areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoffrey Aguirre
Geoffrey, Geoffroy, Geoff, etc., may refer to: People * Geoffrey (name), including a list of people with the name * Geoffroy (surname), including a list of people with the name * Geoffrey of Monmouth (c. 1095–c. 1155), clergyman and one of the major figures in the development of British history * Geoffrey I of Anjou (died 987) * Geoffrey II of Anjou (died 1060) * Geoffrey III of Anjou (died 1096) * Geoffrey IV of Anjou (died 1106) * Geoffrey V, Count of Anjou (1113–1151), father of King Henry II of England * Geoffrey II, Duke of Brittany (1158–1186), one of Henry II's sons * Geoffrey, Archbishop of York (c. 1152–1212) * Geoffroy du Breuil of Vigeois, 12th century French chronicler * Geoffroy de Charney (died 1314), Preceptor of the Knights Templar * Geoffroy IV de la Tour Landry (c. 1320–1391), French nobleman and writer * Geoffrey the Baker (died c. 1360), English historian and chronicler * Geoffroy (musician) (born 1987), Canadian singer, songwriter and multi-ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nancy Kanwisher
Nancy Gail Kanwisher FBA (born 1958) is the Ellen Swallow Richards Professor in the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and an investigator at the McGovern Institute for Brain Research. She studies the neural and cognitive mechanisms underlying human visual perception and cognition. Academic background Nancy Kanwisher received her SB in biology from MIT in 1980 and her PhD in Brain and Cognitive Sciences from MIT in 1986. After obtaining her PhD working with Mary C. Potter, she then did her post-doctoral work with Anne Treisman at UC-Berkeley. Before returning to MIT as a faculty member in 1997 in the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Kanwisher served as a faculty member at both UCLA and Harvard University. Kanwisher is a member and associate editor for journals in areas of cognitive science, including Cognition, Current Opinion in Neurobiology, Journal of Neuroscience, Trends in Cognitive Sciences, and Cog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russell Epstein
Russell Epstein is a professor of Psychology at the University of Pennsylvania, who studies neural mechanisms underlying visual scene perception, event perception, object recognition, and spatial navigation in humans. His lab studies the role of the Parahippocampal and retrosplenial cortices in determining how people orient themselves relative to their surroundings. Education Epstein received an undergraduate degree in physics at the University of Chicago The University of Chicago (UChicago, Chicago, U of C, or UChi) is a private university, private research university in Chicago, Illinois. Its main campus is located in Chicago's Hyde Park, Chicago, Hyde Park neighborhood. The University of Chic ... and a Ph.D. in computer vision with Alan Yuille at Harvard. References Year of birth missing (living people) Living people University of Pennsylvania faculty American psychologists University of Chicago alumni Harvard University alumni {{US-psychologist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Mégevand
Pierre is a masculine given name. It is a French form of the name Peter. Pierre originally meant "rock" or "stone" in French (derived from the Greek word πέτρος (''petros'') meaning "stone, rock", via Latin "petra"). It is a translation of Aramaic כיפא (''Kefa),'' the nickname Jesus gave to apostle Simon Bar-Jona, referred in English as Saint Peter. Pierre is also found as a surname. People with the given name * Abbé Pierre, Henri Marie Joseph Grouès (1912–2007), French Catholic priest who founded the Emmaus Movement * Monsieur Pierre, Pierre Jean Philippe Zurcher-Margolle (c. 1890–1963), French ballroom dancer and dance teacher * Pierre (footballer), Lucas Pierre Santos Oliveira (born 1982), Brazilian footballer * Pierre, Baron of Beauvau (c. 1380–1453) * Pierre, Duke of Penthièvre (1845–1919) * Pierre, marquis de Fayet (died 1737), French naval commander and Governor General of Saint-Domingue * Prince Pierre, Duke of Valentinois (1895–1964), father ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FMRI
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area of the brain is in use, blood flow to that region also increases. The primary form of fMRI uses the blood-oxygen-level dependent (BOLD) contrast, discovered by Seiji Ogawa in 1990. This is a type of specialized brain and body scan used to map neural activity in the brain or spinal cord of humans or other animals by imaging the change in blood flow ( hemodynamic response) related to energy use by brain cells. Since the early 1990s, fMRI has come to dominate brain mapping research because it does not involve the use of injections, surgery, the ingestion of substances, or exposure to ionizing radiation. This measure is frequently corrupted by noise from various sources; hence, statistical procedures are used to extract the underlying signal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusiform Gyrus
The fusiform gyrus, also known as the ''lateral occipitotemporal gyrus'','' ''is part of the temporal lobe and occipital lobe in Brodmann area 37. The fusiform gyrus is located between the lingual gyrus and parahippocampal gyrus above, and the inferior temporal gyrus below. Though the functionality of the fusiform gyrus is not fully understood, it has been linked with various neural pathways related to recognition. Additionally, it has been linked to various neurological phenomena such as synesthesia, dyslexia, and prosopagnosia. Anatomy Anatomically, the fusiform gyrus is the largest macro-anatomical structure within the ventral temporal cortex, which mainly includes structures involved in high-level vision. The term fusiform gyrus (lit. "spindle-shaped convolution") refers to the fact that the shape of the gyrus is wider at its centre than at its ends. This term is based on the description of the gyrus by Emil Huschke in 1854. (see also section on history). The fus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Hemisphere
The vertebrate cerebrum (brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres has an outer layer of grey matter, the cerebral cortex, that is supported by an inner layer of white matter. In eutherian (placental) mammals, the hemispheres are linked by the corpus callosum, a very large bundle of nerve fibers. Smaller commissures, including the anterior commissure, the posterior commissure and the fornix, also join the hemispheres and these are also present in other vertebrates. These commissures transfer information between the two hemispheres to coordinate localized functions. There are three known poles of the cerebral hemispheres: the '' occipital pole'', the '' frontal pole'', and the '' temporal pole''. The central sulcus is a prominent fissure which separates the parietal lobe from the frontal lobe and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_-_inferiror_view.png)