|
P-Toluenesulfonic Acid
''p''-Toluenesulfonic acid (PTSA or ''p''TsOH) or tosylic acid (TsOH) is an organic compound with the formula CH3 C6H4 SO3H. It is a white extremely hygroscopic solid that is soluble in water, alcohols, and other polar organic solvents. The CH3C6H4SO2 group is known as the tosyl group and is often abbreviated as Ts or Tos. Most often, TsOH refers to the monohydrate, TsOH.H2O. As with other aryl sulfonic acids, TsOH is a strong organic acid. It is about one million times stronger than benzoic acid. It is one of the few strong acids that is solid and therefore is conveniently weighed and stored. Preparation and uses TsOH is prepared on an industrial scale by the sulfonation of toluene. Common impurities include benzenesulfonic acid and sulfuric acid. TsOH monohydrate contains an amount of water. To estimate the total moisture present as impurity, the Karl Fischer method is used. Impurities can be removed by recrystallization from its concentrated aqueous solution followed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetonitrile
Acetonitrile, often abbreviated MeCN (methyl cyanide), is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile ( hydrogen cyanide is a simpler nitrile, but the cyanide anion is not classed as organic). It is produced mainly as a byproduct of acrylonitrile manufacture. It is used as a polar aprotic solvent in organic synthesis and in the purification of butadiene. The skeleton is linear with a short distance of 1.16 Å. Acetonitrile was first prepared in 1847 by the French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas. Applications Acetonitrile is used mainly as a solvent in the purification of butadiene in refineries. Specifically, acetonitrile is fed into the top of a distillation column filled with hydrocarbons including butadiene, and as the acetonitrile falls down through the column, it absorbs the butadiene which is then sent from the bottom of the tower to a second separating tower. Heat is then employed in the separatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
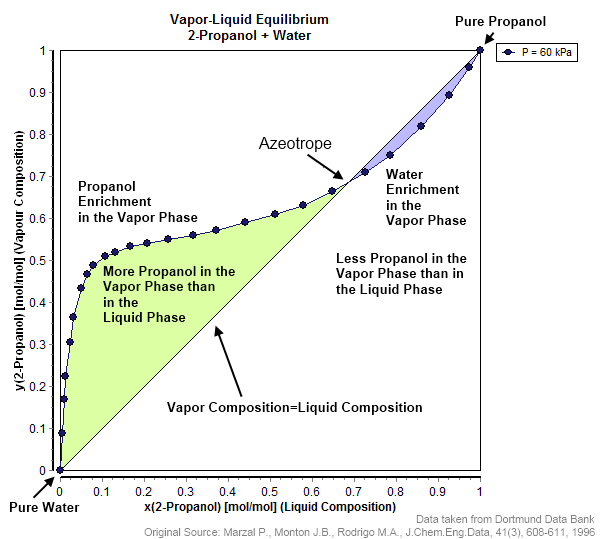
Azeotrope
An azeotrope () or a constant heating point mixture is a mixture of two or more liquids whose proportions cannot be altered or changed by simple distillation.Moore, Walter J. ''Physical Chemistry'', 3rd e Prentice-Hall 1962, pp. 140–142 This happens when an azeotrope is boiled, the vapour has the same proportions of constituents as the unboiled mixture. Because their composition is unchanged by distillation, azeotropes are also called (especially in older texts) ''constant boiling point mixtures''. Some azeotropic mixtures of pairs of compounds are known, and many azeotropes of three or more compounds are also known. In such a case it is not possible to separate the components by fractional distillation and azeotropic distillation is usually used instead. There are two types of azeotropes: minimum boiling azeotrope and maximum boiling azeotrope. A solution that shows greater positive deviation from Raoult's law forms a minimum boiling azeotrope at a specific composition. For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
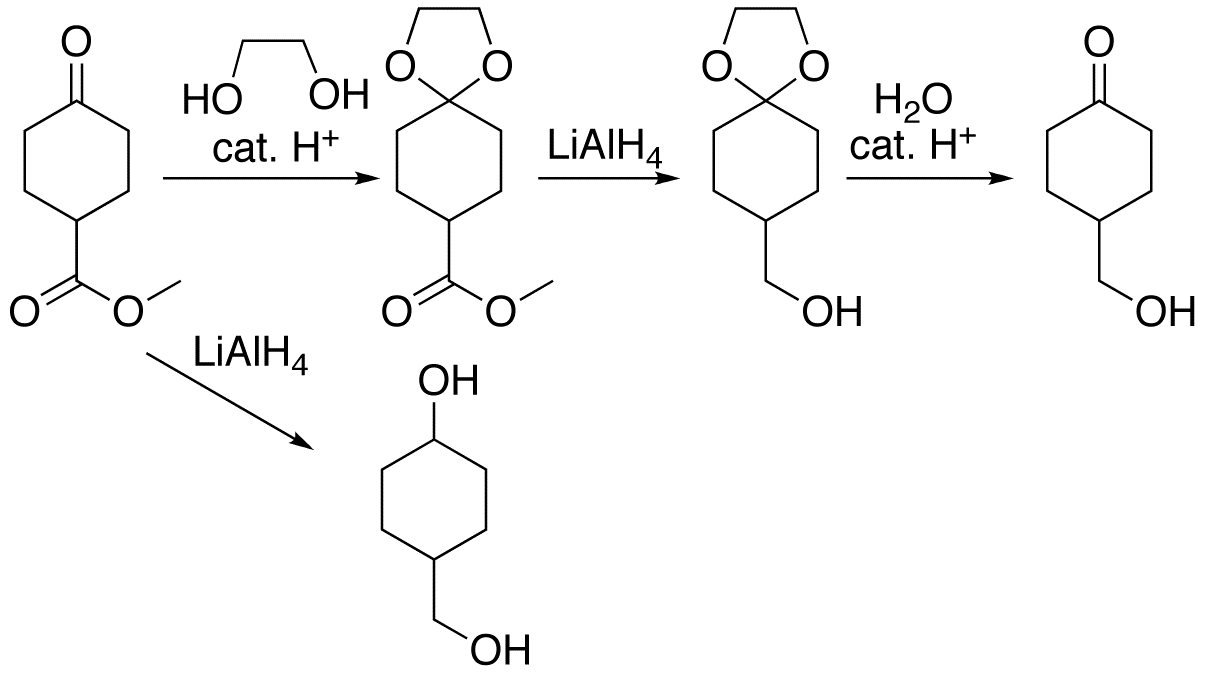
Protecting Group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis. In many preparations of delicate organic compounds, some specific parts of their molecules cannot survive the required reagents or chemical environments. Then, these parts, or groups, must be protected. For example, lithium aluminium hydride is a highly reactive but useful reagent capable of reducing esters to alcohols. It will always react with carbonyl groups, and this cannot be discouraged by any means. When a reduction of an ester is required in the presence of a carbonyl, the attack of the hydride on the carbonyl has to be prevented. For example, the carbonyl is converted into an acetal, which does not react with hydrides. The acetal is then called a protecting group for the carbonyl. After the step involving the hydride is complete, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
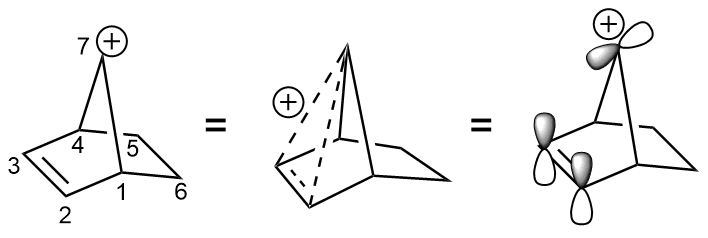
2-Norbornyl Cation
In organic chemistry, the term 2-norbornyl cation (or 2-bicyclo .2.1eptyl cation) describes one of the three carbocations formed from derivatives of norbornane. Though 1-norbornyl and 7-norbornyl cations have been studied, the most extensive studies and vigorous debates have been centered on the exact structure of the 2-norbornyl cation. The 2-norbornyl cation has been formed from a variety of norbornane derivatives and reagents. First reports of its formation and reactivity published by Saul Winstein sparked controversy over the nature of its bonding, as he invoked a three-center two-electron bond to explain the stereochemical outcome of the reaction. Herbert C. Brown challenged this assertion on the grounds that classical resonance structures could explain these observations without needing to adapt a new perspective of bonding. Both researchers' views had its supporters, and dozens of scientists contributed ingeniously designed experiments to provide evidence for one viewpoin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
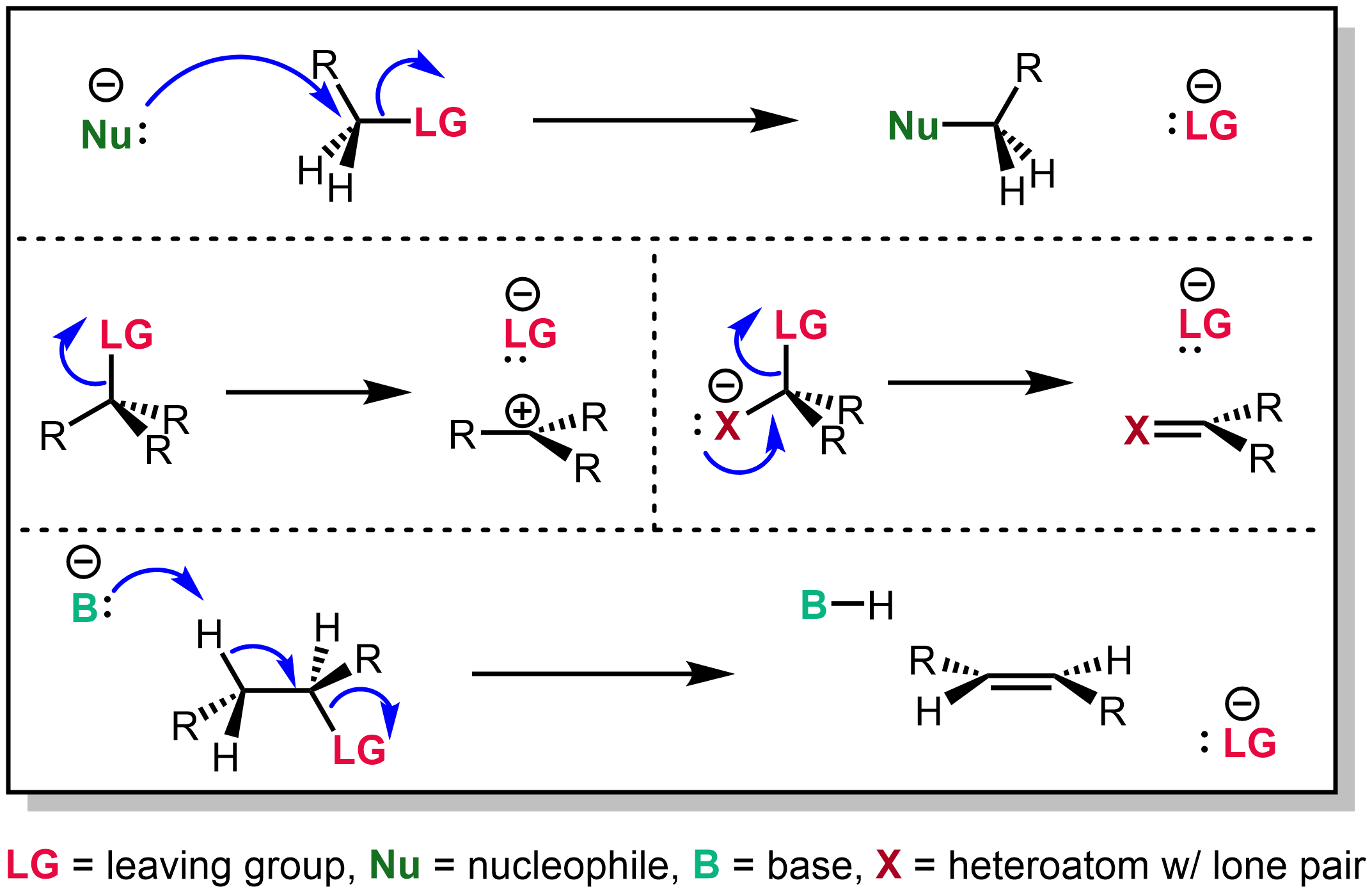
Elimination Reaction
An elimination reaction is a type of organic reaction in which two substituents are removed from a molecule in either a one- or two-step mechanism. The one-step mechanism is known as the E2 reaction, and the two-step mechanism is known as the E1 reaction. The numbers refer not to the number of steps in the mechanism, but rather to the kinetics of the reaction: E2 is bimolecular (second-order) while E1 is unimolecular (first-order). In cases where the molecule is able to stabilize an anion but possesses a poor leaving group, a third type of reaction, E1CB, exists. Finally, the pyrolysis of xanthate and acetate esters proceed through an "internal" elimination mechanism, the Ei mechanism. E2 mechanism The E2 mechanism, where E2 stands for bimolecular elimination, involves a one-step mechanism in which ''carbon-hydrogen'' and ''carbon-halogen'' bonds break to form a double bond (''C=C Pi bond''). The specifics of the reaction are as follows: * E2 is a single step elimination, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleophile
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are Lewis bases. ''Nucleophilic'' describes the affinity of a nucleophile to bond with positively charged atomic nuclei. Nucleophilicity, sometimes referred to as nucleophile strength, refers to a substance's nucleophilic character and is often used to compare the affinity of atoms. Neutral nucleophilic reactions with solvents such as alcohols and water are named solvolysis. Nucleophiles may take part in nucleophilic substitution, whereby a nucleophile becomes attracted to a full or partial positive charge, and nucleophilic addition. Nucleophilicity is closely related to basicity. History The terms ''nucleophile'' and '' electrophile'' were introduced by Christopher Kelk Ingold in 1933, replacing the terms ''anionoid'' and ''catio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaving Group
In chemistry, a leaving group is defined by the IUPAC as an atom or group of atoms that detaches from the main or residual part of a substrate during a reaction or elementary step of a reaction. However, in common usage, the term is often limited to a fragment that departs with a pair of electrons in heterolytic bond cleavage. In this usage, a leaving group is a less formal but more commonly used synonym of the term '' nucleofuge''. In this context, leaving groups are generally anions or neutral species, departing from a neutral or cationic substrates, respectively, though in rare cases, cations leaving from a dicationic substrate are also known. A species' ability to serve as a leaving group depends on its ability to stabilize the additional electron density that results from bond heterolysis. Common anionic leaving groups are halides such as Cl−, Br−, and I−, and sulfonate esters such as tosylate (TsO−), while water (H2O), alcohols (HOR), and amines (R3N) are common neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Withdrawing Group
In chemistry, an electron-withdrawing group (EWG) is a substituent that has some of the following kinetic and thermodynamic implications: *with regards to electron transfer, electron-withdrawing groups enhance the oxidizing power tendency of the appended species. Tetracyanoethylene is an oxidant because the alkene is appended to four cyano substituents, which are electron-withdrawing. *with regards to acid-base reactions, acids with electron-withdrawing groups species have low acid dissociation constants. For EWG's attached to benzene, this effect is described by the Hammett equation, which allows EWGs to be discussed quantitatively. *with regards to nucleophilic substitution reactions, electron-withdrawing groups are susceptible to attack by weak nucleophiles. For example, compared to chlorobenzene, chlorodinitrobenzene is susceptible to reactions that displace chloride.{{cite journal , author=J. F. Bunnett, R. M. Conner, doi=10.15227/orgsyn.040.0034, title=2,4-Dinitr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkylating Agent
Alkylation is the transfer of an alkyl group from one molecule to another. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene (or their equivalents). Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting alkylation. Alkyl groups can also be removed in a process known as dealkylation. Alkylating agents are often classified according to their nucleophilic or electrophilic character. In oil refining contexts, alkylation refers to a particular alkylation of isobutane with olefins. For upgrading of petroleum, alkylation produces a premium blending stock for gasoline. In medicine, alkylation of DNA is used in chemotherapy to damage the DNA of cancer cells. Alkylation is accomplished with the class of drugs called alkylating antineoplastic agents. Nucleophilic alkylating agents Nucleophilic alkylating agents deliver the equivalent of an alkyl anion ( carbanion). The formal "alkyl anion" attacks an electrophile, forming a new covalent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transesterification
In organic chemistry, transesterification is the process of exchanging the organic group R″ of an ester with the organic group R' of an alcohol. These reactions are often catalyzed by the addition of an acid or base catalyst. The reaction can also be accomplished with the help of other enzymes, particularly lipases (one example is the lipase E.C.3.1.1.3). Strong acids catalyse the reaction by donating a proton to the carbonyl group, thus making it a more potent electrophile, whereas bases catalyse the reaction by removing a proton from the alcohol, thus making it more nucleophilic. If the alcohol produced by the reaction can be separated from the reactants by distillation this will drive the equilibrium toward the products, this means that esters with larger alkoxy groups can be made from methyl or ethyl esters in high purity by heating the mixture of ester, acid/base, and large alcohol. Mechanism In the transesterification mechanism, the carbonyl carbon of the startin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fischer–Speier Esterification
Fischer esterification or Fischer–Speier esterification is a special type of esterification by refluxing a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst. The reaction was first described by Emil Fischer and Arthur Speier in 1895. Most carboxylic acids are suitable for the reaction, but the alcohol should generally be primary or secondary. Tertiary alcohols are prone to elimination. Contrary to common misconception found in organic chemistry textbooks, phenols can also be esterified to give good to near quantitative yield of products. Commonly used catalysts for a Fischer esterification include sulfuric acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid, and Lewis acids such as scandium(III) triflate. For more valuable or sensitive substrates (for example, biomaterials) other, milder procedures such as Steglich esterification are used. The reaction is often carried out without a solvent (particularly when a large reagent excess of alcohol is used) or in a non-polar solvent (e.g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |