|
Ostium
* An ostium (plural ostia) in anatomy is a small opening or orifice. Ostium or ostia may refer to: Human anatomy * Ostium of fallopian tube * Ostium of the uterus (other) * Ostium primum of the developing heart * Ostium secundum ( foramen ovale) of the developing heart * Ostium maxillare of the maxillary sinus * Ostium vaginae (vaginal orifice) * Coronary ostium – opening of coronary arteries at root of aorta, superior to aortic valve * Sinus ostium an opening that connects a sinus to the nasal cavity itself. In other animals *Ostium (sponges), the pores of living sponges *Ostia of female lepidoptera genitalia See also * *Pore (other) *Foramen In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (; in [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foramen Ovale (heart)
In the fetal heart, the foramen ovale (), also foramen Botalli, or the ostium secundum of Born, allows blood to enter the left atrium from the right atrium. It is one of two fetal cardiac shunts, the other being the ductus arteriosus (which allows blood that still escapes to the right ventricle to bypass the pulmonary circulation). Another similar adaptation in the fetus is the ductus venosus. In most individuals, the foramen ovale closes at birth. It later forms the fossa ovalis. Development The foramen ovale () forms in the late fourth week of gestation, as a small passageway between the septum secundum and the ostium secundum. Initially the atria are separated from one another by the septum primum except for a small opening below the septum, the ostium primum. As the septum primum grows, the ostium primum narrows and eventually closes. Before it does so, bloodflow from the inferior vena cava wears down a portion of the septum primum, forming the ostium secundum. Some embryo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostium Primum
In the developing heart, the atria are initially open to each other, with the opening known as the primary interatrial foramen or ostium primum (or interatrial foramen primum). The foramen lies beneath the edge of septum primum and the endocardial cushions. It progressively decreases in size as the septum grows downwards, and disappears with the formation of the atrial septum. Structure The foramen lies beneath the edge of septum primum and the endocardial cushions. It progressively decreases in size as the septum grows downwards, and disappears with the formation of the atrial septum. Closure The septum primum, a which grows down to separate the primitive atrium into the left atrium and right atrium, grows in size over the course of heart development. The primary interatrial foramen is the gap between the septum primum and the septum intermedium, which gets progressively smaller until it closes. Clinical significance Failure of the septum primum to fuse with the endocardial c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostium Maxillare
Below the bulla ethmoidalis, and partly hidden by the inferior end of the uncinate process of ethmoid bone, is the maxillary hiatus (or ostium maxillare, or maxillary sinus ostium, or maxillary ostium, or opening from the maxillary sinus); in a frontal section this opening is seen to be placed near the roof of the sinus Sinus may refer to: Anatomy * Sinus (anatomy), a sac or cavity in any organ or tissue ** Paranasal sinuses, air cavities in the cranial bones, especially those near the nose, including: *** Maxillary sinus, is the largest of the paranasal sinuses, .... In the articulated skull this aperture is much reduced in size by the following bones: the uncinate process of the ethmoid above, the ethmoidal process of the inferior nasal concha below, the vertical part of the palatine behind, and a small part of the lacrimal above and in front; the sinus communicates with the middle meatus of the nose, generally by two small apertures left between the above-mentioned bones. Addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinus Ostium
The human nose is the most protruding part of the face. It bears the nostrils and is the first organ of the respiratory system. It is also the principal organ in the olfactory system. The shape of the nose is determined by the nasal bones and the nasal cartilages, including the nasal septum which separates the nostrils and divides the nasal cavity into two. On average the nose of a male is larger than that of a female. The nose has an important function in breathing. The nasal mucosa lining the nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses carries out the necessary conditioning of inhaled air by warming and moistening it. Nasal conchae, shell-like bones in the walls of the cavities, play a major part in this process. Filtering of the air by nasal hair in the nostrils prevents large particles from entering the lungs. Sneezing is a reflex to expel unwanted particles from the nose that irritate the mucosal lining. Sneezing can transmit infections, because aerosols are created in whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
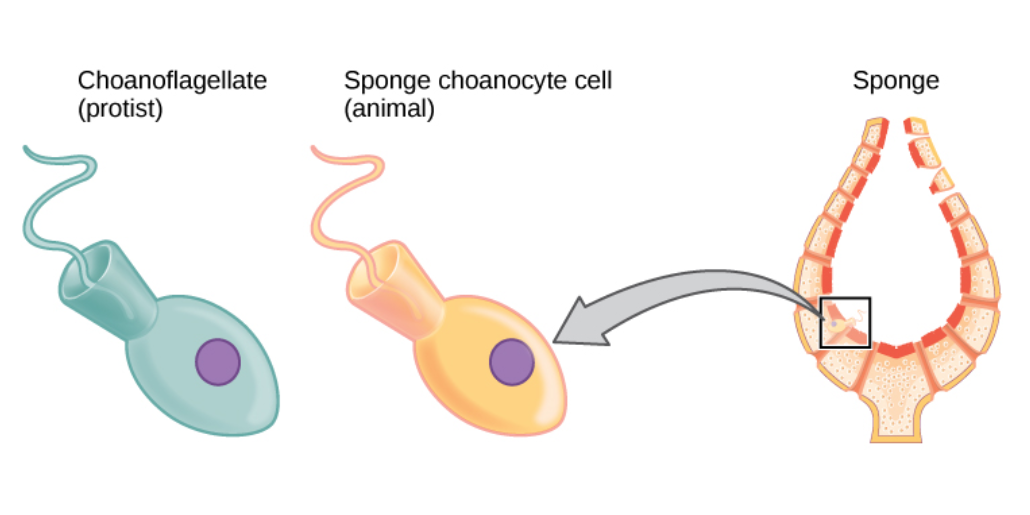
Ostium (sponges)
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. Sponges have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. Sponges do not have nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes. Sponges were first to branch off the evolutionary tree from the last common ancestor of all animals, making them the sister group of all other animals. Etymology The term ''sponge'' derives from the Ancient Greek word ( 'sponge'). Overview Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are multicellular, het ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sponge
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. Sponges have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. Sponges do not have nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes. Sponges were first to branch off the evolutionary tree from the last common ancestor of all animals, making them the sister group of all other animals. Etymology The term ''sponge'' derives from the Ancient Greek word ( 'sponge'). Overview Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are multicellular, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostium Of Fallopian Tube
The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, oviducts or salpinges (singular salpinx), are paired tubes in the human female that stretch from the uterus to the ovaries. The fallopian tubes are part of the female reproductive system. In other mammals they are only called oviducts. Each tube is a muscular hollow organ that is on average between 10 and 14 cm in length, with an external diameter of 1 cm. It has four described parts: the intramural part, isthmus, ampulla, and infundibulum with associated fimbriae. Each tube has two openings a proximal opening nearest and opening to the uterus, and a distal opening furthest and opening to the abdomen. The fallopian tubes are held in place by the mesosalpinx, a part of the broad ligament mesentery that wraps around the tubes. Another part of the broad ligament, the mesovarium suspends the ovaries in place. An egg cell is transported from an ovary to a fallopian tube where it may be fertilized in the ampulla of the tub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostium Of The Uterus (other)
{{disambig ...
Orifice of the uterus may refer to: * External orifice of the uterus * Internal orifice of the uterus Internal may refer to: *Internality as a concept in behavioural economics *Neijia, internal styles of Chinese martial arts *Neigong or "internal skills", a type of exercise in meditation associated with Daoism *''Internal (album)'' by Safia, 2016 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaginal Orifice
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen. At the deep end, the cervix (neck of the uterus) bulges into the vagina. The vagina allows for sexual intercourse and birth. It also channels menstrual flow, which occurs in humans and closely related primates as part of the menstrual cycle. Although research on the vagina is especially lacking for different animals, its location, structure and size are documented as varying among species. Female mammals usually have two external openings in the vulva; these are the urethral opening for the urinary tract and the vaginal opening for the genital tract. This is different from male mammals, who usually have a single urethral opening for both urination and reproduction. The vaginal opening is much larger than the nearby urethral openi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronary Arteries
The coronary arteries are the arterial blood vessels of coronary circulation, which transport oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. The heart requires a continuous supply of oxygen to function and survive, much like any other tissue or organ of the body. The coronary arteries wrap around the entire heart. The two main branches are the left coronary artery and right coronary artery. The arteries can additionally be categorized based on the area of the heart for which they provide circulation. These categories are called ''epicardial'' (above the epicardium, or the outermost tissue of the heart) and ''microvascular'' (close to the endocardium, or the innermost tissue of the heart). Reduced function of the coronary arteries can lead to decreased flow of oxygen and nutrients to the heart. Not only does this affect supply to the heart muscle itself, but it also can affect the ability of the heart to pump blood throughout the body. Therefore, any disorder or disease of the coronary ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the systemic circulation. Structure Sections In anatomical sources, the aorta is usually divided into sections. One way of classifying a part of the aorta is by anatomical compartment, where the thoracic aorta (or thoracic portion of the aorta) runs from the heart to the diaphragm. The aorta then continues downward as the abdominal aorta (or abdominal portion of the aorta) from the diaphragm to the aortic bifurcation. Another system divides the aorta with respect to its course and the direction of blood flow. In this system, the aorta starts as the ascending aorta, travels superiorly from the heart, and then makes a hairpin turn known as the aortic arch. Following the aortic arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aortic Valve
The aortic valve is a valve in the heart of humans and most other animals, located between the left ventricle and the aorta. It is one of the four valves of the heart and one of the two semilunar valves, the other being the pulmonary valve. The aortic valve normally has three cusps or leaflets, although in 1–2% of the population it is found to congenitally have two leaflets. The aortic valve is the last structure in the heart the blood travels through before stopping the flow through the systemic circulation. Structure The aortic valve normally has three cusps however there is some discrepancy in their naming. They may be called the left coronary, right coronary and non-coronary cusp. Some sources also advocate they be named as a left, right and posterior cusp. Anatomists have traditionally named them the left posterior (origin of left coronary), anterior (origin of the right coronary) and right posterior. The three cusps, when the valve is closed, contain a sinus called an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |