|
Orthomolecular Psychiatry
Orthomolecular psychiatry is the use of orthomolecular medicine for mental illness. The approach uses unorthodox forms of individualized testing and diagnosis to attempt to establish an etiology for each patient's specific symptoms, and claims to tailor the treatment accordingly, using a combination of nutrients, dietary changes and medications that are claimed to enhance quality of life and functionality as well as to reduce or eliminate symptoms and the use of xenobiotic drugs. Scientific studies have shown the orthomolecular psychiatry is ineffective. Orthomolecular psychiatry has been rejected by the mainstream medical community. History Orthomolecular psychiatry began with Abram Hoffer and Humphry Osmond in the 1950s and was continued by Carl Pfeiffer, although proponents of orthomolecular psychiatry say that the ideas behind their approach can be traced back to the 1920s and '30s. Orthomolecular psychiatry's goal of weaning patients from conventional neuroleptic drugs follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthomolecular Medicine
Orthomolecular medicine is a form of alternative medicine that aims to maintain human health through nutritional supplementation. The concept builds on the idea of an optimal nutritional environment in the body and suggests that diseases reflect deficiencies in this environment. Treatment for disease, according to this view, involves attempts to correct "imbalances or deficiencies based on individual biochemistry" by use of substances such as vitamins, minerals, amino acids, trace elements and fatty acids. The notions behind orthomolecular medicine are not supported by sound medical evidence, and the therapy is not effective for chronic disease prevention; even the validity of calling the orthomolecular approach a form of medicine has been questioned since the 1970s. The approach is sometimes referred to as megavitamin therapy, because its practice evolved out of, and in some cases still uses, doses of vitamins and minerals many times higher than the recommended dietary intak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Orthomolecular Medicine
The ''Journal of Orthomolecular Medicine'' was established in 1967 by Abram Hoffer. It publishes studies in nutritional and orthomolecular medicine. There is controversy surrounding the journal, as the validity of the field of orthomolecular medicine is not widely accepted by mainstream medicine. The journal is ranked in the bottom 10 percent of all journals about complementary and alternative medicine that are indexed in the bibliographic database Scopus (#74 out of 82 journalsCiteScore2018). History In 1967, Hoffer found it increasingly difficult to publish reports on his studies of megavitamin therapies and claimed that his studies were rejected in a conspiracy of mainstream medicine, prompted by what he alleged to be extended conflicts of interest on the part of the American Psychiatric Association. The ''Journal of Schizophrenia'' followed the formation of the Canadian Schizophrenia Foundation and the American Schizophrenia Association. Hoffer and Humphry Osmond, who develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
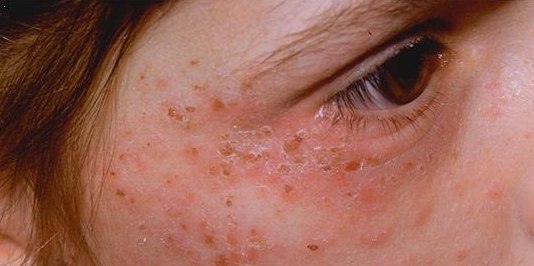
Acute Intermittent Porphyria
Acute intermittent porphyria (AIP) is a rare metabolic disorder affecting the production of heme resulting from a deficiency of the enzyme porphobilinogen deaminase. It is the most common of the acute porphyrias. Signs and symptoms The clinical presentation of AIP is highly variable and non-specific. The patients are typically asymptomatic, with most gene carriers having no family history because the condition had remained latent for several generations. The syndrome marked by acute attacks affects only 10% of gene carriers. The mean age at diagnosis is 33 years old. Like other porphyrias, AIP is more likely to present in women. A distinguishing feature of AIP that separates it from other porphyrias is the absence of photosensitive cutaneous symptoms that occur in addition to acute attacks. Acute attacks AIP is one of the four porphyrias that presents as an acute attack. 90% of affected individuals never experience an acute attack and are asymptomatic, while an estimated 5% of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyria
Porphyria is a group of liver disorders in which substances called porphyrins build up in the body, negatively affecting the skin or nervous system. The types that affect the nervous system are also known as acute porphyria, as symptoms are rapid in onset and short in duration. Symptoms of an attack include abdominal pain, chest pain, vomiting, confusion, constipation, fever, high blood pressure, and high heart rate. The attacks usually last for days to weeks. Complications may include paralysis, low blood sodium levels, and seizures. Attacks may be triggered by alcohol, smoking, hormonal changes, fasting, stress, or certain medications. If the skin is affected, blisters or itching may occur with sunlight exposure. Most types of porphyria are inherited from one or both of a person's parents and are due to a mutation in one of the genes that make heme. They may be inherited in an autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or X-linked dominant manner. One type, ''porphyria c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrrole
Pyrrole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula C4 H4 NH. It is a colorless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., ''N''-methylpyrrole, C4H4NCH3. Porphobilinogen, a trisubstituted pyrrole, is the biosynthetic precursor to many natural products such as heme. Pyrroles are components of more complex macrocycles, including the porphyrinogens and products derived therefrom, including porphyrins of heme, the chlorins, bacteriochlorins, and chlorophylls. Properties Pyrrole is a colorless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air, and is usually purified by distillation immediately before use. Pyrrole has a nutty odor. Pyrrole is a 5-membered aromatic heterocycle, like furan and thiophene. Unlike furan and thiophene, it has a dipole in which the positive end lies on the side of the heteroatom, with a dipole moment of 1.58 D. In CDCl3, it has ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Amalgam Controversy
This discussion of the dental amalgam controversy outlines the debate over whether dental amalgam (the mercury alloy in dental fillings) should be used. Supporters claim that it is safe, effective and long-lasting while critics argue that claims have been made since the 1840s that amalgam is unsafe because it may cause mercury poisoning and other toxicity. Supporters of amalgam fillings point out that it is safe, durable, relatively inexpensive, and easy to use. On average, amalgam lasts twice as long as resin composites, takes less time to place, is tolerant of saliva or blood contamination during placement (unlike composites), and is often about 20–30% less expensive. ''Consumer Reports'' has suggested that many who claim dental amalgam is not safe are "prospecting for disease" and using pseudoscience to scare patients into more lucrative treatment options. Those opposed to amalgam use suggest that modern composites are improving in strength. In addition to their claims of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Metal (chemistry)
upright=1.2, Crystals of osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">lead.html" ;"title="osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead Heavy metals are generally defined as metals with relatively high density, densities, atomic weights, or atomic numbers. The criteria used, and whether metalloids are included, vary depending on the author and context. In metallurgy, for example, a heavy metal may be defined on the basis of density, whereas in physics the distinguishing criterion might be atomic number, while a chemist would likely be more concerned with chemical property, chemical behaviour. More specific definitions have been published, but none of these have been widely accepted. The definitions surveyed in this article encompass up to 96 out of the 118 known chemical elements; only mercury, lead and bismuth meet all of them. Despite this lack of agreement, the term (plural or singular) is widely used in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
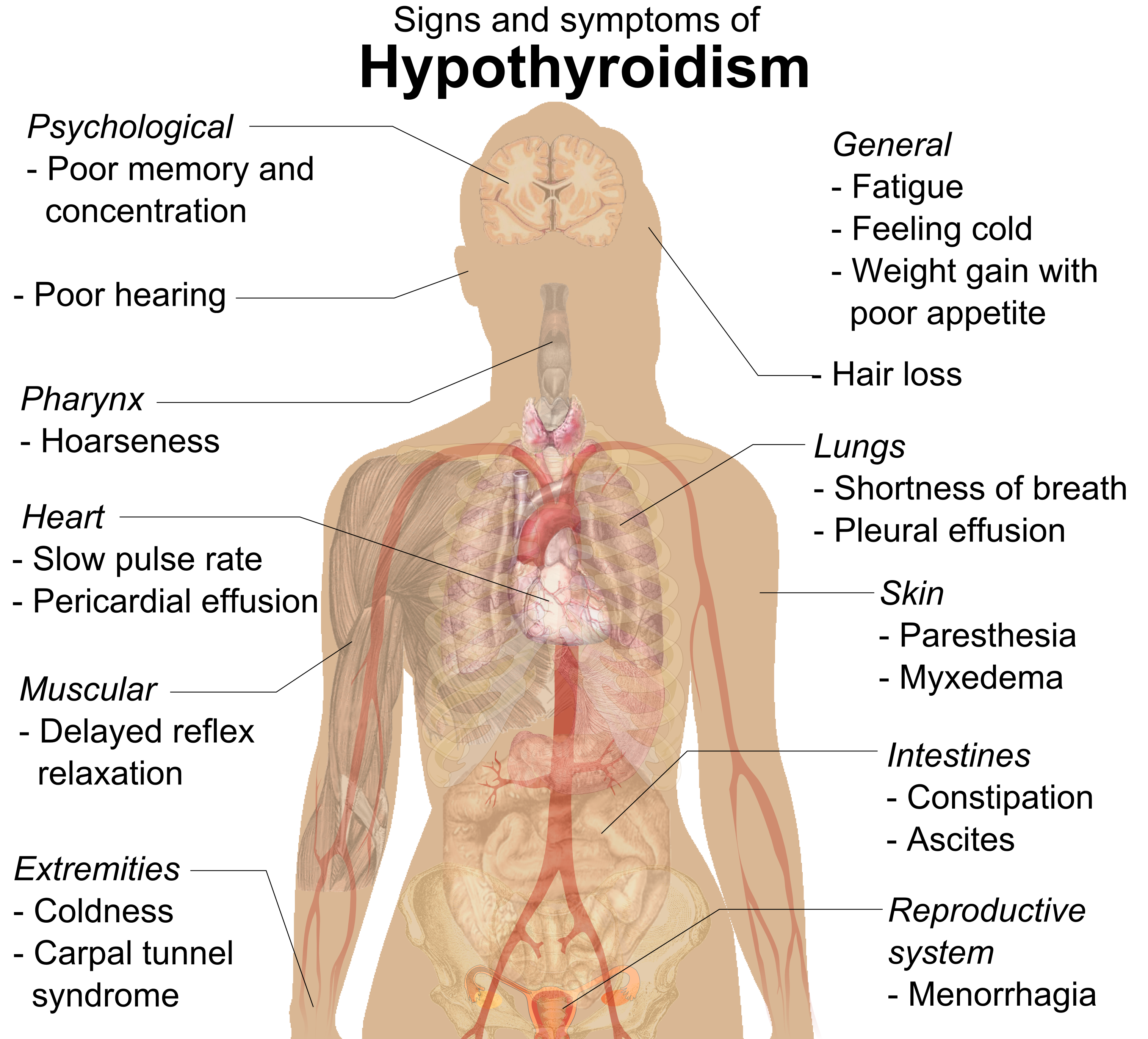
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as poor ability to tolerate cold, a feeling of tiredness, constipation, slow heart rate, depression, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling of the front part of the neck due to goiter. Untreated cases of hypothyroidism during pregnancy can lead to delays in growth and intellectual development in the baby or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome. Worldwide, too little iodine in the diet is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. Hashimoto's thyroiditis is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in countries with sufficient dietary iodine. Less common causes include previous treatment with radioactive iodine, injury to the hypothalamus or the anterior pituitary gland, certain medications, a lack of a functioning thyroid at bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L), symptoms associated with hypoglycemia, and resolution of symptoms when blood sugar returns to normal. Hypoglycemia may result in headache, tiredness, clumsiness, trouble talking, confusion, fast heart rate, sweating, shakiness, nervousness, hunger, loss of consciousness, seizures, or death. Symptoms typically come on quickly. The most common cause of hypoglycemia is medications used to treat diabetes such as insulin, sulfonylureas, and biguanides. Risk is greater in diabetics who have eaten less than usual, recently exercised, or consumed alcohol. Other causes of hypoglycemia include severe illness, sepsis, kidney failure, liver disease, hormone deficiency, tumors such as insulinomas or non-B cell tumo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Allergy
A food allergy is an abnormal immune response to food. The symptoms of the allergic reaction may range from mild to severe. They may include itchiness, swelling of the tongue, vomiting, diarrhea, hives, trouble breathing, or low blood pressure. This typically occurs within minutes to several hours of exposure. When the symptoms are severe, it is known as anaphylaxis. A food intolerance and food poisoning are separate conditions, not due to an immune response. Common foods involved include cow's milk, peanuts, eggs, shellfish, fish, tree nuts, soy, wheat, and sesame. The common allergies vary depending on the country. Risk factors include a family history of allergies, vitamin D deficiency, obesity, and high levels of cleanliness. Allergies occur when immunoglobulin E (IgE), part of the body's immune system, binds to food molecules. A protein in the food is usually the problem. This triggers the release of inflammatory chemicals such as histamine. Diagnosis is usually based o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megavitamin Therapy
Megavitamin therapy is the use of large doses of vitamins, often many times greater than the recommended dietary allowance (RDA) in the attempt to prevent or treat diseases. Megavitamin therapy is typically used in alternative medicine by practitioners who call their approach orthomolecular medicine. Vitamins are useful in preventing and treating illnesses specifically associated with dietary vitamin shortfalls, but the conclusions of medical research are that the broad claims of disease treatment by advocates of megavitamin therapy are unsubstantiated by the available evidence. It is generally accepted that doses of any vitamin greatly in excess of nutritional requirements will result either in toxicity (vitamins A and D) or in the excess simply being metabolised; thus evidence in favour of vitamin supplementation supports only doses in the normal range. Critics have described some aspects of orthomolecular medicine as food faddism or even quackery. A short summary is ithe journal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |