|
Organopalladium Chemistry
Organopalladium chemistry is a branch of organometallic chemistry that deals with organic palladium compounds and their reactions. Palladium is often used as a catalyst in the reduction of alkenes and alkynes with hydrogen. This process involves the formation of a palladium-carbon covalent bond. Palladium is also prominent in carbon-carbon coupling reactions, as demonstrated in tandem reactions. Organopalladium chemistry timeline * 1873 - A. N. Zaitsev reports reduction of benzophenone over palladium with hydrogen. * 1894 - Phillips reports that palladium(II) chloride reduces to palladium metal by contact with ethylene. * 1907 - Autoclave technology introduced by Vladimir Ipatieff makes it possible to carry out high pressure hydrogenation. * 1956 - In the Wacker process ethylene and oxygen react to acetaldehyde with catalyst PdCl2/CuCl2 * 1957 - Tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0) is reported by Malatesta and Angoletta. * 1972 - The Heck reaction is a coupling react ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organometallic Chemistry
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide (metal carbonyls), cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term " metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are repres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heck Reaction
The Heck reaction (also called the Mizoroki–Heck reaction) is the chemical reaction of an unsaturated halide (or triflate) with an alkene in the presence of a base and a palladium catalyst (or palladium nanomaterial-based catalyst) to form a substituted alkene. It is named after Tsutomu Mizoroki and Richard F. Heck. Heck was awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, which he shared with Ei-ichi Negishi and Akira Suzuki, for the discovery and development of this reaction. This reaction was the first example of a carbon-carbon bond-forming reaction that followed a Pd(0)/Pd(II) catalytic cycle, the same catalytic cycle that is seen in other Pd(0)-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions. The Heck reaction is a way to substitute alkenes. History The original reaction by Tsutomu Mizoroki (1971) describes the coupling between iodobenzene and styrene in methanol to form stilbene at 120 °C (autoclave) with potassium acetate base and palladium chloride catalysis. This work was an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Metal Allyl Complex
Transition-metal allyl complexes are coordination complexes with allyl and its derivatives as ligands. Allyl is the radical with the connectivity CH2CHCH2, although as a ligand it is usually viewed as an allyl anion CH2=CH−CH2−, which is usually described as two equivalent resonance structures. Examples The allyl ligand is commonly found in organometallic chemistry. Most commonly, allyl ligands bind to metals via all three carbon atoms, the η3-binding mode. The η3-allyl group is classified as an LX-type ligand in the Green LXZ ligand classification scheme, serving as a 3e– donor using neutral electron counting and 4e– donor using ionic electron counting. More common are complexes with allyl and other ligands. Examples include (η3-allyl)Mn(CO)4 and CpPd(allyl). Homoleptic complexes * bis(allyl)nickel * bis(allyl)palladium * bis(allyl)platinum *tris(allyl)chromium * tris(allyl)rhodium * tris(allyl)iridium Synthetic methods Allyl complexes are often generated by ox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
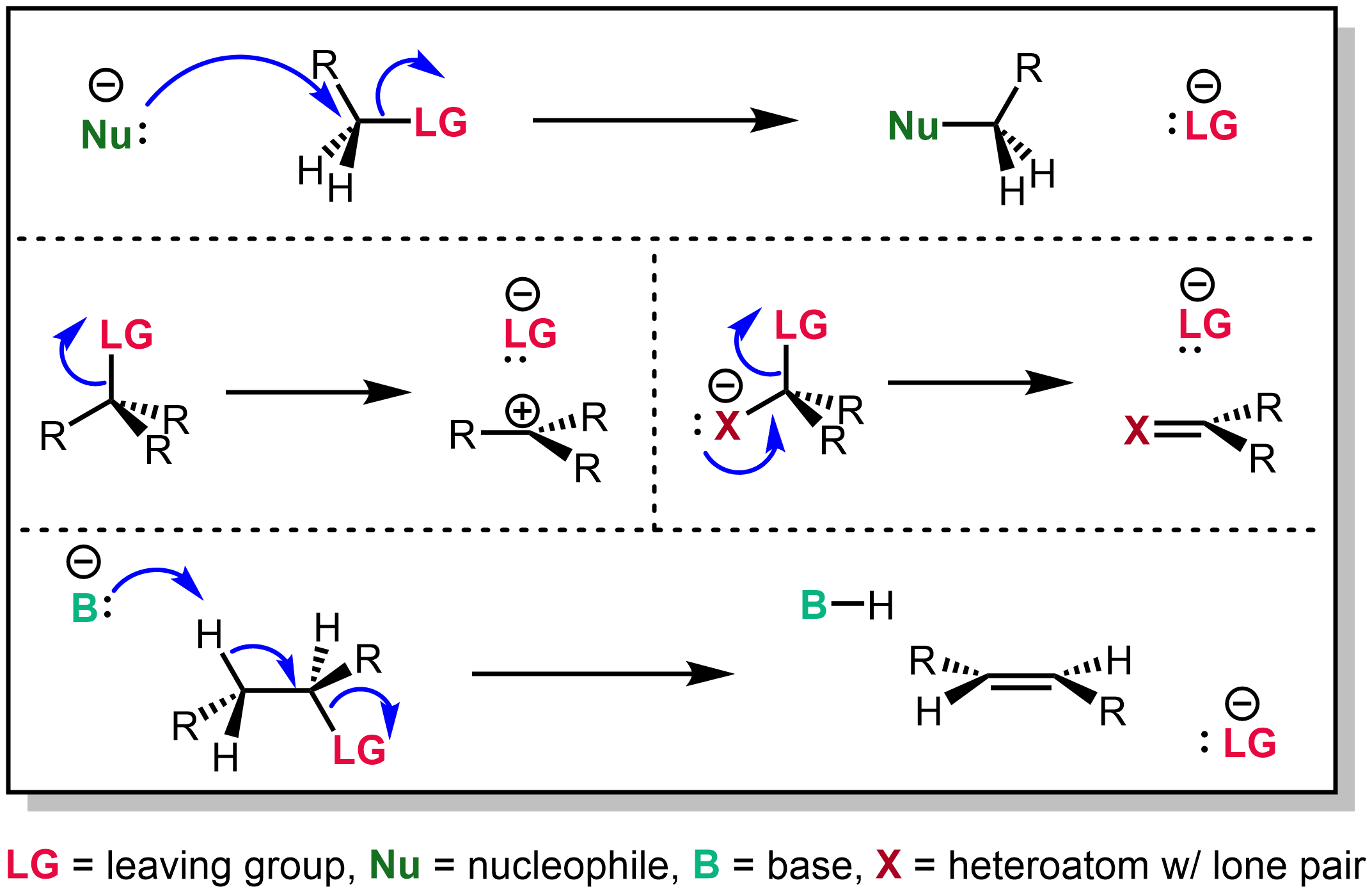
Leaving Group
In chemistry, a leaving group is defined by the IUPAC as an atom or group of atoms that detaches from the main or residual part of a substrate during a reaction or elementary step of a reaction. However, in common usage, the term is often limited to a fragment that departs with a pair of electrons in heterolytic bond cleavage. In this usage, a leaving group is a less formal but more commonly used synonym of the term '' nucleofuge''. In this context, leaving groups are generally anions or neutral species, departing from a neutral or cationic substrates, respectively, though in rare cases, cations leaving from a dicationic substrate are also known. A species' ability to serve as a leaving group depends on its ability to stabilize the additional electron density that results from bond heterolysis. Common anionic leaving groups are halides such as Cl−, Br−, and I−, and sulfonate esters such as tosylate (TsO−), while water (H2O), alcohols (HOR), and amines (R3N) are common neutr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
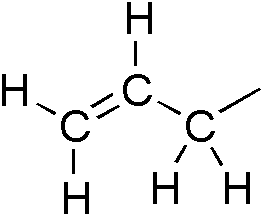
Allyl
In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula , where R is the rest of the molecule. It consists of a methylene bridge () attached to a vinyl group (). The name is derived from the scientific name for garlic, . In 1844, Theodor Wertheim isolated an allyl derivative from garlic oil and named it "". The term allyl applies to many compounds related to , some of which are of practical or of everyday importance, for example, allyl chloride. Allylation is any chemical reaction that adds an allyl group to a substrate. Nomenclature A site adjacent to the unsaturated carbon atom is called the allylic position or allylic site. A group attached at this site is sometimes described as allylic. Thus, "has an allylic hydroxyl group". Allylic C−H bonds are about 15% weaker than the C−H bonds in ordinary sp3 carbon centers and are thus more reactive. Benzylic and allylic are related in terms of structure, bond strength, and reactivity. Other re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allylpalladium Chloride Dimer
Allylpalladium(II) chloride dimer (APC) is a chemical compound with the formula η3-C3H5)PdCl">hapticity.html" ;"title="hapticity">η3-C3H5)PdClsub>2. This yellow air-stable compound is an important catalyst used in organic synthesis.Tatsuno, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Otsuka, S. "(η3-allyl)palladium(II) Complexes" Inorganic Syntheses, 1990, volume 28, pages 342-345. It is one of the most widely used transition metal allyl complexes. Structure The compound has a dimeric structure that is centrosymmetric. Each allyl group lies in a plane at an angle of about 111.5° to the square formed by the palladium and carbon atoms, and the Pd–C distances are all equal. Its unit cell is monoclinic. Synthesis The compound is prepared by purging carbon monoxide through a methanolic aqueous solution of sodium tetrachloropalladate (prepared from palladium(II) chloride and sodium chloride), and allyl chloride. :2 Na2PdCl4 + 2 CH2=CHCH2Cl + 2 CO + & ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decarboxylation
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide (CO2). Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. The reverse process, which is the first chemical step in photosynthesis, is called carboxylation, the addition of CO2 to a compound. Enzymes that catalyze decarboxylations are called decarboxylases or, the more formal term, carboxy-lyases (Enzyme Commission number, EC number 4.1.1). In organic chemistry The term "decarboxylation" usually means replacement of a carboxyl group () with a hydrogen atom: :RCO2H -> RH + CO2 Decarboxylation is one of the oldest known organic reactions. It is one of the processes assumed to accompany pyrolysis and destructive distillation. Metal salts, especially copper compounds, facilitate the reaction via the intermediacy of metal carboxylate complexes. Decarboxylation of aryl carboxylates can generate the equivalent of the correspond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
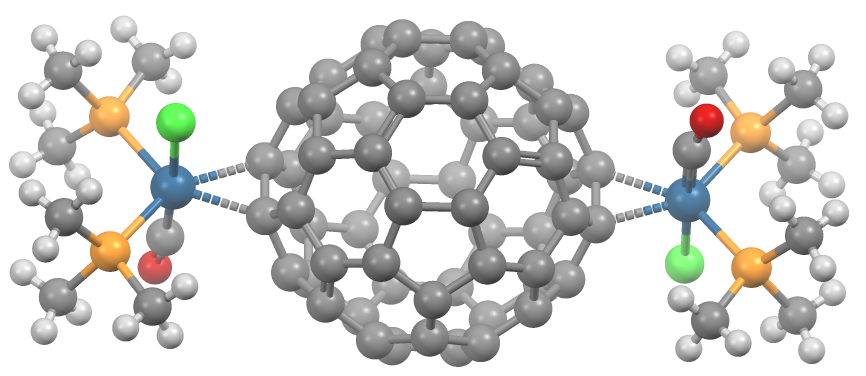
Fullerene Ligands
A transition metal fullerene complex is a coordination complex wherein fullerene serves as a ligand. Fullerenes are typically spheroidal carbon compounds, the most prevalent being buckminsterfullerene, C60. One year after it was prepared in milligram quantities in 1990, C60 was shown to function as a ligand in the complex h3Psub>2Pt(η2-C60). Since this report, a variety of transition metals and binding modes were demonstrated. Most transition metal fullerene complex are derived from C60, although other fullerenes also coordinate to metals as seen with C70Rh(H)(CO)(PPh3)2. Binding modes As ligands, fullerenes behave similarly to electron-deficient alkenes such as tetracyanoethylene. Thus, their complexes are a subset of metal-alkene complexes. They almost always coordinate in a dihapto fashion and prefer electron-rich metal centers.Spessard, p. 162 This binding occurs on the junction of two 6-membered rings. Hexahapto and pentahapto bonding is rarely observed.Spessard, p. 165 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichloro(1,5‐cyclooctadiene)palladium
Dichloro(1,5-cyclooctadiene)palladium is the organopalladium compound with the formula PdCl2(C8H12) where C8H12 is cycloocta-1,5-diene (cod) or abbreviated PdCl2(cod). It is a yellow solid that is soluble in chloroform. According to X-ray crystallography, the Pd center is square planar.{{cite journal, journal=Acta Crystallogr. C, year=1993, volume=49, pages=1766–1767, title=The Pbca polymorph of dichloro(η4-1,5-cyclooctadiene)palladium(II), author1=R. Kumar, author2=A. W. Maverick, author3=F. R. Fronczek, author4=J. R. Doyle, author5=N. C. Baenziger, author6=M. A. M. Howells, issue=10 , doi=10.1107/S0108270193003889, doi-access=free See also *Dichloro(cycloocta-1,5-diene)platinum(II) Dichloro(1,5-cyclooctadiene)platinum(II) (Pt(cod)Cl2) is an organometallic compound of platinum. This colourless solid is an entry point to other platinum compounds through the displacement of the cod and/or chloride ligands. It is one of several ... References Palladium compounds Homogeneo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PdCl2(cod)sample
Palladium(II) chloride, also known as palladium dichloride and palladous chloride, are the chemical compounds with the formula PdCl2. PdCl2 is a common starting material in palladium chemistry – palladium-based catalysts are of particular value in organic synthesis. It is prepared by the reaction of chlorine with palladium metal at high temperatures. Structure Two forms of PdCl2 are known, denoted α and β. In both forms, the palladium centres adopt a square-planar coordination geometry that is characteristic of Pd(II). Furthermore, in both forms, the Pd(II) centers are linked by μ2-chloride bridges. The α-form of PdCl2 is a polymer, consisting of "infinite" slabs or chains. The β-form of PdCl2 is molecular, consisting of an octahedral cluster of six Pd atoms. Each of the twelve edges of this octahedron is spanned by Cl−. PtCl2 adopts similar structures, whereas NiCl2 adopts the CdCl2 motif, featuring hexacoordinated Ni(II). Two further polymorphs, γ-PdCl2 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
sample.jpg)




-chloride-xtal-3D-balls.png)