|
Organisms At High Altitude
Organisms can live at high altitude, either on land, in water, or while flying. Decreased oxygen availability and decreased temperature make life at such altitudes challenging, though many species have been successfully adapted via considerable physiological changes. As opposed to short-term acclimatisation (immediate physiological response to changing environment), high-altitude adaptation means irreversible, evolved physiological responses to high-altitude environments, associated with heritable behavioural and genetic changes. Among animals, only few mammals (such as yaks, ibexes, Tibetan gazelles, vicunas, llamas, mountain goats, etc.) and certain birds are known to have completely adapted to high-altitude environments. Human populations such as some Tibetans, South Americans and Ethiopians live in the otherwise uninhabitable high mountains of the Himalayas, Andes and Ethiopian Highlands respectively. The adaptation of humans to high altitude is an example of natural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People Of Ethiopia
Ethiopians are the native inhabitants of Ethiopia, as well as the global diaspora of Ethiopia. Ethiopians constitute several component ethnic groups, many of which are closely related to ethnic groups in neighboring Eritrea and other parts of the Horn of Africa. The first documented use of the name "Ethiopia" from Greek name "Αἰθίοψ" (Ethiopian) was in the 4th century during the reign of Aksumite king Ezana. There were three ethnolinguistic groups in the Kingdom of Aksum; Semitic, Cushitic, and Nilo-Saharan (ancestors of the modern-day Kunama and Nara). The Kingdom of Aksum remained a geopolitically influential entity until the pillage of its capital — also named Axum — in the 10th century by Queen Gudit. Nevertheless, the core Aksumite civilization was preserved and continued into the successive Zagwe dynasty. By this time, new ethnic groups emerged – the Tigrayans and Amharas. During the Solomonic period, the latter established major political and cultural i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
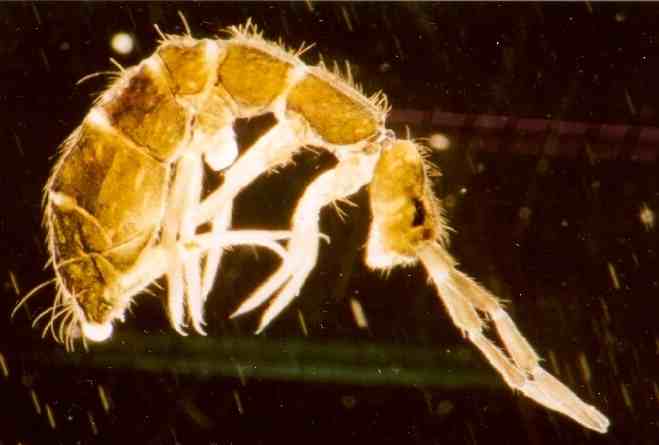
Springtail
Springtails (Collembola) form the largest of the three lineages of modern hexapods that are no longer considered insects (the other two are the Protura and Diplura). Although the three orders are sometimes grouped together in a class called Entognatha because they have internal mouthparts, they do not appear to be any more closely related to one another than they are to all insects, which have external mouthparts. Collembolans are omnivorous, free-living organisms that prefer moist conditions. They do not directly engage in the decomposition of organic matter, but contribute to it indirectly through the fragmentation of organic matter and the control of soil microbial communities. The word ''Collembola'' is from the ancient Greek "glue" and "peg"; this name was given due to the existence of the collophore, which was previously thought to stick to surfaces to stabilize the creature. Some DNA sequence studies suggest that Collembola represent a separate evolutionary line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euophrys Omnisuperstes
''Euophrys omnisuperstes'' (the species name means ''standing above everything''), the Himalayan jumping spider, is a small and toxic jumping spider that lives at elevations of up to in the Himalayas, including Mount Everest, making it a candidate for the highest known permanent resident on Earth. They are found among rocky debris, feeding on tiny, stray springtails and flies. Discovery In 1924, Richard Hingston was the naturalist on the British expedition to Mount Everest. In 1925, he reported that spiders had been observed living permanently in rocky areas surrounded by snow and ice at , about above the highest plant growth. His observation that "for food they eat one another" was later described as a "self-defeating notion" and helped to support the view that the spiders had been blown there and were not permanent residents. In 1954, Lawrence W. Swan joined an American expedition to Makalu in the Himalayas, and re-discovered the jumping spiders that Hingston had obser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |