|
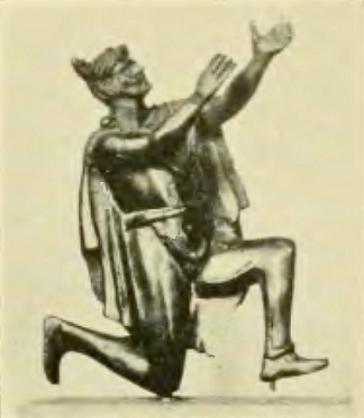
Orans
Orans, a loanword from Medieval Latin ''orans'' () translated as "one who is praying or pleading", also orant or orante, as well as lifting up holy hands, is a posture or attitude (art), bodily attitude of prayer, usually standing, with the elbows close to the sides of the body and with the hands outstretched sideways, palms up. The orans posture of prayer has a Scriptural basis in 1 Timothy 2 (): "I desire, then, that in every place the men should pray, lifting up holy hands without anger or argument" (NRSV). It was common in early Christianity and can frequently be seen in early Christian art, being advised by several early Church Fathers, who saw it as "the outline of the cross". In modern times, the orans position is still preserved in Oriental Orthodoxy, as when Coptic Christian believers pray the seven canonical hours of the Agpeya at fixed prayer times. The orans also occurs within parts of the Catholic, Oriental Orthodox, Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox, Luther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Prayer
File:Prayers-collage.png, 300px, alt=Collage of various religionists praying – Clickable Image, Collage of various religionists praying ''(Clickable image – use cursor to identify.)'' rect 0 0 1000 1000 Shinto festivalgoer praying in front of the Tagata fertility shrine rect 1000 0 2000 1000 Balinese Hindu bride praying during a traditional wedding ceremony rect 2000 0 3000 1000 Muslim pilgrim praying at the Masjid al-Haram rect 0 1000 1000 2000 Catholic Trappist monk praying before a crucifix rect 1000 1000 2000 2000 Ethiopian priest praying in Lalibela rect 2000 1000 3000 2000 Buddhists praying in Leh rect 0 2000 1000 3000 Sikh praying in Front of the Golden Temple in Amritsar rect 1000 2000 2000 3000 Members of the Mengjia Longshan Temple Association gather for a traditional Chinese prayer service rect 2000 2000 3000 3000 Jewish people praying at the Western Wall Prayer is an invocation or act that seeks to activate a rapport with an object of worship through d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Noah Catacombe
Noah (; , also Noach) appears as the last of the Antediluvian patriarchs in the traditions of Abrahamic religions. His story appears in the Hebrew Bible (Book of Genesis, chapters 5–9), the Quran and Baha'i writings, and extracanonically. The Genesis flood narrative is among the best-known stories of the Bible. In this account, God "regrets" making mankind because they filled the world with evil. Noah then labors faithfully to build the Ark at God's command, ultimately saving not only his own family, but mankind itself and all land animals, from extinction during the Flood. Afterwards, God makes a covenant with Noah and promises never again to destroy the earth with a flood. Noah is also portrayed as a "tiller of the soil" who is the first to cultivate the vine. After the flood, God commands Noah and his sons to "be fruitful, and multiply, and replenish the earth." The story of Noah in the Pentateuch is similar to the flood narrative in the Mesopotamian ''Epic of Gilgames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Charismatic Movement
The charismatic movement in Christianity is a movement within established or mainstream denominations to adopt beliefs and practices of Charismatic Christianity, with an emphasis on baptism with the Holy Spirit, and the use of spiritual gifts (''charismata''). It has affected most denominations in the United States, and has spread widely across the world. The movement is deemed to have begun in 1960 in Anglicanism ( Episcopal Church) and spread to other mainstream Protestant denominations, including American Protestant both Lutherans and Presbyterians by 1962, and to Roman Catholicism by 1967. Methodists became involved in the charismatic movement in the 1970s. The movement was not initially influential in evangelical churches. Although this changed in the 1980s in the so-called Third Wave, the charismatic movement was often expressed in the formation of separate evangelical churches such as the Vineyard Movement—neo-charismatic organisations that mirrored the establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Crucifix
A crucifix (from the Latin meaning '(one) fixed to a cross') is a cross with an image of Jesus on it, as distinct from a bare cross. The representation of Jesus himself on the cross is referred to in English as the (Latin for 'body'). The crucifix emphasizes Jesus' sacrifice, including his death by crucifixion, which Christians believe brought about the redemption of mankind. Most crucifixes portray Jesus on a Latin cross, rather than a Tau cross or a Coptic cross. The crucifix is a principal symbol for many groups of Christians, and one of the most common forms of the Crucifixion in the arts. It is especially important in the Catholic Church, and is also used in the Lutheran Churches, Anglican Churches, Eastern Orthodox Church, and in most Oriental Orthodox Churches (except the Armenian Church and Syriac Church). The symbol is less common in churches of other Protestant denominations, and in the Assyrian Church of the East and Armenian Apostolic Church, which prefer to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tertullian
Tertullian (; ; 155 – 220 AD) was a prolific Early Christianity, early Christian author from Roman Carthage, Carthage in the Africa (Roman province), Roman province of Africa. He was the first Christian author to produce an extensive corpus of Latin literature, Latin Christian literature and was an early Christian apologetics, Christian apologist and a polemicist against Heresy in Christianity, heresy, including contemporary Christian Gnosticism. Tertullian was the first theologian to write in Latin, and so has been called "the father of Latin Christianity", as well as "History of Christian theology, the founder of Western theology". He is perhaps most famous for being the first writer in Latin known to use the term ''trinity'' (Latin: ''trinitas''). Tertullian originated new theological concepts and advanced the development of early Church doctrine. However, some of his teachings, such as the Subordinationism, subordination of God the Son, the Son and Holy Spirit in C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Clement Of Alexandria
Titus Flavius Clemens, also known as Clement of Alexandria (; – ), was a Christian theology, Christian theologian and philosopher who taught at the Catechetical School of Alexandria. Among his pupils were Origen and Alexander of Jerusalem. A convert to Christianity, he was an educated man who was familiar with Ancient Greek philosophy, classical Greek philosophy and Ancient Greek literature, literature. As his three major works demonstrate, Clement was influenced by Hellenistic philosophy to a greater extent than any other Christian thinker of his time, and in particular, by Plato and the Stoicism, Stoics. His secret works, which exist only in fragments, suggest that he was familiar with pre-Christian Judaism, Jewish esotericism and Gnosticism as well. In one of his works he argued that Greek philosophy had its origin among non-Greeks, claiming that both Plato and Pythagoras were taught by Egyptian scholars. Clement is usually regarded as a Church Father. He is venerated as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Clement Of Rome
Clement of Rome (; ; died ), also known as Pope Clement I, was the Pope, Bishop of Rome in the Christianity in the 1st century, late first century AD. He is considered to be the first of the Apostolic Fathers of the Church. Little is known about Clement's life. Tertullian claimed that Clement was ordained by Saint Peter. Early church lists place him as the second or third bishop of Rome. Eusebius, in his book ''Ecclesiastical History (Eusebius), Church History'' mentioned Clement as the third bishop of Rome and as the "co-laborer" of Paul the Apostle, Paul. In Against Heresies (Irenaeus), Against Heresies, Irenaeus described Clement as the successor to Pope Anacletus, Anacletus, who was the third bishop of Rome, and as a personal acquaintance of the Apostles in the New Testament, Apostles. According to the ''Annuario Pontificio'', Clement was the fourth bishop of Rome, holding office at the very end of the 1st century. It is likely that Clement died in exile, and was possibly mart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Marcus Minucius Felix
__NOTOC__ Marcus Minucius Felix (died c. 250 AD in Rome) was one of the earliest of the Latin apologists for Christianity. Nothing is known of his personal history, and even the date at which he wrote can be only approximately ascertained as between AD 150 and 270. Jerome's '' De Viris Illustribus'' No. 58 speaks of him as "''Romae insignis causidicus''" ne of Rome's notable solicitors but in that he is probably only improving on the expression of Lactantius who speaks of him as "''non ignobilis inter causidicos loci''" ot unknown among solicitors of the place Octavius He is now exclusively known by his '' Octavius'', a dialogue on Christianity between the pagan Caecilius Natalis and the Christian Octavius Januarius. Written for educated non-Christians, the arguments are borrowed chiefly from Cicero, especially his ''De natura deorum'' ("Concerning the Nature of the Gods"), and Christian material, mainly from the Greek Apologists. The ''Octavius'' is admittedly earlier than C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Second Temple Judaism
Second Temple Judaism is the Judaism, Jewish religion as it developed during the Second Temple period, which began with the construction of the Second Temple around 516 BCE and ended with the Siege of Jerusalem (70 CE), destruction of Jerusalem in 70CE. This period was marked by the emergence of multiple religious currents as well as extensive cultural, religious, and political developments among Jews. It saw the progression of the development of the Hebrew Bible canon, Hebrew Bible canon, the synagogue, and Jewish eschatology. Additionally, the Early Christianity, rise of Christianity began in the final years of the Second Temple period. According to Jewish tradition, Prophets in Judaism, authentic prophecy (, ) ceased during the early years of the Second Temple period; this left Jews without their version of divine guidance at a time when they felt most in need of support and direction. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Book Of Psalms
The Book of Psalms ( , ; ; ; ; , in Islam also called Zabur, ), also known as the Psalter, is the first book of the third section of the Tanakh (Hebrew Bible) called ('Writings'), and a book of the Old Testament. The book is an anthology of Hebrew religious hymns. In the Jewish and Western Christian traditions, there are 150 psalms, and several more in the Eastern Christian churches. The book is divided into five sections, each ending with a doxology, a hymn of praise. There are several types of psalms, including hymns or songs of praise, communal and individual laments, royal psalms, imprecation, and individual thanksgivings. The book also includes psalms of communal thanksgiving, wisdom, pilgrimage and other categories. Many of the psalms contain attributions to the name of King David and other Biblical figures including Asaph, the sons of Korah, Moses and Solomon. Davidic authorship of the Psalms is not accepted as historical fact by modern scholars, who view it a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Isaiah
Isaiah ( or ; , ''Yəšaʿyāhū'', "Yahweh is salvation"; also known as Isaias or Esaias from ) was the 8th-century BC Israelite prophet after whom the Book of Isaiah is named. The text of the Book of Isaiah refers to Isaiah as "the prophet", but the exact relationship between the Book of Isaiah and the actual prophet Isaiah is complicated. The traditional view is that all 66 chapters of the book of Isaiah were written by one man, Isaiah, possibly in two periods between 740 BC and 686 BC, separated by approximately 15 years. Another widely held view suggests that parts of the first half of the book (chapters 1–39) originated with the historical prophet, interspersed with prose commentaries written in the time of King Josiah 100 years later, and that the remainder of the book dates from immediately before and immediately after the end of the 6th-century BC exile in Babylon (almost two centuries after the time of the historical prophet), and that perhaps these later cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Old Testament
The Old Testament (OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible, or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew and occasionally Aramaic writings by the Israelites. The second division of Christian Bibles is the New Testament, written in Koine Greek. The Old Testament consists of many distinct books by various authors produced over a period of centuries. Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections: the first five books or Pentateuch (which corresponds to the Jewish Torah); the history books telling the history of the Israelites, from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon; the poetic and wisdom literature, which explore themes of human experience, morality, and divine justice; and the books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God. The Old Testament canon differs among Christian denominations. The Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |