|
Orangespotted Sunfish
The orangespotted sunfish (''Lepomis humilis'') is a North American species of freshwater fish in the sunfish family (Centrarchidae) of order Perciformes. These fish are widely distributed across the middle and eastern United States, from the Rocky Mountains to the east, from the Great Lakes south into the Gulf Coast. The orangespotted sunfish is ecologically unique and thrives in turbid, shallow systems that have few predators and low oxygen contents. The species prefers vegetated areas in sluggish backwaters or lakes, and can also be found in turbid rivers. The orangespotted sunfish can extend its range in lower-quality waters, which is not characteristic of other sunfish. Orangespotted sunfish vary in total length and age for different river basin originations, but can be found to live four to seven years, and recorded lengths are up to . Males make grunting noises to attract females to mate, and are known to nest in ‘colonies’ or aggregations. Spawning patterns are similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Frédéric Girard
Charles Frédéric Girard (8 March 1822 – 29 January 1895) was a French biologist specializing in ichthyology and herpetology. Born in Mulhouse, France, he studied at the College of Neuchâtel, Switzerland, as a student of Louis Agassiz. In 1847, he accompanied Agassiz as his assistant to Harvard University. Three years later, Spencer Fullerton Baird called him to the Smithsonian Institution to work on its growing collection of North American reptiles, amphibians and fishes. He worked at the museum for the next ten years and published numerous papers, many in collaboration with Baird. In 1854, he was naturalized as a U.S. citizen. Besides his work at the Smithsonian, he managed to earn an M.D. from Georgetown University in Washington, D.C. in 1856. In 1859 he returned to France and was awarded the Cuvier Prize by the Institute of France for his work on the North American reptiles and fishes two years later. When the American Civil War broke out, he joined the Confederate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay ( crj, text=ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, translit=Wînipekw; crl, text=ᐐᓂᐹᒄ, translit=Wînipâkw; iu, text=ᑲᖏᖅᓱᐊᓗᒃ ᐃᓗᐊ, translit=Kangiqsualuk ilua or iu, text=ᑕᓯᐅᔭᕐᔪᐊᖅ, translit=Tasiujarjuaq; french: baie d'Hudson), sometimes called Hudson's Bay (usually historically), is a large body of saltwater in northeastern Canada with a surface area of . It is located north of Ontario, west of Quebec, northeast of Manitoba and southeast of Nunavut, but politically entirely part of Nunavut. Although not geographically apparent, it is for climatic reasons considered to be a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It Hudson Bay drainage basin, drains a very large area, about , that includes parts of southeastern Nunavut, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Ontario, Quebec, all of Manitoba, and parts of the U.S. states of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota, and Montana. Hudson Bay's southern arm is called James Bay. The Cree language, Eastern Cree name for Hudson an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentation
Sedimentation is the deposition of sediments. It takes place when particles in suspension settle out of the fluid in which they are entrained and come to rest against a barrier. This is due to their motion through the fluid in response to the forces acting on them: these forces can be due to gravity, centrifugal acceleration, or electromagnetism. Settling is the falling of suspended particles through the liquid, whereas sedimentation is the final result of the settling process. In geology, sedimentation is the deposition of sediments which results in the formation of sedimentary rock. The term is broadly applied to the entire range of processes that result in the formation of sedimentary rock, from initial erosion through sediment transport and settling to the lithification of the sediments. However, the strict geological definition of sedimentation is the mechanical deposition of sediment particles from an initial suspension in air or water. Sedimentation may pertain to ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fyke
A fishing net is a net used for fishing. Nets are devices made from fibers woven in a grid-like structure. Some fishing nets are also called fish traps, for example fyke nets. Fishing nets are usually meshes formed by knotting a relatively thin thread. Early nets were woven from grasses, flaxes and other fibrous plant material. Later cotton was used. Modern nets are usually made of artificial polyamides like nylon, although nets of organic polyamides such as wool or silk thread were common until recently and are still used. History Fishing nets have been used widely in the past, including by stone age societies. The oldest known fishing net is the net of Antrea, found with other fishing equipment in the Karelian town of Antrea, Finland, in 1913. The net was made from willow, and dates back to 8300 BC. Recently, fishing net sinkers from 27,000 BC were discovered in Korea, making them the oldest fishing implements discovered, to date, in the world. The remnants of another fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrofishing
Electrofishing is a fishing technique that uses direct current electricity flowing between a submerged cathode and anode. This affects the movements of nearby fish so that they swim toward the anode, where they can be caught or stunned."FISHNET SHOCKINGS" . ''Toronto Star'', December 3, page IN3. Paul Hunter Electrofishing is a common scientific survey method used to sample fish populations to determine abundance, density and species composition. When performed correctly, electrofishing results in no permanent harm to the fish, which return to their natural mobility state in as little as two minutes after being caught. Method Electrofishing relies on two |
Floodplain Lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger oceans, they do form part of the Earth's water cycle. Lakes are distinct from lagoons, which are generally coastal parts of the ocean. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which also lie on land, though there are no official or scientific definitions. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams, which usually flow in a channel on land. Most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams. Natural lakes are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zones, and areas with ongoing glaciation. Other lakes are found in endorheic basins or along the courses of mature rivers, where a river channel has widened into a basin. Some parts of the world have many lakes formed by the chaotic drainage patterns left over from the last ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topeka Shiner
The Topeka shiner (''Notropis topeka'') is a North American species of cyprinid freshwater fish. The Topeka shiner is a type of minnow that does not grow longer than a few inches. This minnow is a shiny silver color its main physical characteristic is the black colored stripe that runs along the side of the body. It is distributed in the Mississippi River basin, from southern Minnesota and southeastern South Dakota south to central Missouri and southern Kansas. The Topeka shiner lives mainly in prairie streams. In order for the Topeka shiner to survive the water must be cold and clear. The streams in which this Minnow lives are typically consistent and run year long. In cases in which the stream does dry up, the Topeka Shiner needs to find a new stream or permanent body of water to survive. The Topeka shiner was listed as Endangered by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service in 1998. The species is endangered primarily because of the water quality need. This species relies on clea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepomis
''Lepomis'' or true sunfish is a genus of North American freshwater fish from the family Centrarchidae in the order Perciformes (perch-like fish). The generic name ''Lepomis'' derives from the Greek ("scale") and ("cover", "plug", " operculum"). The genus' most recognizable type species is perhaps the bluegill. Some ''Lepomis'' species can grow to a maximum overall length of , though most average around . Many species are sought by anglers as popular panfishes, and large numbers are bred and stocked in lakes, rivers, ponds and wetlands. They are widely distributed throughout the freshwater lakes and river tributaries of the United States and Canada, and several species have been translocated and flourished around the world, even becoming pests PESTS was an anonymous American activist group formed in 1986 to critique racism, tokenism, and exclusion in the art world. PESTS produced newsletters, posters, and other print material highlighting examples of discrimination in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
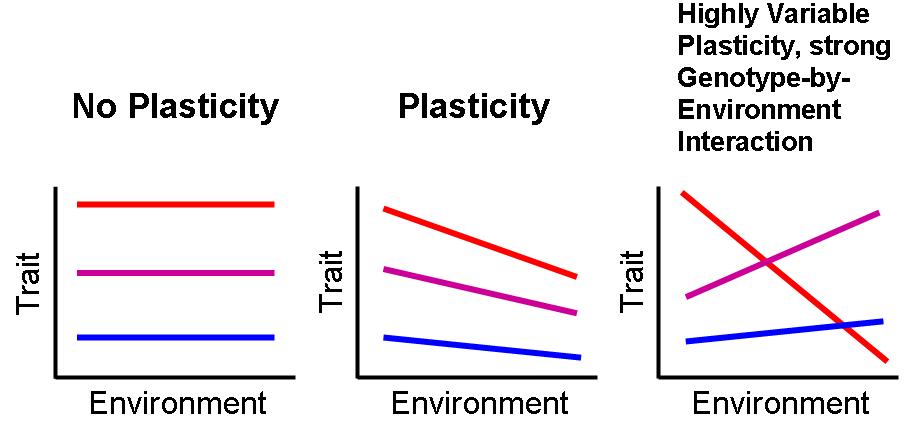
Phenotypic Plasticity
Phenotypic plasticity refers to some of the changes in an organism's behavior, morphology and physiology in response to a unique environment. Fundamental to the way in which organisms cope with environmental variation, phenotypic plasticity encompasses all types of environmentally induced changes (e.g. morphological, physiological, behavioural, phenological) that may or may not be permanent throughout an individual's lifespan. The term was originally used to describe developmental effects on morphological characters, but is now more broadly used to describe all phenotypic responses to environmental change, such as acclimation (acclimatization), as well as learning. The special case when differences in environment induce discrete phenotypes is termed polyphenism. Generally, phenotypic plasticity is more important for immobile organisms (e.g. plants) than mobile organisms (e.g. most animals), as mobile organisms can often move away from unfavourable environments. Nevertheless, mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by currents in the ocean, or by currents in seas, lakes or rivers. Zooplankton can be contrasted with phytoplankton, which are the plant component of the plankton community ("phyto" comes from the Greek word for ''plant''). Zooplankton are heterotrophic (other-feeding), whereas phytoplankton are autotrophic (self-feeding). This means zooplankton cannot manufacture their own food but must eat other plants or animals instead — in particular they eat phytoplankton. Zooplankton are generally larger than phytoplankton, most are microscopic, but some (such as jellyfish) are macroscopic and can be seen with the naked eye. Many protozoans (single-celled protists that prey on other microscopic life) are zooplankton, including zooflagellates, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
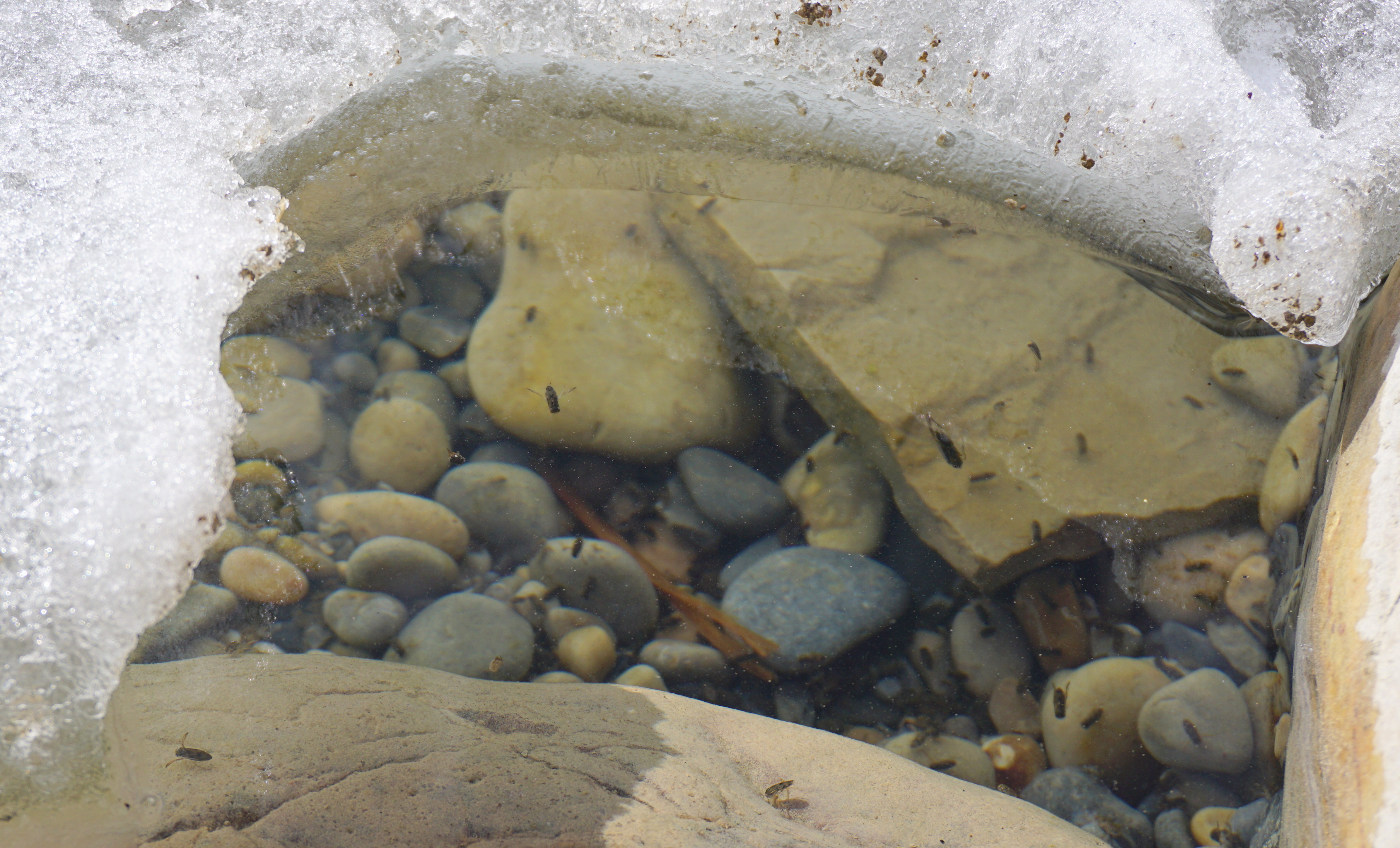
Chironomidae
The Chironomidae (informally known as chironomids, nonbiting midges, or lake flies) comprise a family of nematoceran flies with a global distribution. They are closely related to the Ceratopogonidae, Simuliidae, and Thaumaleidae. Many species superficially resemble mosquitoes, but they lack the wing scales and elongated mouthparts of the Culicidae. The name Chironomidae stems from the Ancient Greek word ''kheironómos'', "a pantomimist". Common names and biodiversity This is a large taxon of insects; some estimates of the species numbers suggest well over 10,000 world-wide. Males are easily recognized by their plumose antennae. Adults are known by a variety of vague and inconsistent common names, largely by confusion with other insects. For example, chironomids are known as "lake flies" in parts of Canada and Lake Winnebago, Wisconsin, but "bay flies" in the areas near the bay of Green Bay, Wisconsin. They are called "sand flies", "muckleheads", "muffleheads", "Canadian so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corixidae
Corixidae is a family of aquatic insects in the order Hemiptera. They are found worldwide in virtually any freshwater habitat and a few species live in saline water. There are about 500 known species worldwide, in 55 genera, including the genus '' Sigara''. Members of the Corixidae are commonly known as water boatmen, a term that is sometimes used in the United Kingdom for ''Notonecta glauca'', an insect of a different family, Notonectidae. ''Corixa punctata'' is the "lesser water boatman". Morphology and ecology Corixidae generally have a long flattened body ranging from long. Many have extremely fine dark brown or black striations marking the wings. They tend to have four long rear legs and two short front ones. The forelegs are covered with hairs and shaped like oars, hence the name "water boatman". Their four hindmost legs have scoop- or oar-shaped tarsi to aid swimming. They also have a triangular head with short, triangular mouthparts. Corixidae dwell in slow rivers and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)