|
Optical Mapping
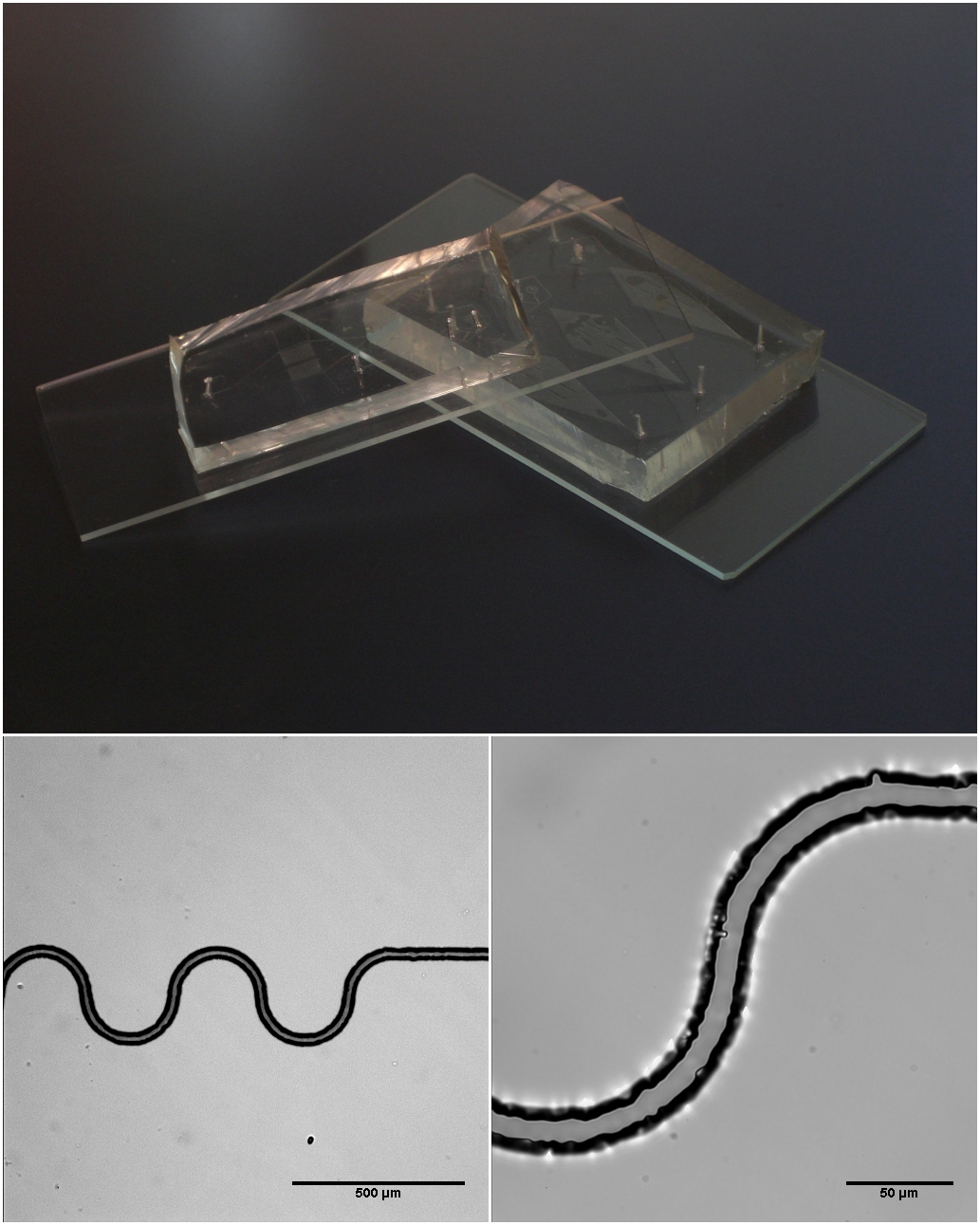
Optical mapping is a technique for constructing ordered, genome-wide, high-resolution restriction maps from single, stained molecules of DNA, called "optical maps". By mapping the location of restriction enzyme sites along the unknown DNA of an organism, the spectrum of resulting DNA fragments collectively serves as a unique "fingerprint" or "barcode" for that sequence. Originally developed by Dr. David C. Schwartz and his lab at NYU in the 1990s Schwartz, D. C., et al. "Ordered Restriction Maps of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Chromosomes Constructed by Optical Mapping." Science 262.5130 (1993): 110–4. this method has since been integral to the assembly process of many large-scale sequencing projects for both microbial and eukaryotic genomes. Later technologies use DNA melting, DNA competitive binding or enzymatic labelling in order to create the optical mappings. Technology The modern optical mapping platform works as follows:Dimalanta, E.T. ''et al.'' A microfluidic system for larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elsevier
Elsevier () is a Dutch academic publishing company specializing in scientific, technical, and medical content. Its products include journals such as ''The Lancet'', ''Cell'', the ScienceDirect collection of electronic journals, '' Trends'', the '' Current Opinion'' series, the online citation database Scopus, the SciVal tool for measuring research performance, the ClinicalKey search engine for clinicians, and the ClinicalPath evidence-based cancer care service. Elsevier's products and services also include digital tools for data management, instruction, research analytics and assessment. Elsevier is part of the RELX Group (known until 2015 as Reed Elsevier), a publicly traded company. According to RELX reports, in 2021 Elsevier published more than 600,000 articles annually in over 2,700 journals; as of 2018 its archives contained over 17 million documents and 40,000 e-books, with over one billion annual downloads. Researchers have criticized Elsevier for its high profit marg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Restriction Map
A restriction map is a map of known restriction sites within a sequence of DNA. Restriction mapping requires the use of restriction enzymes. In molecular biology, restriction maps are used as a reference to engineer plasmids or other relatively short pieces of DNA, and sometimes for longer genomic DNA. There are other ways of mapping features on DNA for longer length DNA molecules, such as mapping by transduction. One approach in constructing a restriction map of a DNA molecule is to sequence the whole molecule and to run the sequence through a computer program that will find the recognition sites that are present for every restriction enzyme known. Before sequencing was automated, it would have been prohibitively expensive to sequence an entire DNA strand. To find the relative positions of restriction sites on a plasmid, a technique involving single and double restriction digests is used. Based on the sizes of the resultant DNA fragments the positions of the sites can be infer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Mapping
Optical mapping is a technique for constructing ordered, genome-wide, high-resolution restriction maps from single, stained molecules of DNA, called "optical maps". By mapping the location of restriction enzyme sites along the unknown DNA of an organism, the spectrum of resulting DNA fragments collectively serves as a unique "fingerprint" or "barcode" for that sequence. Originally developed by Dr. David C. Schwartz and his lab at NYU in the 1990s Schwartz, D. C., et al. "Ordered Restriction Maps of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Chromosomes Constructed by Optical Mapping." Science 262.5130 (1993): 110–4. this method has since been integral to the assembly process of many large-scale sequencing projects for both microbial and eukaryotic genomes. Later technologies use DNA melting, DNA competitive binding or enzymatic labelling in order to create the optical mappings. Technology The modern optical mapping platform works as follows:Dimalanta, E.T. ''et al.'' A microfluidic system for larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microfluidic
Microfluidics refers to the behavior, precise control, and manipulation of fluids that are geometrically constrained to a small scale (typically sub-millimeter) at which surface forces dominate volumetric forces. It is a multidisciplinary field that involves engineering, physics, chemistry, biochemistry, nanotechnology, and biotechnology. It has practical applications in the design of systems that process low volumes of fluids to achieve multiplexing, automation, and high-throughput screening. Microfluidics emerged in the beginning of the 1980s and is used in the development of inkjet printheads, DNA chips, lab-on-a-chip technology, micro-propulsion, and micro-thermal technologies. Typically, micro means one of the following features: * Small volumes (μL, nL, pL, fL) * Small size * Low energy consumption * Microdomain effects Typically microfluidic systems transport, mix, separate, or otherwise process fluids. Various applications rely on passive fluid control using capillary for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Restriction Mapping
A restriction map is a map of known restriction sites within a sequence of DNA. Restriction mapping requires the use of restriction enzymes. In molecular biology, restriction maps are used as a reference to engineer plasmids or other relatively short pieces of DNA, and sometimes for longer genomic DNA. There are other ways of mapping features on DNA for longer length DNA molecules, such as mapping by transduction. One approach in constructing a restriction map of a DNA molecule is to sequence the whole molecule and to run the sequence through a computer program that will find the recognition sites that are present for every restriction enzyme known. Before sequencing was automated, it would have been prohibitively expensive to sequence an entire DNA strand. To find the relative positions of restriction sites on a plasmid, a technique involving single and double restriction digests is used. Based on the sizes of the resultant DNA fragments the positions of the sites can be infer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Microarrays
A DNA microarray (also commonly known as DNA chip or biochip) is a collection of microscopic DNA spots attached to a solid surface. Scientists use DNA microarrays to measure the expression levels of large numbers of genes simultaneously or to genotype multiple regions of a genome. Each DNA spot contains picomoles (10−12 moles) of a specific DNA sequence, known as '' probes'' (or ''reporters'' or '' oligos''). These can be a short section of a gene or other DNA element that are used to hybridize a cDNA or cRNA (also called anti-sense RNA) sample (called ''target'') under high-stringency conditions. Probe-target hybridization is usually detected and quantified by detection of fluorophore-, silver-, or chemiluminescence-labeled targets to determine relative abundance of nucleic acid sequences in the target. The original nucleic acid arrays were macro arrays approximately 9 cm × 12 cm and the first computerized image based analysis was published in 1981. It was inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulsed Field Gel Electrophoresis
Pulsed field gel electrophoresis is a technique used for the separation of large DNA molecules by applying to a gel matrix an electric field that periodically changes direction. Historical background Standard gel electrophoresis techniques for separation of DNA molecules provided huge advantages for molecular biology research. However, it was unable to separate very large molecules of DNA effectively. DNA molecules larger than 15–20 kb migrating through a gel will essentially move together in a size-independent manner. At Columbia University in 1984, David C. Schwartz and Charles Cantor developed a variation on the standard protocol by introducing an alternating voltage gradient to improve the resolution of larger molecules. This technique became known as pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). The development of PFGE expanded the range of resolution for DNA fragments by as much as two orders of magnitude. Procedure The procedure for this technique is relatively similar to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytogenetics
Cytogenetics is essentially a branch of genetics, but is also a part of cell biology/cytology (a subdivision of human anatomy), that is concerned with how the chromosomes relate to cell behaviour, particularly to their behaviour during mitosis and meiosis. Techniques used include karyotyping, analysis of G-banded chromosomes, other cytogenetic banding techniques, as well as molecular cytogenetics such as fluorescent ''in situ'' hybridization (FISH) and comparative genomic hybridization (CGH). History Beginnings Chromosomes were first observed in plant cells by Carl Nägeli in 1842. Their behavior in animal (salamander) cells was described by Walther Flemming, the discoverer of mitosis, in 1882. The name was coined by another German anatomist, von Waldeyer in 1888. The next stage took place after the development of genetics in the early 20th century, when it was appreciated that the set of chromosomes (the karyotype) was the carrier of the genes. Levitsky seems to have been t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paired-end Tag
Paired-end tags (PET) (sometimes "Paired-End diTags", or simply "ditags") are the short sequences at the 5’ and 3' ends of a DNA fragment which are unique enough that they (theoretically) exist together only once in a genome, therefore making the sequence of the DNA in between them available upon search (if full-genome sequence data is available) or upon further sequencing (since tag sites are unique enough to serve as primer annealing sites). Paired-end tags (PET) exist in PET libraries with the intervening DNA absent, that is, a PET "represents" a larger fragment of genomic or cDNA by consisting of a short 5' linker sequence, a short 5' sequence tag, a short 3' sequence tag, and a short 3' linker sequence. It was shown conceptually that 13 base pairs are sufficient to map tags uniquely.Fullwood MJ, Wei CL, Liu ET, Ruan Y. 2009. Next-Generation DNA sequencing of paired-end tags (PET) for transcriptome and genome analyses. Genome Research. 19:521–532. {{PMID, 19339662 However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SMRT Sequencing
Single-molecule real-time (SMRT) sequencing is a parallelized single molecule DNA sequencing method. Single-molecule real-time sequencing utilizes a zero-mode waveguide (ZMW). A single DNA polymerase enzyme is affixed at the bottom of a ZMW with a single molecule of DNA as a template. The ZMW is a structure that creates an illuminated observation volume that is small enough to observe only a single nucleotide of DNA being incorporated by DNA polymerase. Each of the four DNA bases is attached to one of four different fluorescent dyes. When a nucleotide is incorporated by the DNA polymerase, the fluorescent tag is cleaved off and diffuses out of the observation area of the ZMW where its fluorescence is no longer observable. A detector detects the fluorescent signal of the nucleotide incorporation, and the base call is made according to the corresponding fluorescence of the dye. Technology The DNA sequencing is done on a chip that contains many ZMWs. Inside each ZMW, a single active ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescence Microscopy
A fluorescence microscope is an optical microscope that uses fluorescence instead of, or in addition to, scattering, reflection, and attenuation or absorption, to study the properties of organic or inorganic substances. "Fluorescence microscope" refers to any microscope that uses fluorescence to generate an image, whether it is a simple set up like an epifluorescence microscope or a more complicated design such as a confocal microscope, which uses optical sectioning to get better resolution of the fluorescence image. Principle The specimen is illuminated with light of a specific wavelength (or wavelengths) which is absorbed by the fluorophores, causing them to emit light of longer wavelengths (i.e., of a different color than the absorbed light). The illumination light is separated from the much weaker emitted fluorescence through the use of a spectral emission filter. Typical components of a fluorescence microscope are a light source (xenon arc lamp or mercury-vapor lamp are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Cycle
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the classical electromagnetic description of light. Complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are, however, often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive model of light, which includes wave effects such as diffraction and interference that cannot be acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |