|
Optical Instrument
An optical instrument (or "optic" for short) is a device that processes light waves (or photons), either to enhance an image for viewing or to analyze and determine their characteristic properties. Common examples include periscopes, microscopes, telescopes, and cameras. Image enhancement The first optical instruments were telescopes used for magnification of distant images, and microscopes used for magnifying very tiny images. Since the days of Galileo and Van Leeuwenhoek, these instruments have been greatly improved and extended into other portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. The binocular device is a generally compact instrument for both eyes designed for mobile use. A camera could be considered a type of optical instrument, with the pinhole camera and camera obscura being very simple examples of such devices. Analysis Another class of optical instrument is used to analyze the properties of light or optical materials. They include: *Interferometer for measuring th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertometer
A lensmeter or lensometer (sometimes even known as focimeter or vertometer), is an ophthalmic instrument. It is mainly used by optometrists and opticians to measure the back or front vertex power of a spectacle lens and verify the correct prescription in a pair of eyeglasses, to properly orient and mark uncut lenses, and to confirm the correct mounting of lenses in spectacle frames. Lensmeters can also verify the power of contact lenses, if a special lens support is used. The parameters appraised by a lensmeter are the values specified by an ophthalmologist or optometrist on the patient's prescription: sphere, cylinder, axis, add, and in some cases, prism. The lensmeter is also used to check the accuracy of progressive lenses, and is often capable of marking the lens center and various other measurements critical to proper performance of the lens. It may also be used prior to an eye examination to obtain the last prescription the patient was given, in order to expedite the subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Devices England 1858
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the classical electromagnetic description of light. Complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are, however, often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive model of light, which includes wave effects such as diffraction and interference that cannot b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarimeter
A polarimeter is a scientific instrument used to measure the angle of rotation caused by passing polarized light through an optically active substance.Polarimeter kenyon.edu Some chemical substances are optically active, and polarized (uni-directional) light will rotate either to the left (counter-clockwise) or right (clockwise) when passed through these substances. The amount by which the light is rotated is known as the angle of rotation. The direction (clockwise or counterclockwise) and magnitude of the rotation reveals information about the sample's chiral properties such as the relative concentration of ena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Plasmon Resonance
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) is the resonant oscillation of conduction electrons at the interface between negative and positive permittivity material in a particle stimulated by incident light. SPR is the basis of many standard tools for measuring adsorption of material onto planar metal (typically gold or silver) surfaces or onto the surface of metal nanoparticles. It is the fundamental principle behind many color-based biosensor applications and lab-on-a-chip sensors. It should be stressed that SPR is not a resonance on the planar surface and it is a polariton or surface-wave like phenomenon. Explanation The surface plasmon polariton is a non-radiative electromagnetic surface wave that propagates in a direction parallel to the negative permittivity/dielectric material interface. Since the wave is on the boundary of the conductor and the external medium (air, water or vacuum for example), these oscillations are very sensitive to any change of this boundary, such as the adso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
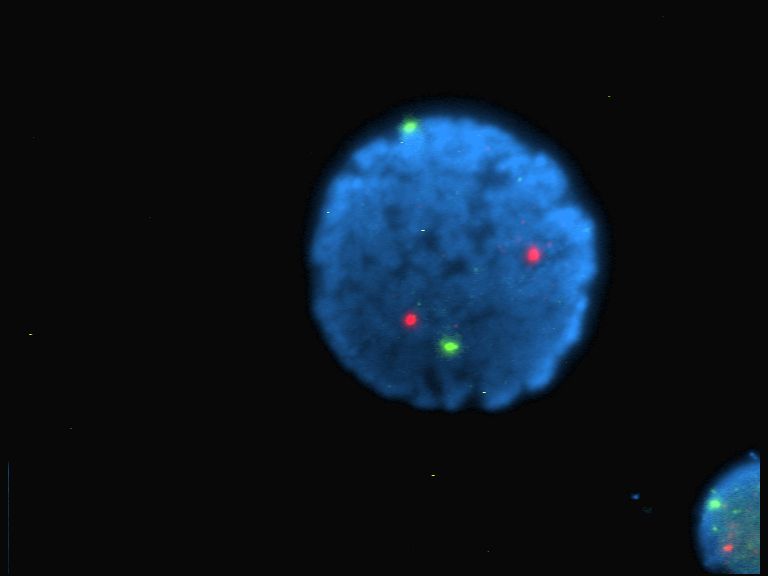
Fluorochrome
A fluorophore (or fluorochrome, similarly to a chromophore) is a fluorescent chemical compound that can re-emit light upon light excitation. Fluorophores typically contain several combined aromatic groups, or planar or cyclic molecules with several π bonds. Fluorophores are sometimes used alone, as a tracer in fluids, as a dye for staining of certain structures, as a substrate of enzymes, or as a probe or indicator (when its fluorescence is affected by environmental aspects such as polarity or ions). More generally they are covalently bonded to a macromolecule, serving as a marker (or dye, or tag, or reporter) for affine or bioactive reagents ( antibodies, peptides, nucleic acids). Fluorophores are notably used to stain tissues, cells, or materials in a variety of analytical methods, i.e., fluorescent imaging and spectroscopy. Fluorescein, via its amine-reactive isothiocyanate derivative fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), has been one of the most popular fluorophores. Fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Sequencer
A DNA sequencer is a scientific instrument used to automate the DNA sequencing process. Given a sample of DNA, a DNA sequencer is used to determine the order of the four bases: G (guanine), C (cytosine), A ( adenine) and T (thymine). This is then reported as a text string, called a read. Some DNA sequencers can be also considered optical instruments as they analyze light signals originating from fluorochromes attached to nucleotides. The first automated DNA sequencer, invented by Lloyd M. Smith, was introduced by Applied Biosystems in 1987. It used the Sanger sequencing method, a technology which formed the basis of the "first generation" of DNA sequencers and enabled the completion of the human genome project in 2001. This first generation of DNA sequencers are essentially automated electrophoresis systems that detect the migration of labelled DNA fragments. Therefore, these sequencers can also be used in the genotyping of genetic markers where only the length of a DNA fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autocollimator
An autocollimator is an optical instrument for non-contact measurement of angles. They are typically used to align components and measure deflections in optical or mechanical systems. An autocollimator works by projecting an image onto a target mirror and measuring the deflection of the returned image against a scale, either visually or by means of an electronic detector. A visual autocollimator can measure angles as small as 1 arcsecond (4.85 microradians), while an electronic autocollimator can have up to 100 times more resolution. Visual autocollimators are often used for aligning laser rod ends and checking the face parallelism of optical windows and wedges. Electronic and digital autocollimators are used as angle measurement standards, for monitoring angular movement over long periods of time and for checking angular position repeatability in mechanical systems. Servo autocollimators are specialized compact forms of electronic autocollimators that are used in high-speed servo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
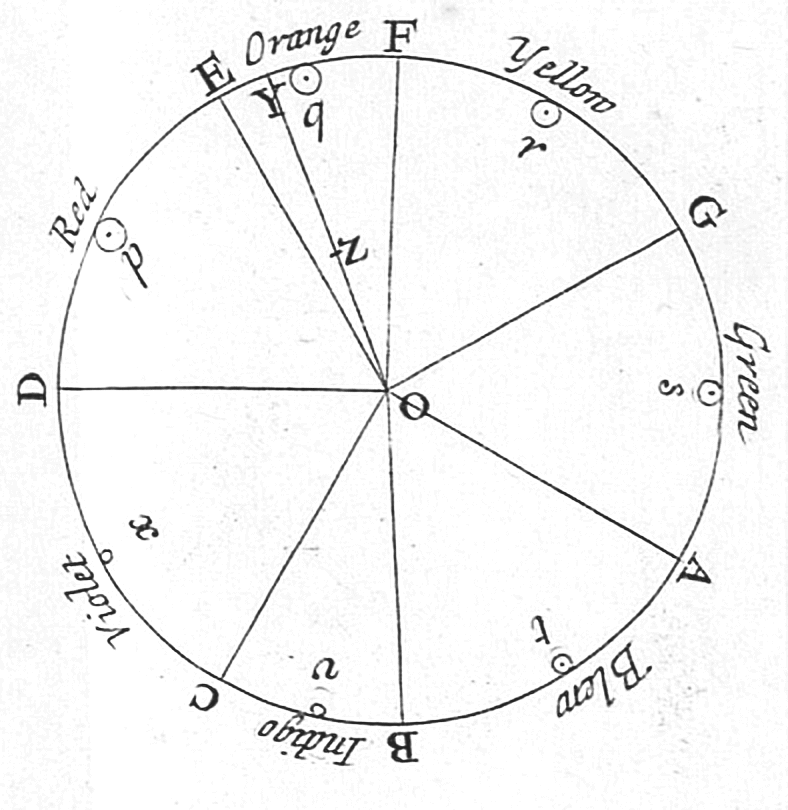
Visible Spectrum
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called ''visible light'' or simply light. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 380 to about 750 nanometers. In terms of frequency, this corresponds to a band in the vicinity of 400–790 terahertz. These boundaries are not sharply defined and may vary per individual. Under optimal conditions these limits of human perception can extend to 310 nm (ultraviolet) and 1100 nm ( near infrared). The optical spectrum is sometimes considered to be the same as the visible spectrum, but some authors define the term more broadly, to include the ultraviolet and infrared parts of the electromagnetic spectrum as well. The spectrum does not contain all the colors that the human visual system can distinguish. '' Unsaturated colors'' such as pink, or purple variations like magenta, for example, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monochromator
A monochromator is an optical device that transmits a mechanically selectable narrow band of wavelengths of light or other radiation chosen from a wider range of wavelengths available at the input. The name is from the Greek roots ''mono-'', "single", and ''chroma'', "colour", and the Latin suffix ''-ator'', denoting an agent. Uses A device that can produce monochromatic light has many uses in science and in optics because many optical characteristics of a material are dependent on wavelength. Although there are a number of useful ways to select a narrow band of wavelengths (which, in the visible range, is perceived as a pure color), there are not as many other ways to easily select any wavelength band from a wide range. See below for a discussion of some of the uses of monochromators. In hard X-ray and neutron optics, crystal monochromators are used to define wave conditions on the instruments. Techniques A monochromator can use either the phenomenon of optical dispersion i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrometer
A spectrometer () is a scientific instrument used to separate and measure spectral components of a physical phenomenon. Spectrometer is a broad term often used to describe instruments that measure a continuous variable of a phenomenon where the spectral components are somehow mixed. In visible light a spectrometer can separate white light and measure individual narrow bands of color, called a spectrum. A mass spectrometer measures the spectrum of the masses of the atoms or molecules present in a gas. The first spectrometers were used to split light into an array of separate colors. Spectrometers were developed in early studies of physics, astronomy, and chemistry. The capability of spectroscopy to determine chemical composition drove its advancement and continues to be one of its primary uses. Spectrometers are used in astronomy to analyze the chemical composition of stars and planets, and spectrometers gather data on the origin of the universe. Examples of spectrometer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, , where ''θ''1 and ''θ''2 are the angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices ''n''1 and ''n''2. The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity (Fresnel's equations) and Brewster's angle. The refractive index can be seen as the factor by which the speed and the wavelength of the radiation are reduced with respect to their vacuum values: the speed of light in a medium is , and similarly the wavelength in that medium is , where ''� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractometer
A refractometer is a laboratory or field device for the measurement of an index of refraction (refractometry). The index of refraction is calculated from the observed refraction angle using Snell's law. For mixtures, the index of refraction then allows to determine the concentration using mixing rules such as the Gladstone–Dale relation and Lorentz–Lorenz equation. Refractometry Standard refractometers measure the extent of light refraction (as part of a refractive index) of transparent substances in either a liquid or solid-state; this is then used in order to identify a liquid sample, analyze the sample's purity, and determine the amount or concentration of dissolved substances within the sample. As light passes through the liquid from the air it will slow down and create a ‘bending’ illusion, the severity of the ‘bend’ will depend on the amount of substance dissolved in the liquid. For example, the amount of sugar in a glass of water. Types There are four ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)