|
Optic Atrophy, Hereditary, Leber
Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) is a mitochondrially inherited (transmitted from mother to offspring) degeneration of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) and their axons that leads to an acute or subacute loss of central vision; it predominantly affects young adult males. LHON is transmitted only through the mother, as it is primarily due to mutations in the mitochondrial (not nuclear) genome, and only the egg contributes mitochondria to the embryo. LHON is usually due to one of three pathogenic mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) point mutations. These mutations are at nucleotide positions 11778 G to A, 3460 G to A and 14484 T to C, respectively in the ND4, ND1 and ND6 subunit genes of complex I of the oxidative phosphorylation chain in mitochondria. Men cannot pass on the disease to their offspring. Signs and symptoms Clinically, there is an acute onset of visual loss, first in one eye, and then a few weeks to months later in the other. Onset is usually young adulthoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Mitochondrial Genetics
Human mitochondrial genetics is the study of the genetics of human mitochondrial DNA (the DNA contained in human mitochondria). The human mitochondrial genome is the entirety of hereditary information contained in human mitochondria. Mitochondria are small structures in cells that generate energy for the cell to use, and are hence referred to as the "powerhouses" of the cell. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is not transmitted through nuclear DNA (nDNA). In humans, as in most multicellular organisms, mitochondrial DNA is inherited only from the mother's ovum. There are theories, however, that paternal mtDNA transmission in humans can occur under certain circumstances. Mitochondrial inheritance is therefore non-Mendelian, as Mendelian inheritance presumes that half the genetic material of a fertilized egg (zygote) derives from each parent. Eighty percent of mitochondrial DNA codes for mitochondrial RNA, and therefore most mitochondrial DNA mutations lead to functional problems, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Eye
The human eye is a sensory organ, part of the sensory nervous system, that reacts to visible light and allows humans to use visual information for various purposes including seeing things, keeping balance, and maintaining circadian rhythm. The eye can be considered as a living optical device. It is approximately spherical in shape, with its outer layers, such as the outermost, white part of the eye (the sclera) and one of its inner layers (the pigmented choroid) keeping the eye essentially light tight except on the eye's optic axis. In order, along the optic axis, the optical components consist of a first lens (the cornea—the clear part of the eye) that accomplishes most of the focussing of light from the outside world; then an aperture (the pupil) in a diaphragm (the iris—the coloured part of the eye) that controls the amount of light entering the interior of the eye; then another lens (the crystalline lens) that accomplishes the remaining focussing of light into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MT-ND1
MT-ND1 is a gene of the mitochondrial genome coding for the NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain 1 (ND1) protein. The ND1 protein is a subunit of NADH dehydrogenase, which is located in the mitochondrial inner membrane and is the largest of the five complexes of the electron transport chain. Variants of the human MT-ND1 gene are associated with mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS), Leigh's syndrome (LS), Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) and increases in adult BMI. Structure MT-ND1 is located in mitochondrial DNA from base pair 3,307 to 4,262. The MT-ND1 gene produces a 36 kDa protein composed of 318 amino acids. MT-ND1 is one of seven mitochondrial genes encoding subunits of the enzyme NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone), together with MT-ND2, MT-ND3, MT-ND4, MT-ND4L, MT-ND5, and MT-ND6. Also known as Complex I, this enzyme is the largest of the respiratory complexes. The structure is L-shaped with a long, hydrophobic transme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondrial Genome
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants and algae, also in plastids such as chloroplasts. Human mitochondrial DNA was the first significant part of the human genome to be sequenced. This sequencing revealed that the human mtDNA includes 16,569 base pairs and encodes 13 proteins. Since animal mtDNA evolves faster than nuclear genetic markers, it represents a mainstay of phylogenetics and evolutionary biology. It also permits an examination of the relatedness of populations, and so has become important in anthropology and biogeography. Origin Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA are thought to be of separate evolutionary origin, with the mtDNA being derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants and algae, also in plastids such as chloroplasts. Human mitochondrial DNA was the first significant part of the human genome to be sequenced. This sequencing revealed that the human mtDNA includes 16,569 base pairs and encodes 13 proteins. Since animal mtDNA evolves faster than nuclear genetic markers, it represents a mainstay of phylogenetics and evolutionary biology. It also permits an examination of the relatedness of populations, and so has become important in anthropology and biogeography. Origin Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA are thought to be of separate evolutionary origin, with the mtDNA being derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple (cerebral) sclerosis (MS), also known as encephalomyelitis disseminata or disseminated sclerosis, is the most common demyelinating disease, in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This damage disrupts the ability of parts of the nervous system to transmit signals, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. Specific symptoms can include double vision, blindness in one eye, muscle weakness, and trouble with sensation or coordination. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either occurring in isolated attacks (relapsing forms) or building up over time (progressive forms). In the relapsing forms of MS, between attacks, symptoms may disappear completely, although some permanent neurological problems often remain, especially as the disease advances. While the cause is unclear, the underlying mechanism is thought to be either destruction by the immune system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults – is called tachycardia, and a resting heart rate that is too slow – below 60 beats per minute – is called bradycardia. Some types of arrhythmias have no symptoms. Symptoms, when present, may include palpitations or feeling a pause between heartbeats. In more serious cases, there may be lightheadedness, passing out, shortness of breath or chest pain. While most cases of arrhythmia are not serious, some predispose a person to complications such as stroke or heart failure. Others may result in sudden death. Arrhythmias are often categorized into four groups: extra beats, supraventricular tachycardias, ventricular arrhythmias and bradyarrhythmias. Extra beats include premature atrial contractions, premature ventricular contra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
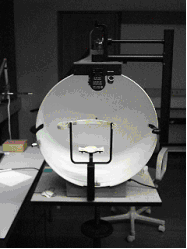
Perimetry
A visual field test is an eye examination that can detect dysfunction in central and peripheral vision which may be caused by various medical conditions such as glaucoma, stroke, pituitary disease, brain tumours or other neurological deficits. Visual field testing can be performed clinically by keeping the subject's gaze fixed while presenting objects at various places within their visual field. Simple manual equipment can be used such as in the tangent screen test or the Amsler grid. When dedicated machinery is used it is called a perimeter. The exam may be performed by a technician in one of several ways. The test may be performed by a technician directly, with the assistance of a machine, or completely by an automated machine. Machine-based tests aid diagnostics by allowing a detailed printout of the patient's visual field. Other names for this test may include perimetry, Tangent screen exam, Automated perimetry exam, Goldmann visual field exam, or brand names such as Hen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotoma
A scotoma is an area of partial alteration in the field of vision consisting of a partially diminished or entirely degenerated visual acuity that is surrounded by a field of normal – or relatively well-preserved – vision. Every normal mammalian eye has a scotoma in its field of vision, usually termed its blind spot. This is a location with no photoreceptor cells, where the retinal ganglion cell axons that compose the optic nerve exit the retina. This location is called the optic disc. There is no direct conscious awareness of visual scotomas. They are simply regions of reduced information within the visual field. Rather than recognizing an incomplete image, patients with scotomas report that things "disappear" on them. The presence of the blind spot scotoma can be demonstrated subjectively by covering one eye, carefully holding fixation with the open eye, and placing an object (such as one's thumb) in the lateral and horizontal visual field, about 15 degrees from fix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Vision
Color vision, a feature of visual perception, is an ability to perceive differences between light composed of different wavelengths (i.e., different spectral power distributions) independently of light intensity. Color perception is a part of the larger visual system and is mediated by a complex process between neurons that begins with differential stimulation of different types of photoreceptors by light entering the eye. Those photoreceptors then emit outputs that are propagated through many layers of neurons and then ultimately to the brain. Color vision is found in many animals and is mediated by similar underlying mechanisms with common types of biological molecules and a complex history of evolution in different animal taxa. In primates, color vision may have evolved under selective pressure for a variety of visual tasks including the foraging for nutritious young leaves, ripe fruit, and flowers, as well as detecting predator camouflage and emotional states in other pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Gunn Pupil
A relative afferent pupillary defect (RAPD), also known as a Marcus Gunn pupil, is a medical sign observed during the swinging-flashlight test whereupon the patient's pupils dilate when a bright light is swung from the unaffected eye to the affected eye. The affected eye still senses the light and produces pupillary sphincter constriction to some degree, albeit reduced. Depending on severity, different symptoms may appear during the swinging flash light test: Mild RAPD will presents as a weak pupil constriction initially, after which dilation continues to happen. When RAPD is moderate, pupil size will remain, after which it dilates When RAPD is severe, the pupil will dilate quickly Cause The most common cause of Marcus Gunn pupil is a lesion of the optic nerve (between the retina and the optic chiasm) due to glaucoma, or severe retinal disease, or due to multiple sclerosis. It is named after Scottish ophthalmologist Robert Marcus Gunn. A second common cause of Marcus Gunn p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fundoscopy
Ophthalmoscopy, also called funduscopy, is a test that allows a health professional to see inside the fundus of the eye and other structures using an ophthalmoscope (or funduscope). It is done as part of an eye examination and may be done as part of a routine physical examination. It is crucial in determining the health of the retina, optic disc, and vitreous humor. The pupil is a hole through which the eye's interior will be viewed. Opening the pupil wider (dilating it) is a simple and effective way to better see the structures behind it. Therefore, dilation of the pupil ( mydriasis) is often accomplished with medicated eye drops before funduscopy. However, although dilated fundus examination is ideal, undilated examination is more convenient and is also helpful (albeit not as comprehensive), and it is the most common type in primary care. An alternative or complement to ophthalmoscopy is to perform a fundus photography, where the image can be analysed later by a professional. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)