|
On-time Performance
In public transportation, schedule adherence or on-time performance refers to the level of success of the service (such as a bus or train) remaining on the published schedule. On time performance, sometimes referred to as on time running, is normally expressed as a percentage, with a higher percentage meaning more vehicles are on time. The level of on time performance for many transport systems is a very important measure of the effectiveness of the system. Background On time performance is a measure of the ability of transport services to be on time. Almost all transportation systems have timetables, which describe when vehicles are to arrive at scheduled stops. Transport services have a higher utility where services run on time, as anyone planning on making use of the service can align their activities with that of the transport system. On time performance is particularly important where services are infrequent, and people need to plan to meet services. The ability of different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Transportation
Public transport (also known as public transportation, public transit, mass transit, or simply transit) is a system of transport for passengers by group travel systems available for use by the general public unlike private transport, typically managed on a schedule, operated on established routes, and that charge a posted fee for each trip. There is no rigid definition; the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' specifies that public transportation is within urban areas, and air travel is often not thought of when discussing public transport—dictionaries use wording like "buses, trains, etc." Examples of public transport include city buses, trolleybuses, trams (or light rail) and passenger trains, rapid transit (metro/subway/underground, etc.) and ferries. Public transport between cities is dominated by airlines, coaches, and intercity rail. High-speed rail networks are being developed in many parts of the world. Most public transport systems run along fixed routes with set embarka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bus Rapid Transit
Bus rapid transit (BRT), also called a busway or transitway, is a bus-based public transport system designed to have much more capacity, reliability and other quality features than a conventional bus system. Typically, a BRT system includes roadways that are dedicated to buses, and gives priority to buses at intersections where buses may interact with other traffic; alongside design features to reduce delays caused by passengers boarding or leaving buses, or paying fares. BRT aims to combine the capacity and speed of a light rail or metro system (LRT, HRT) with the flexibility, lower cost and simplicity of a bus system. The world's first BRT system was the Busway in Runcorn New Town, England, which entered service in 1971. , a total of 166 cities in six continents have implemented BRT systems, accounting for of BRT lanes and about 32.2 million passengers every day. The majority of these are in Latin America, where about 19.6 million passengers ride daily, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grade Separation
In civil engineering (more specifically highway engineering), grade separation is a method of aligning a junction of two or more surface transport axes at different heights (grades) so that they will not disrupt the traffic flow on other transit routes when they cross each other. The composition of such transport axes does not have to be uniform; it can consist of a mixture of roads, footpaths, railways, canals, or airport runways. Bridges (or overpasses, also called flyovers), tunnels (or underpasses), or a combination of both can be built at a junction to achieve the needed grade separation. In North America, a grade-separated junction may be referred to as a ''grade separation'' or as an '' interchange'' – in contrast with an '' intersection'', ''at-grade'', a '' diamond crossing'' or a ''level crossing'', which are not grade-separated. Effects Advantages Roads with grade separation generally allow traffic to move freely, with fewer interruptions, and at higher ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
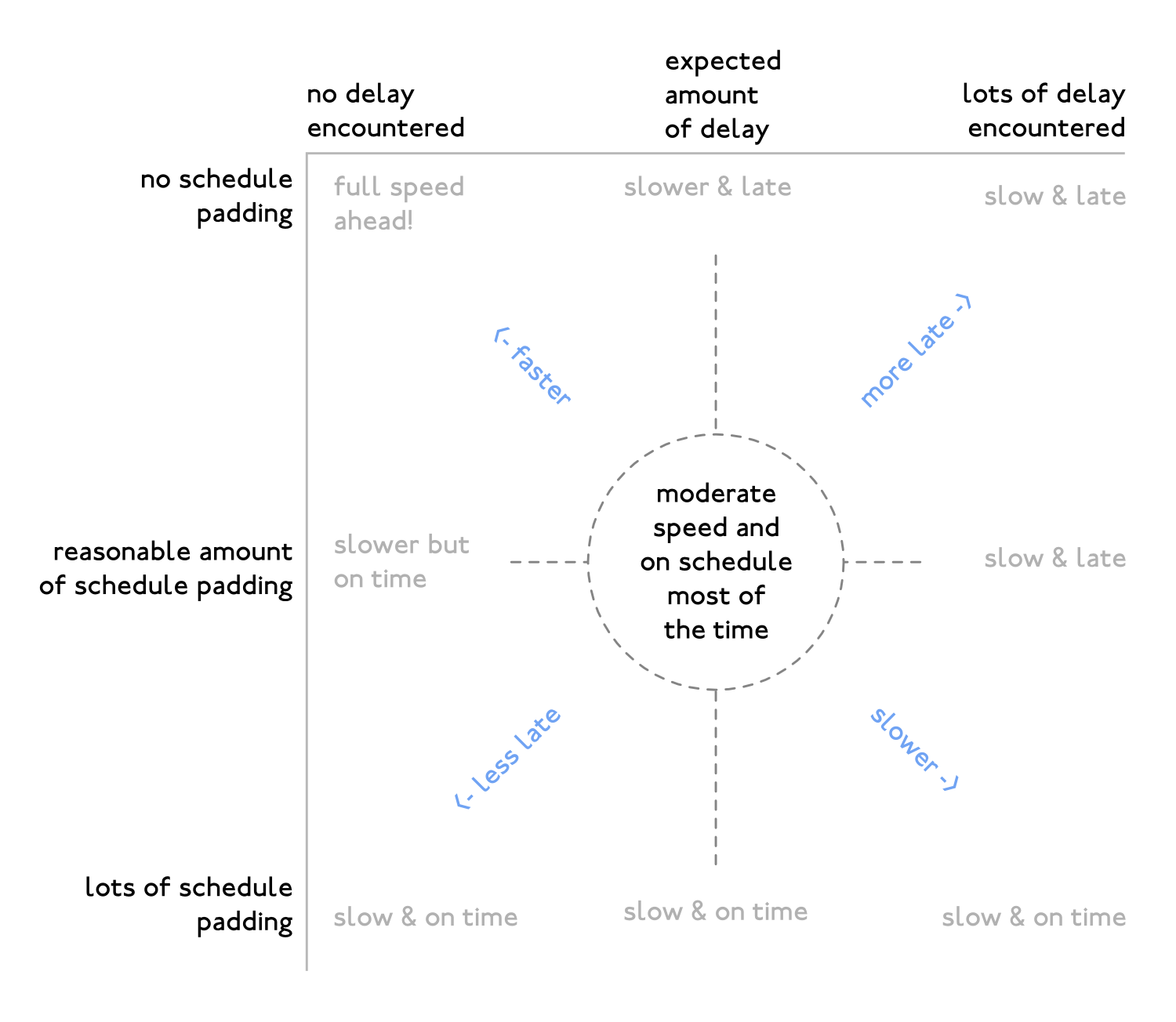
Schedule Padding
Schedule padding—sometimes called simply padding, or recovery time—is some amount of 'additional' time added to part or all of a schedule, in excess of the expected duration, that allows it to be resilient to anticipated delays and increase the chance that the published schedule will be met. In some cases, excessive padding may be intentionally added to make it unlikely that the schedule won't be met, or to prefabricate an earlier-than-scheduled completion. Padding may have only a temporary positive impact, and many clients perceive this as a deceptive strategy. In transportation, airlines and public transit agencies often use schedule padding to improve schedule adherence and on-time performance, as the percentage of ''on-time'' trips is typically a key performance indicator for operators. In project management or project planning, padding is added to a project schedule to account for known risks and other unforeseen circumstances that may prevent a project from being delive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Route Capacity
Route capacity is the maximum number of vehicles, people, or amount of freight than can travel a given route in a given amount of time, usually an hour. It may be limited by the worst bottleneck in the system, such as a stretch of road with fewer lanes. Air traffic route capacity is affected by weather. For a metro or a light rail system, route capacity is generally the capacity of each vehicle, times the number of vehicles per train, times the number of trains per hour (tph). In this way, route capacity is highly dependent on headway. Beyond this mathematical theory, capacity may be influenced by other factors such as slow zones, single-tracked areas, and infrastructure limitations, e.g. to useful train lengths. Overview Any assessment of the effectiveness of a transport network includes a calculation of what capacity is used, how it is used, and whether it is used effectively. For instance, overloaded routes may need to be upgraded, or capacity provided by other routes. Unus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bus Bunching
In public transport, bus bunching, clumping, convoying, piggybacking or platooning is a phenomenon whereby two or more transit vehicles (such as buses or trains) that were scheduled at regular intervals along a common route instead bunch together and form a platoon. This occurs when leading vehicles are unable to keep their schedule and fall behind to such an extent that trailing vehicles catch up to them. Theory A bus that is running slightly late will, in addition to its normal load, pick up passengers who would have taken the next bus if the first bus had not been late. These extra passengers delay the first bus even further. In contrast, the bus behind the late bus has a lighter passenger load than it otherwise would have, and may therefore run ahead of schedule. The classical theory causal model for irregular intervals is based on the observation that a late bus tends to get later and later as it completes its run, while the bus following it tends to get earlier and earlier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Signal
A railway signal is a visual display device that conveys instructions or provides warning of instructions regarding the driver’s authority to proceed. The driver interprets the signal's indication and acts accordingly. Typically, a signal might inform the driver of the speed at which the train may safely proceed or it may instruct the driver to stop. Application and positioning of signals Originally, signals displayed simple stop or proceed indications. As traffic density increased, this proved to be too limiting and refinements were added. One such refinement was the addition of distant signals on the approach to stop signals. The distant signal gave the driver warning that they were approaching a signal which might require a stop. This allowed for an overall increase in speed, since train drivers no longer had to drive at a speed within sighting distance of the stop signal. Under timetable and train order operation, the signals did not directly convey orders to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slippery Rail
Slippery rail, or low railhead adhesion, is a condition of railways (railroads) where contamination of the railhead reduces the traction between the wheel and the rail. This can lead to wheelslip when the train is taking power, and wheelslide when the train is braking. One common cause of contamination is fallen leaves that adhere to the railhead (top surface) of railway tracks. The condition results in significant reduction in friction between train wheels and rails, and in extreme cases can render the track temporarily unusable. In Britain, the situation is colloquially referred to as "leaves on the line". Low adhesion caused by weather Railhead contamination caused by weather conditions can occur at any time of year. The leaf fall season causes the most disruption to rail operations. In heavily deciduous forested areas like the American Mid-Atlantic states, New England, many parts of Europe including the UK, and Southern Ontario, Canada, the problem can arise. Where the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloud cover, cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere, the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather refers to day-to-day temperature, precipitation, and other atmospheric conditions, whereas climate is the term for the averaging of atmospheric conditions over longer periods of time. When used without qualification, "weather" is generally understood to mean the weather of Earth. Weather is driven by atmospheric pressure, air pressure, temperature, and moisture differences between one place and another. These differences can occur due to the effect of Sun angle on climate, Sun's angle at any particular spot, which varies with latitude. The strong temperature contrast between polar and tropical air gives rise to the largest scale atmospheric circulations: the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Layover
250px, Layover for buses at LACMTA's Warner Center Transit Hub, Los Angeles ">Los_Angeles.html" ;"title="Warner Center Transit Hub, Los Angeles">Warner Center Transit Hub, Los Angeles In scheduled transportation, a layover (also waypoint, way station, or connection) is a point where a vehicle stops, with passengers possibly changing vehicles. In public transit, this typically takes a few minutes at a trip terminal. For air travel, where layovers are longer, passengers will exit the vehicle and wait in the terminal, often to board another vehicle traveling elsewhere. A stopover is a longer form of layover, allowing time to leave the transport system for sightseeing or overnight accommodation. History Historically, a way station was a facility for resting or changing a team of horses drawing a stagecoach. Typically a simple meal was available to passengers, who were also able to use Public toilet, restrooms. Basic overnight accommodations were sometimes available in remote ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headway
Headway is the distance or duration between vehicles in a transit system measured in space or time. The ''minimum headway'' is the shortest such distance or time achievable by a system without a reduction in the speed of vehicles. The precise definition varies depending on the application, but it is most commonly measured as the distance from the tip (front end) of one vehicle to the tip of the next one behind it. It can be expressed as the distance between vehicles, or as time it will take for the trailing vehicle to cover that distance. A "shorter" headway signifies closer spacing between the vehicles. Airplanes operate with headways measured in hours or days, freight trains and commuter rail systems might have headways measured in parts of an hour, metro and light rail systems operate with headways on the order of 90 seconds to 20 minutes, and vehicles on a freeway can have as little as 2 seconds headway between them. Headway is a key input in calculating the overall route c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |