|
Omegasome
] Omegasome is a Cell (biology), cell organelle consisting of lipid bilayer membranes enriched for phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (abbreviated PI(3)P or PtdIns3P), and related to a process of autophagy. It is a subdomain of the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER), and has a morphology resembling the Greek capital letter Omega (Ω). Omegasomes are the sites from which phagophores (also called "isolation membranes") form, which are sack-like structures that mature into autophagosomes, and fuse with lysosomes in order to degrade the contents of the autophagosomes. The formation of omegasomes depends on various factors, however in general, formation of omegasomes is increased as a response to starvation, and in some biochemical situations the presence of PI(3)P leads to the formation of omegasomes. Macroautophagy Autophagy (from Greek words for “self” and “eating”) is a process of digesting or degrading cytoplasmic molecules (proteins, lipids, sugars and organelles). Macroautophagy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysosomes
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane proteins, and its lumenal proteins. The lumen's pH (~4.5–5.0) is optimal for the enzymes involved in hydrolysis, analogous to the activity of the stomach. Besides degradation of polymers, the lysosome is involved in various cell processes, including secretion, plasma membrane repair, apoptosis, cell signaling, and energy metabolism. Lysosomes act as the waste disposal system of the cell by digesting used materials in the cytoplasm, from both inside and outside the cell. Material from outside the cell is taken up through endocytosis, while material from the inside of the cell is digested through autophagy. The sizes of the organelles vary greatly—the larger ones can be more than 10 times the size of the smaller ones. They were discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and Fungus, fungi. Mitochondria have a double lipid bilayer, membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term ''mitochondrion'' was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase coined by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 article of the same name. Some cells in some multicellular organisms lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cells). A large number of unicellular organisms, such as microsporidia, parabasalids and diplomonads, have reduced or transformed their mitochondria into mitosome, other structures. One eukaryote, ''Monocercomonoides'', is known to have completely lost its mitocho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autophagy
Autophagy (or autophagocytosis; from the Ancient Greek , , meaning "self-devouring" and , , meaning "hollow") is the natural, conserved degradation of the cell that removes unnecessary or dysfunctional components through a lysosome-dependent regulated mechanism. It allows the orderly degradation and recycling of cellular components. Although initially characterized as a primordial degradation pathway induced to protect against starvation, it has become increasingly clear that autophagy also plays a major role in the homeostasis of non-starved cells. Defects in autophagy have been linked to various human diseases, including neurodegeneration and cancer, and interest in modulating autophagy as a potential treatment for these diseases has grown rapidly. Four forms of autophagy have been identified: macroautophagy, microautophagy, chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), and crinophagy. In macroautophagy (the most thoroughly researched form of autophagy), cytoplasmic components (like mit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' the suffix ''-elle'' being a diminutive. Organelles are either separately enclosed within their own lipid bilayers (also called membrane-bound organelles) or are spatially distinct functional units without a surrounding lipid bilayer (non-membrane bound organelles). Although most organelles are functional units within cells, some function units that extend outside of cells are often termed organelles, such as cilia, the flagellum and archaellum, and the trichocyst. Organelles are identified by microscopy, and can also be purified by cell fractionation. There are many types of organelles, particularly in eukaryotic cells. They include structures that make up the endomembrane system (such as the nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, and G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugar Acid
A Sugar acid or acidic sugar is a monosaccharide with a carboxyl group at one end or both ends of its chain. Main classes of sugar acids include: * Aldonic acids, in which the aldehyde group (−CHO) located at the initial end ( position 1) of an aldose is oxidized. * Ulosonic acids, in which the −CH2(OH) group at the initial end of a 2-ketose is oxidized creating an α-ketoacid. * Uronic acids, in which the −CH2(OH) group at the terminal end of an aldose or ketose is oxidized. * Aldaric acids, in which both ends (−CHO and −CH2(OH)) of an aldose are oxidized. Examples Examples of sugar acids include: * Aldonic acids ** Glyceric acid (3C) ** Xylonic acid (5C) ** Gluconic acid (6C) ** Ascorbic acid (6C, unsaturated lactone) * Ulosonic acids ** Neuraminic acid (5-amino-3,5-dideoxy-D- ''glycero''-D- ''galacto''-non-2-ulosonic acid) ** Ketodeoxyoctulosonic acid (KDO or 3-deoxy-D- ''manno''-oct-2-ulosonic acid) * Uronic acids ** Glucuronic acid (6C) ** Galacturonic acid (6C) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing energy, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids have applications in the cosmetic and food industries, and in nanotechnology. Lipids may be broadly defined as hydrophobic or amphiphilic small molecules; the amphiphilic nature of some lipids allows them to form structures such as vesicles, multilamellar/unilamellar liposomes, or membranes in an aqueous environment. Biological lipids originate entirely or in part from two distinct types of biochemical subunits or "building-blocks": ketoacyl and isoprene groups. Using this approach, lipids may be divided into eight categories: fatty acyls, glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, saccharolipids, and polyketides (derived from condensati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starvation Response
Starvation response in animals (including humans) is a set of adaptive biochemical and physiological changes, triggered by lack of food or extreme weight loss, in which the body seeks to conserve energy by reducing the amount of calories it burns.Adapted from #wang2006, Wang et al. 2006, p 223. Equivalent or closely related terms include famine response, starvation mode, famine mode, starvation resistance, starvation tolerance, adapted starvation, adaptive thermogenesis, fat adaptation, and metabolic adaptation. Bacteria become highly tolerant to antibiotics when nutrients are limited. Starvation contributes to antibiotic tolerance during infection, as nutrients become limited when they are sequestered by host defenses and consumed by proliferating bacteria. One of the most important causes of starvation induced tolerance in vivo is biofilm growth, which occurs in many chronic infections. Starvation in biofilms is due to nutrient consumption by cells located on the periphery of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
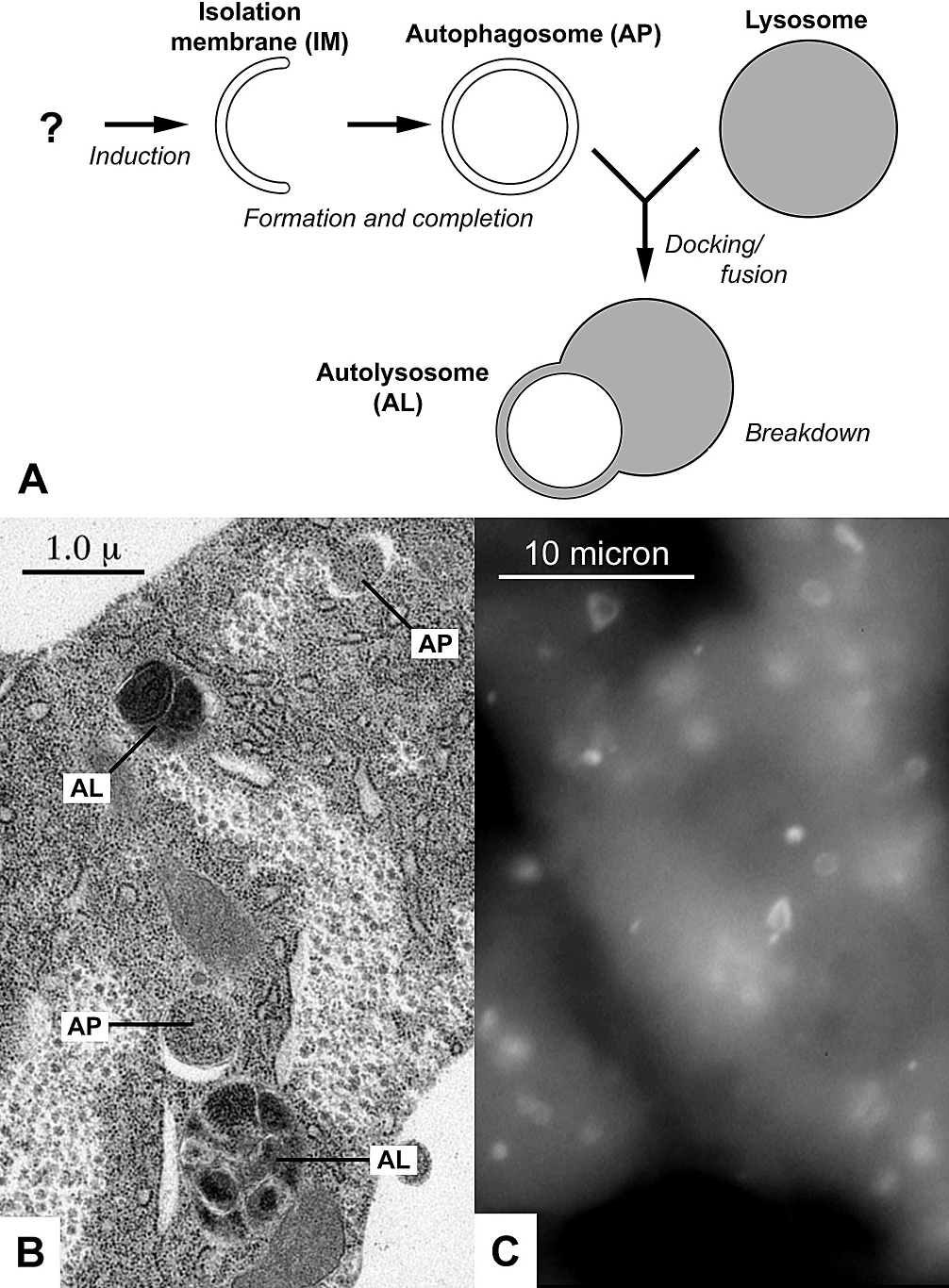
Autophagosomes
An autophagosome is a spherical structure with double layer membranes. It is the key structure in macroautophagy, the intracellular degradation system for cytoplasmic contents (e.g., abnormal intracellular proteins, excess or damaged organelles, invading microorganisms). After formation, autophagosomes deliver cytoplasmic components to the lysosomes. The outer membrane of an autophagosome fuses with a lysosome to form an autolysosome. The lysosome's hydrolases degrade the autophagosome-delivered contents and its inner membrane. The formation of autophagosomes is regulated by genes that are well-conserved from yeast to higher eukaryotes. The nomenclature of these genes has differed from paper to paper, but it has been simplified in recent years. The gene families formerly known as APG, AUT, CVT, GSA, PAZ, and PDD are now unified as the ATG (AuTophaGy related) family. The size of autophagosomes vary between mammals and yeast. Yeast autophagosomes are about 500-900 nm, while mam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omega
Omega (; capital: Ω, lowercase: ω; Ancient Greek ὦ, later ὦ μέγα, Modern Greek ωμέγα) is the twenty-fourth and final letter in the Greek alphabet. In the Greek numeric system/isopsephy (gematria), it has a value of 800. The word literally means "great O" (''ō mega'', mega meaning "great"), as opposed to omicron, which means "little O" (''o mikron'', micron meaning "little"). In phonetic terms, the Ancient Greek Ω represented a long open-mid back rounded vowel , comparable to the "aw" of the English word ''raw'' in dialects without the cot–caught merger, in contrast to omicron which represented the close-mid back rounded vowel , and the digraph ''ου'' which represented the long close-mid back rounded vowel . In Modern Greek, both omega and omicron represent the mid back rounded vowel or . The letter omega is transliterated into a Latin-script alphabet as ''ō'' or simply ''o''. As the final letter in the Greek alphabet, omega is often used t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |