|
Ochronotic Pigment
Ochronosis is a syndrome caused by the accumulation of homogentisic acid in connective tissues. The condition was named after the yellowish (ocher-like) discoloration of the tissue seen on microscopic examination. Macroscopically, though, the affected tissues appear bluish-grey because of a light-scattering phenomenon known as the Tyndall effect. The condition is most often associated with alkaptonuria, but can occur from exogenous administration of phenol complexes such as hydroquinone. It was first described by Rudolf Virchow in 1865.Findlay GH, et al. Ochronosis. Clinics in Dermatology 1989;7:28-35 Types The two types of ochronosis are endogenous and exogenous. The endogenous variety is an autosomal-recessive disease, known as alkaptonuria, that is caused by a lack of homogentisate oxidase enzyme.Charlín, R., Barcaui, C. B., Kac, B. K., Soares, D. B., Rabello-Fonseca, R. and Azulay-Abulafia, L. (2008), Hydroquinone-induced exogenous ochronosis: a report of four cases and u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homogentisic Acid
Homogentisic acid (2,5-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid) is a phenolic acid usually found in ''Arbutus unedo'' (strawberry-tree) honey. It is also present in the bacterial plant pathogen ''Xanthomonas campestris'' pv. ''phaseoli'' as well as in the yeast ''Yarrowia lipolytica'' where it is associated with the production of brown pigments. It is oxidatively dimerised to form hipposudoric acid, one of the main constituents of the 'blood sweat' of hippopotamuses. It is less commonly known as melanic acid, the name chosen by William Prout. Human pathology Accumulation of excess homogentisic acid and its oxide, named alkapton, is a result of the failure of the enzyme homogentisic acid 1,2-dioxygenase (typically due to a mutation) in the degradative pathway of tyrosine, consequently associated with alkaptonuria. Intermediate It is an intermediate in the catabolism of aromatic amino acids such as phenylalanine and tyrosine. 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate (produced by transamination of tyrosin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melasma
Melasma (also known as chloasma faciei,James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. . or the mask of pregnancy when present in pregnant women) is a tan or dark skin discoloration. Melasma is thought to be caused by sun exposure, genetic predisposition, hormone changes, and skin irritation. Although it can affect anyone, it is particularly common in women, especially pregnant women and those who are taking oral or patch contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy medications. Signs and symptoms The symptoms of melasma are dark, irregular, well-demarcated, hyperpigmented macules to patches. These patches often develop gradually over time. Melasma does not cause any other symptoms beyond the cosmetic discoloration. Patches can vary in size from 0.5 cm to larger than 10 cm depending on the person. Its location can be categorized as centrofacial, malar, or mandibular. The most common is ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid Metabolism Disorders
In chemistry, amines (, ) are chemical compound, compounds and functional groups that contain a base (chemistry), basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivative (chemistry), derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group (these may respectively be called alkylamines and arylamines; amines in which both types of substituent are attached to one nitrogen atom may be called alkylarylamines). Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline; Inorganic compound, Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine (). The substituent is called an amino group. Compounds with a nitrogen atom attached to a carbonyl group, thus having the structure , are called amides and have different chemical properties from amines. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number of substituents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ILDS
The International League of Dermatological Societies (ILDS) is a non-governmental organization that works closely with the World Health Organization. It was founded in 1935, but because of World War II no congresses were held until 1952. It is governed by the International Committee of Dermatology. The ILDS is the parent organization of the International Foundation for Dermatology, founded in 1987. After the publication of ICD-10, the ILDS produced a series of compatible extensions for use in dermatology Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin.''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.'' Random House, Inc. 2001. Page 537. . It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A dermatologist is a specialist medical .... References External links Official site HistoryInternational Foundation for DermatologyApplication to Dermatology of International Classification of Disease (ICD-11) Organizations established in 1935 Dermatology organi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cutaneous Conditions
Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the body and composed of skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment. The skin weighs an average of four kilograms, covers an area of two square metres, and is made of three distinct layers: the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. The two main types of human skin are: glabrous skin, the hairless skin on the palms and soles (also referred to as the "palmoplantar" surfaces), and hair-bearing skin.Burns, Tony; ''et al''. (2006) ''Rook's Textbook of Dermatology CD-ROM''. Wiley-Blackwell. . Within the latter type, the hairs occur in structures called pilosebaceous units, each with hair follicle, sebaceous gland, and associated arrector pili muscle. In the embryo, the epidermis, hair, and glands form from the ectoderm, which is chemically influenced by the underlying mesoderm th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylketonuria
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an inborn error of metabolism that results in decreased metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine. Untreated PKU can lead to intellectual disability, seizures, behavioral problems, and mental disorders. It may also result in a musty smell and lighter skin. A baby born to a mother who has poorly treated PKU may have heart problems, a small head, and low birth weight. Phenylketonuria is an inherited genetic disorder. It is due to mutations in the '' PAH'' gene, which results in low levels of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase. This results in the buildup of dietary phenylalanine to potentially toxic levels. It is autosomal recessive, meaning that both copies of the gene must be mutated for the condition to develop. There are two main types, classic PKU and variant PKU, depending on whether any enzyme function remains. Those with one copy of a mutated gene typically do not have symptoms. Many countries have newborn screening programs for the disease. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosinemia
Tyrosinemia or tyrosinaemia is an error of metabolism, usually inborn, in which the body cannot effectively break down the amino acid tyrosine. Symptoms of untreated tyrosinemia include liver and kidney disturbances. Without treatment, tyrosinemia leads to liver failure. Today, tyrosinemia is increasingly detected on newborn screening tests before any symptoms appear. With early and lifelong management involving a low-protein diet, special protein formula, and sometimes medication, people with tyrosinemia develop normally, are healthy, and live normal lives. Cause All tyrosinemias result from dysfunction of various genes in the phenylalanine and tyrosine catabolic pathway, and are inherited in an autosomal-recessive pattern. Type I tyrosinemia results from a mutation in the ''FAH'' gene, which encodes the enzyme fumarylacetoacetase. As a result of ''FAH'' deficiency, the substrate fumarylacetoacetate can accumulate in proximal renal tubular cells and hepatocytes, resulting in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaptonuria
Alkaptonuria is a rare inherited genetic disease which is caused by a mutation in the ''HGD'' gene for the enzyme homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase (); if a person inherits an abnormal copy from both parents (it is a recessive condition), the body accumulates an intermediate substance called homogentisic acid in the blood and tissues. Homogentisic acid and its oxidized form ''alkapton'' are excreted in the urine, giving it an unusually dark color. The accumulating homogentisic acid causes damage to cartilage (ochronosis, leading to osteoarthritis) and heart valves, as well as precipitating as kidney stones and stones in other organs. Symptoms usually develop in people over 30 years old, although the dark discoloration of the urine is present from birth. Apart from treatment of the complications (such as pain relief and joint replacement for the cartilage damage), the drug nitisinone has been found to suppress homogentisic acid production, and research is ongoing as to whether it can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
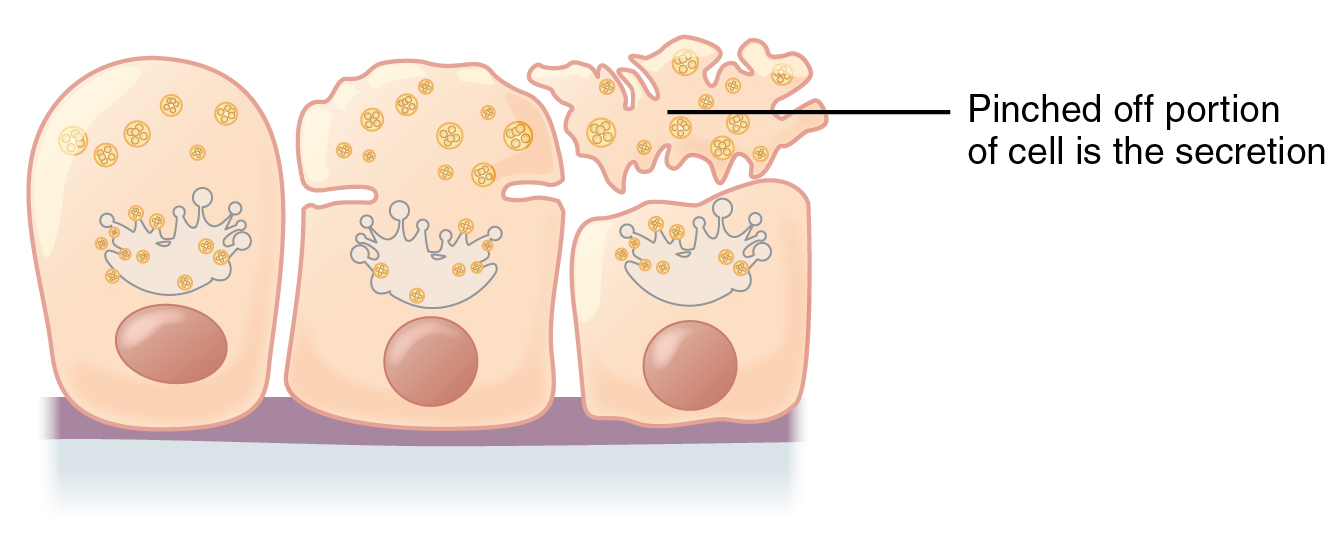
Apocrine
Apocrine () glands are a type of exocrine gland, which are themselves a type of gland, i.e. a group of cells specialized for the release of secretions. Exocrine glands secrete by one of three means: holocrine, merocrine and apocrine. In apocrine secretion, secretory cells accumulate material at their apical (anatomy), apical ends, and this material then buds off from the cells, forming extracellular vesicle (biology and chemistry), vesicles. The secretory cells therefore lose part of their cytoplasm in the process of secretion. An example of true apocrine glands is the mammary glands, responsible for secreting breast milk. Apocrine glands are also found in the anogenital region and axillae. Apocrine secretion is less damaging to the gland than holocrine secretion (which destroys a cell) but more damaging than merocrine secretion (exocytosis). Apocrine metaplasia Apocrine metaplasia is a reversible transformation of cells to an apocrine phenotype. It is common in the breast in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxyapatite
Hydroxyapatite, also called hydroxylapatite (HA), is a naturally occurring mineral form of calcium apatite with the formula Ca5(PO4)3(OH), but it is usually written Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 to denote that the crystal unit cell comprises two entities. Hydroxyapatite is the hydroxyl endmember of the complex apatite group. The OH− ion can be replaced by fluoride, chloride or carbonate, producing fluorapatite or chlorapatite. It crystallizes in the hexagonal crystal system. Pure hydroxyapatite powder is white. Naturally occurring apatites can, however, also have brown, yellow, or green colorations, comparable to the discolorations of dental fluorosis. Up to 50% by volume and 70% by weight of human bone is a modified form of hydroxyapatite, known as bone mineral. Carbonated calcium-deficient hydroxyapatite is the main mineral of which dental enamel and dentin are composed. Hydroxyapatite crystals are also found in pathological calcifications such as those found in breast tumors, as w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenols
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (— O H) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, . Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule. Phenols are both synthesized industrially and produced by plants and microorganisms. Properties Acidity Phenols are more acidic than typical alcohols. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12). Deprotonation of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides (aryloxides according to the IUPAC Gold Book). Condensation with aldehydes and ketones Phenols are susceptible to Electrophilic aromatic substitutions. Condensation with formald ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |