|
Observer Effect (physics)
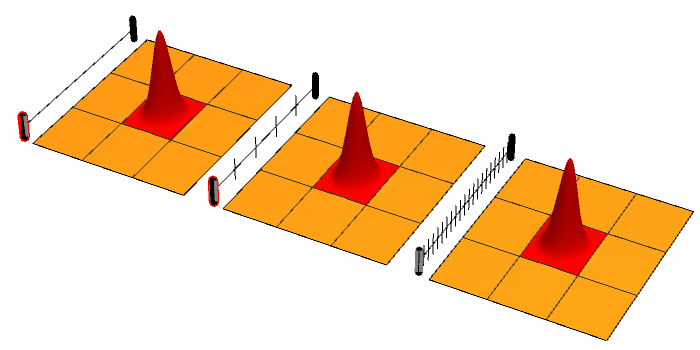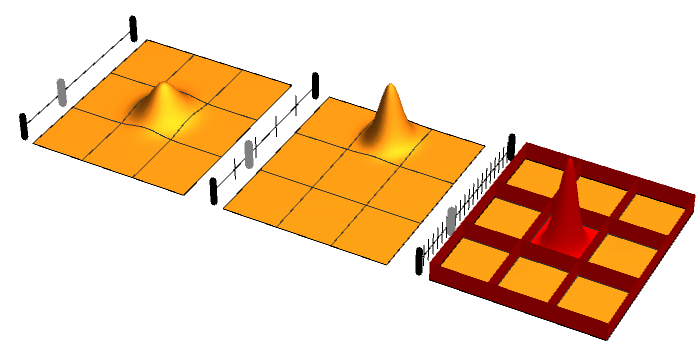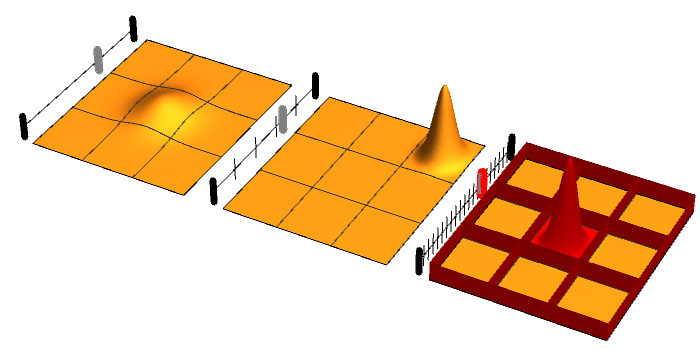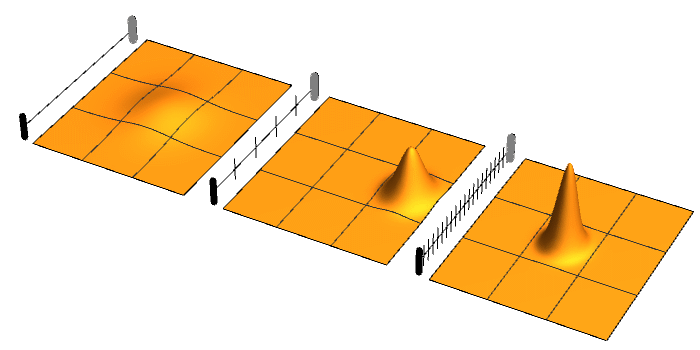
In physics, the observer effect is the disturbance of an observed system by the act of observation. This is often the result of instruments that, by necessity, alter the state of what they measure in some manner. A common example is checking the pressure in an automobile tire; this is difficult to do without letting out some of the air, thus changing the pressure. Similarly, seeing non-luminous objects requires light hitting the object, and causing it to reflect that light. While the effects of observation are often negligible, the object still experiences a change. This effect can be found in many domains of physics, but can usually be reduced to insignificance by using different instruments or observation techniques. A notable example of the observer effect occurs in quantum mechanics, as demonstrated by the double-slit experiment. Physicists have found that observation of quantum phenomena can change the measured results of this experiment. Despite the "observer effect" in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current Clamp
In electrical and electronic engineering, a current clamp, also known as current probe, is an electrical device with jaws which open to allow clamping around an electrical conductor. This allows measurement of the current in a conductor without the need to make physical contact with it, or to disconnect it for insertion through the probe. Current clamps are typically used to read the magnitude of alternating current (AC) and, with additional instrumentation, the phase and waveform can also be measured. Some clamp meters can measure currents of 1000 A and more. Hall effect and vane type clamps can also measure direct current (DC). Types of current clamp Current transformer A common form of current clamp comprises a split ring made of ferrite or soft iron. A wire coil is wound round one or both halves, forming one winding of a current transformer. The conductor it is clamped around forms the other winding. Like any transformer this type works only with AC or pulse waveforms, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Zeno Effect
The quantum Zeno effect (also known as the Turing paradox) is a feature of quantum-mechanical systems allowing a particle's time evolution to be slowed down by measuring it frequently enough with respect to some chosen measurement setting. Sometimes this effect is interpreted as "a system cannot change while you are watching it". One can "freeze" the evolution of the system by measuring it frequently enough in its known initial state. The meaning of the term has since expanded, leading to a more technical definition, in which time evolution can be suppressed not only by measurement: the quantum Zeno effect is the suppression of unitary time evolution in quantum systems provided by a variety of sources: measurement, interactions with the environment, stochastic fields, among other factors. As an outgrowth of study of the quantum Zeno effect, it has become clear that applying a series of sufficiently strong and fast pulses with appropriate symmetry can also ''decouple'' a system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franco Selleri
Franco Selleri (Bologna, Italy, 9 October 1936 – 20 November 2013) was an Italian theoretical physicist and professor at the Università degli Studi di Bari Aldo Moro. He received his Doctorate / Ph.D. cum laude at the Università di Bologna in 1958, and was a fellow of the Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare beginning 1959. He was a member of the New York Academy of Sciences and the Fondation Louis de Broglie, and served on the board of directors of the Italian Physical Society. He is known for his analysis of the foundations of relativity theory and quantum mechanics. Several solutions have been proposed for the paradoxes pointed out by him. Philosophically, his position was that of a realist. He was in close contact with Karl Popper who, though very old, took part in a conference on the subject that Selleri organized in 1985 in Bari.Obituary CERN Courier cerncourier.com/cws/article/cern/56228 He had numerous visiting professorships and fellowships, including CERN, Saclay, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decoherence
Quantum decoherence is the loss of quantum coherence. In quantum mechanics, particles such as electrons are described by a wave function, a mathematical representation of the quantum state of a system; a probabilistic interpretation of the wave function is used to explain various quantum effects. As long as there exists a definite phase relation between different states, the system is said to be coherent. A definite phase relationship is necessary to perform quantum computing on quantum information encoded in quantum states. Coherence is preserved under the laws of quantum physics. If a quantum system were perfectly isolated, it would maintain coherence indefinitely, but it would be impossible to manipulate or investigate it. If it is not perfectly isolated, for example during a measurement, coherence is shared with the environment and appears to be lost with time; a process called quantum decoherence. As a result of this process, quantum behavior is apparently lost, just as e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Superposition
Quantum superposition is a fundamental principle of quantum mechanics. It states that, much like waves in classical physics, any two (or more) quantum states can be added together ("superposed") and the result will be another valid quantum state; and conversely, that every quantum state can be represented as a sum of two or more other distinct states. Mathematically, it refers to a property of solutions to the Schrödinger equation; since the Schrödinger equation is linear, any linear combination of solutions will also be a solution(s) . An example of a physically observable manifestation of the wave nature of quantum systems is the interference peaks from an electron beam in a double-slit experiment. The pattern is very similar to the one obtained by diffraction of classical waves. Another example is a quantum logical qubit state, as used in quantum information processing, which is a quantum superposition of the "basis states" , 0 \rangle and , 1 \rangle . Here , 0 \r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors
In linear algebra, an eigenvector () or characteristic vector of a linear transformation is a nonzero vector that changes at most by a scalar factor when that linear transformation is applied to it. The corresponding eigenvalue, often denoted by \lambda, is the factor by which the eigenvector is scaled. Geometrically, an eigenvector, corresponding to a real nonzero eigenvalue, points in a direction in which it is stretched by the transformation and the eigenvalue is the factor by which it is stretched. If the eigenvalue is negative, the direction is reversed. Loosely speaking, in a multidimensional vector space, the eigenvector is not rotated. Formal definition If is a linear transformation from a vector space over a field into itself and is a nonzero vector in , then is an eigenvector of if is a scalar multiple of . This can be written as T(\mathbf) = \lambda \mathbf, where is a scalar in , known as the eigenvalue, characteristic value, or characteristic root ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave Function Collapse
In quantum mechanics, wave function collapse occurs when a wave function—initially in a superposition of several eigenstates—reduces to a single eigenstate due to interaction with the external world. This interaction is called an ''observation'', and is the essence of a measurement in quantum mechanics, which connects the wave function with classical observables such as position and momentum. Collapse is one of the two processes by which quantum systems evolve in time; the other is the continuous evolution governed by the Schrödinger equation. : Collapse is a black box for a thermodynamically irreversible interaction with a classical environment. Calculations of quantum decoherence show that when a quantum system interacts with the environment, the superpositions ''apparently'' reduce to mixtures of classical alternatives. Significantly, the combined wave function of the system and environment continue to obey the Schrödinger equation throughout this ''apparent'' col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interpretations Of Quantum Mechanics
An interpretation of quantum mechanics is an attempt to explain how the mathematical theory of quantum mechanics might correspond to experienced reality. Although quantum mechanics has held up to rigorous and extremely precise tests in an extraordinarily broad range of experiments, there exist a number of contending schools of thought over their interpretation. These views on interpretation differ on such fundamental questions as whether quantum mechanics is deterministic or stochastic, which elements of quantum mechanics can be considered real, and what the nature of measurement is, among other matters. Despite nearly a century of debate and experiment, no consensus has been reached among physicists and philosophers of physics concerning which interpretation best "represents" reality. History The definition of quantum theorists' terms, such as ''wave function'' and ''matrix mechanics'', progressed through many stages. For instance, Erwin Schrödinger originally viewed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measurement In Quantum Mechanics
In quantum physics, a measurement is the testing or manipulation of a physical system to yield a numerical result. The predictions that quantum physics makes are in general probabilistic. The mathematical tools for making predictions about what measurement outcomes may occur were developed during the 20th century and make use of linear algebra and functional analysis. Quantum physics has proven to be an empirical success and to have wide-ranging applicability. However, on a more philosophical level, debates continue about the meaning of the measurement concept. Mathematical formalism "Observables" as self-adjoint operators In quantum mechanics, each physical system is associated with a Hilbert space, each element of which represents a possible state of the physical system. The approach codified by John von Neumann represents a measurement upon a physical system by a self-adjoint operator on that Hilbert space termed an "observable". These observables play the role of measurable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), the latter being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible to extract energy as heat from a body at that temperature. Temperature is important in all fields of natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Energy
The term "thermal energy" is used loosely in various contexts in physics and engineering. It can refer to several different well-defined physical concepts. These include the internal energy or enthalpy of a body of matter and radiation; heat, defined as a type of energy transfer (as is thermodynamic work); and the characteristic energy of a degree of freedom, k_T, in a system that is described in terms of its microscopic particulate constituents (where T denotes temperature and k_ denotes the Boltzmann constant). Relation to heat and internal energy In thermodynamics, heat is energy transferred to or from a thermodynamic system by mechanisms other than thermodynamic work or transfer of matter, such as conduction, radiation, and friction. Heat refers to a quantity transferred between systems, not to a property of any one system, or "contained" within it. On the other hand, internal energy and enthalpy are properties of a single system. Heat and work depend on the way in which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |