|
Ovulation Cycle
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that make pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eggs and the cyclic release of estrogen and progesterone. The uterine cycle governs the preparation and maintenance of the lining of the uterus (womb) to receive an embryo. These cycles are concurrent and coordinated, normally last between 21 and 35 days, with a median length of 28 days, and continue for about 30–45 years. Naturally occurring hormones drive the cycles; the cyclical rise and fall of the follicle stimulating hormone prompts the production and growth of oocytes (immature egg cells). The hormone estrogen stimulates the uterus lining (endometrium) to thicken to accommodate an embryo should fertilization occur. The blood supply of the thickened lining provides nutrients to a successfully implanted embryo. If implantation does not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menstruation
Menstruation (also known as a period, among other colloquial terms) is the regular discharge of blood and mucosal tissue from the inner lining of the uterus through the vagina. The menstrual cycle is characterized by the rise and fall of hormones. Menstruation is triggered by falling progesterone levels and is a sign that pregnancy has not occurred. The first period, a point in time known as menarche, usually begins between the ages of 12 and 15. Menstruation starting as young as 8 years would still be considered normal. The average age of the first period is generally later in the developing world, and earlier in the developed world. The typical length of time between the first day of one period and the first day of the next is 21 to 45 days in young women. In adults, the range is between 21 and 31 days with the average being 28 days. Bleeding usually lasts around 2 to 7 days. Periods stop during pregnancy and typically do not resume during the initial months of breastfeed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovary
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body. The ovaries also secrete hormones that play a role in the menstrual cycle and fertility. The ovary progresses through many stages beginning in the prenatal period through menopause. It is also an endocrine gland because of the various hormones that it secretes. Structure The ovaries are considered the female gonads. Each ovary is whitish in color and located alongside the lateral wall of the uterus in a region called the ovarian fossa. The ovarian fossa is the region that is bounded by the external iliac artery and in front of the ureter and the internal iliac artery. This area is about 4 cm x 3 cm x 2 cm in size.Daftary, Shirish; Chakravarti, Sudip (2011). Manual of Obstetrics, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1-16. . The ovari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovarian Follicle
An ovarian follicle is a roughly spheroid cellular aggregation set found in the ovaries. It secretes hormones that influence stages of the menstrual cycle. At the time of puberty, women have approximately 200,000 to 300,000 follicles, each with the potential to release an egg cell (ovum) at ovulation for fertilization. These eggs are developed once every menstrual cycle with around 450–500 being ovulated during a woman's reproductive lifetime. Structure Ovarian follicles are the basic units of female reproductive biology. Each of them contains a single oocyte (immature ovum or egg cell). These structures are periodically initiated to grow and develop, culminating in ovulation of usually a single competent oocyte in humans. They also consist of granulosa cells and theca of follicle. Oocyte Once a month, one of the ovaries releases a mature egg (ovum), known as an oocyte. The nucleus of such an oocyte is called a '' germinal vesicle (see picture).'' Cumulus oophorus Cumulu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Figure 28 02 07
Figure may refer to: General *A shape, drawing, depiction, or geometric configuration *Figure (wood), wood appearance *Figure (music), distinguished from musical motif *Noise figure, in telecommunication *Dance figure, an elementary dance pattern *A person's figure, human physical appearance Arts *Figurine, a miniature statuette representation of a creature *Action figure, a posable jointed solid plastic character figurine *Figure painting, realistic representation, especially of the human form *Figure drawing *Model figure, a scale model of a creature Writing *figure, in writing, a type of floating block (text, table, or graphic separate from the main text) *Figure of speech, also called a rhetorical figure *Christ figure, a type of character * in typesetting, text figures and lining figures Accounting *Figure, a synonym for number *Significant figures in a decimal number Science *Figure of the Earth, the size and shape of the Earth in geodesy Sports *Figure (horse), a st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormonal Birth Control
Hormonal contraception refers to birth control methods that act on the endocrine system. Almost all methods are composed of steroid hormones, although in India one selective estrogen receptor modulator is marketed as a contraceptive. The original hormonal method—the combined oral contraceptive pill—was first marketed as a contraceptive in 1960. In the ensuing decades many other delivery methods have been developed, although the oral and injectable methods are by far the most popular. Hormonal contraception is highly effective: when taken on the prescribed schedule, users of steroid hormone methods experience pregnancy rates of less than 1% per year. Perfect-use pregnancy rates for most hormonal contraceptives are usually around the 0.3% rate or less. Currently available methods can only be used by women; the development of a male hormonal contraceptive is an active research area. There are two main types of hormonal contraceptive formulations: ''combined methods'' which conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysmenorrhea
Dysmenorrhea, also known as period pain, painful periods or menstrual cramps, is pain during menstruation. Its usual onset occurs around the time that menstruation begins. Symptoms typically last less than three days. The pain is usually in the pelvis or lower abdomen. Other symptoms may include back pain, diarrhea or nausea. Dysmenorrhea can occur without an underlying problem. Underlying issues that can cause dysmenorrhea include uterine fibroids, adenomyosis, and most commonly, endometriosis. It is more common among those with heavy periods, irregular periods, those whose periods started before twelve years of age and those who have a low body weight. A pelvic exam and ultrasound in individuals who are sexually active may be useful for diagnosis. Conditions that should be ruled out include ectopic pregnancy, pelvic inflammatory disease, interstitial cystitis and chronic pelvic pain. Dysmenorrhea occurs less often in those who exercise regularly and those who have childre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder
Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) is a mood disorder characterized by emotional, cognitive, and physical symptoms that cause significant distress or impairment in menstruating women during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle. The symptoms occur in the luteal phase, (between ovulation and menses), improve within a few days after the onset of menses, and are minimal or absent in the week after menses. Code: 625.4 (N94.3) PMDD has a profound impact on a person's quality of life and dramatically increases the risk of suicidal ideation and even suicide attempts. Many females of reproductive age experience discomfort or mild mood changes prior to menstruation. However, 5-8% experience severe premenstrual syndrome causing significant distress or functional impairment. Within this population of reproductive age, some women will meet the criteria for PMDD. PMDD is most common from age 25–35, but can occur anytime during a woman's reproductive years. The exact cause of PMDD is cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatigue
Fatigue describes a state of tiredness that does not resolve with rest or sleep. In general usage, fatigue is synonymous with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that normally follows prolonged physical or mental activity. When it does not resolve after rest or sleep, or occurs independently of physical or mental exertion, it may be a symptom of a medical condition that may become severe or progressive. Fatigue can be a feature of a mental disorder such as depression; may be associated with conditions of chronic pain such as fibromyalgia; it may also feature in conditions of chronic low-level inflammation, and be a disease-related symptom in many other conditions. Fatigue often has no known cause, and is recognised as being very complex in nature. Fatigability describes a susceptibility to fatigue. Physical fatigue results from muscle fatigue brought about by intense physical activity. Mental fatigue results from prolonged periods of cognitive activity which impairs cognitive abil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Tenderness
Breast pain is the symptom of discomfort in either one or both breasts. Pain in both breasts is often described as ''breast tenderness'', is usually associated with the menstrual period and is not serious. Pain that involves only one part of a breast is more concerning, particularly if a hard mass or nipple discharge is also present. Causes may be related to the menstrual cycle, birth control pills, hormone therapy, or psychiatric medication. Pain may also occur in those with large breasts, during menopause, and in early pregnancy. In about 2% of cases breast pain is related to breast cancer. Diagnosis involves examination, with medical imaging if only a specific part of the breast hurts. In more than 75% of people the pain resolves without any specific treatment. Otherwise treatments may include paracetamol or NSAIDs. A well fitting bra may also help. In those with severe pain tamoxifen or danazol may be used. About 70% of women have breast pain at some point in time. Breast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premenstrual Syndrome
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) refers to emotional and physical symptoms that regularly occur in the one to two weeks before the start of each menstrual period. Symptoms resolve around the time menstrual bleeding begins. Different women experience different symptoms. Premenstrual syndrome is commonly noted by at least one physical, emotional, or behavioral symptom, that resolves with menses. The range of symptoms is wide, and most commonly are breast tenderness, bloating, headache, mood swings, depression, anxiety, anger, and irritability. They must interfere with daily living, during two menstrual cycles of prospective recording. These symptoms are nonspecific and may be seen in women without PMS. Often PMS-related symptoms are present for about six days. An individual's pattern of symptoms may change over time. Symptoms do not occur during pregnancy or following menopause.> Diagnosis requires a consistent pattern of emotional and physical symptoms occurring after ovulation and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
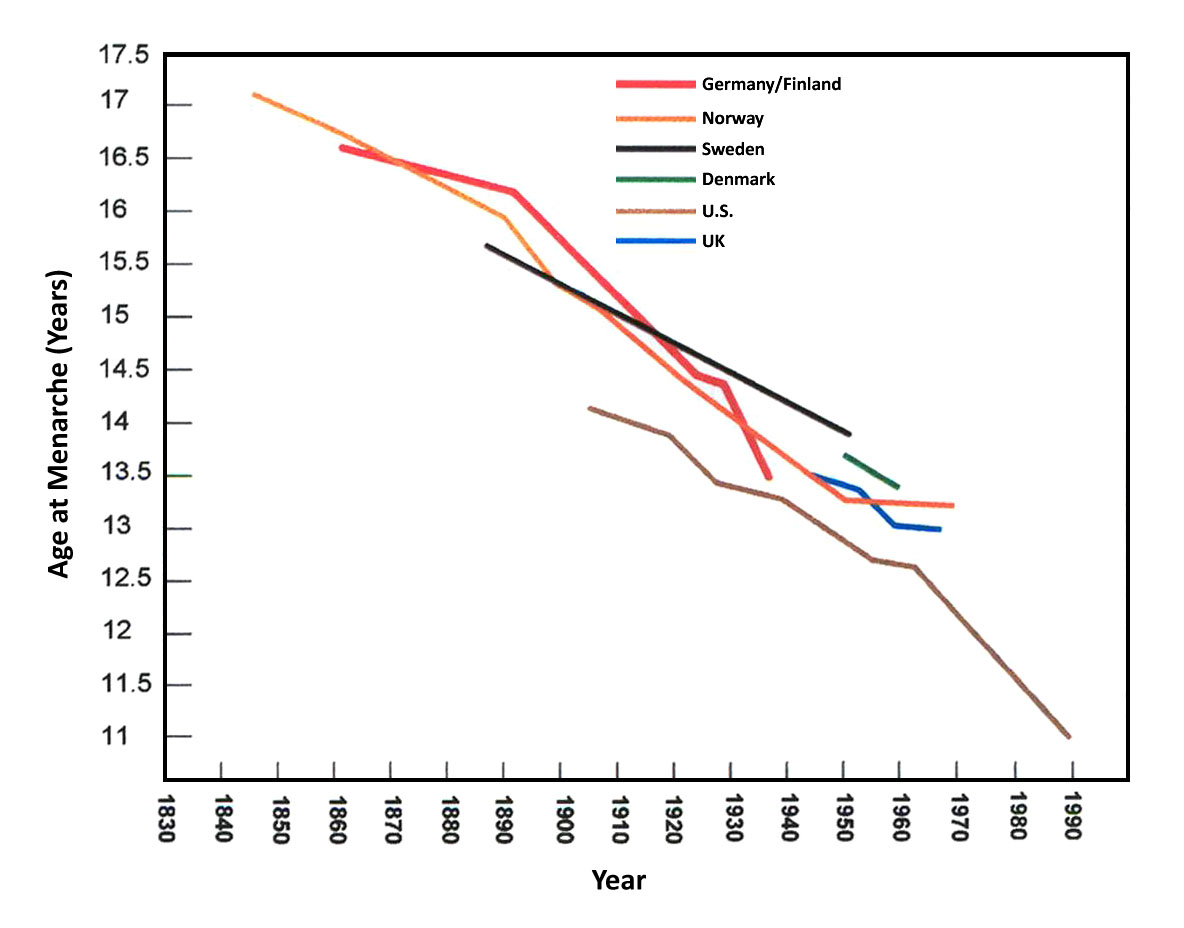
Menarche
Menarche ( ; ) is the first menstrual cycle, or first menstrual bleeding, in female humans. From both social and medical perspectives, it is often considered the central event of female puberty, as it signals the possibility of fertility. Girls experience menarche at different ages. Having menarche occur between the ages of 9–16 in the west is considered normal.US National Health Statistics Report September 2020 Canadian psychological researcher Niva Piran claims that menarche or the perceived average age of puberty is used in many cultures to separate girls from activity with boys, and to begin confinement as a woman and future wife. The timing of menarche is influenced by female , as we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |