|
Overclocking
In computing, overclocking is the practice of increasing the clock rate of a computer to exceed that certified by the manufacturer. Commonly, operating voltage is also increased to maintain a component's operational stability at accelerated speeds. Semiconductor devices operated at higher frequencies and voltages increase power consumption and heat. An overclocked device may be unreliable or fail completely if the additional heat load is not removed or power delivery components cannot meet increased power demands. Many device warranties state that overclocking or over-specification voids any warranty, but some manufacturers allow overclocking as long as it is done (relatively) safely. Overview The purpose of overclocking is to increase the operating speed of a given component. Normally, on modern systems, the target of overclocking is increasing the performance of a major chip or subsystem, such as the main processor or graphics controller, but other components, such as sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
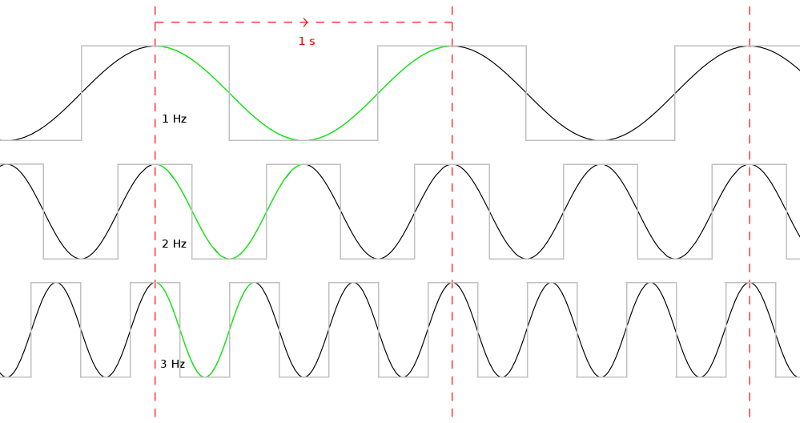
Clock Rate
Clock rate or clock speed in computing typically refers to the frequency at which the clock generator of a processor can generate pulses used to synchronize the operations of its components. It is used as an indicator of the processor's speed. Clock rate is measured in the SI unit of frequency hertz (Hz). The clock rate of the first generation of computers was measured in hertz or kilohertz (kHz), the first personal computers from the 1970s through the 1980s had clock rates measured in megahertz (MHz). In the 21st century the speed of modern CPUs is commonly advertised in gigahertz (GHz). This metric is most useful when comparing processors within the same family, holding constant other features that may affect performance. Determining factors Binning Manufacturers of modern processors typically charge higher prices for processors that operate at higher clock rates, a practice called binning. For a given CPU, the clock rates are determined at the end of the manufact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Underclocking
Underclocking, also known as downclocking, is modifying a computer or electronic circuit's timing settings to run at a lower clock rate than is specified. Underclocking is used to reduce a computer's power consumption, increase battery life, reduce heat emission, and it may also increase the system's stability, lifespan/reliability and compatibility. Underclocking may be implemented by the factory, but many computers and components may be underclocked by the end user. Underclocking is the opposite of overclocking. Types CPU underclocking For microprocessors, the purpose is generally to decrease the need for heat dissipation devices or decrease the electrical power consumption. This can provide increased system stability in high-heat environments, or can allow a system to run with a lower airflow (and therefore quieter) cooling fan or without one at all. For example, a Pentium 4 processor normally clocked at 3.4 GHz can be "underclocked" to 2 GHz and can then be safel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Enthusiast Computing
A gaming computer, also known as a gaming PC, is a specialized personal computer designed for playing PC games at high standards. They typically differ from mainstream personal computers by using high-performance graphics cards, a high core-count CPU with higher raw performance and higher-performance RAM. Gaming PCs are also used for other demanding tasks such as video editing. While often in desktop form, gaming PCs may also be laptops or handhelds. History Early history The Nimrod, designed by John Makepeace Bennett, built by Raymond Stuart-Williams and exhibited in the 1951 Festival of Britain, is regarded as the first gaming computer. Bennett did not intend for it to be a real gaming computer, however, as it was supposed to be an exercise in mathematics as well as to prove computers could "carry out very complex practical problems", not purely for enjoyment. Few years later, game consoles like the Magnavox Odyssey (released in 1972) and the Atari 2600 (released ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
CPU Multiplier
In computing, the clock multiplier (or CPU multiplier or bus/core ratio) sets the ratio of an internal CPU clock rate to the externally supplied clock. This may be implemented with phase-locked loop (PLL) frequency multiplier circuitry. A CPU with a 10x multiplier will thus see 10 internal cycles for every external clock cycle. For example, a system with an external clock of 100 MHz and a 36x clock multiplier will have an internal CPU clock of 3.6 GHz. The external address and data buses of the CPU (often collectively termed front side bus (FSB) in PC contexts) also use the external clock as a fundamental timing base; however, they could also employ a (small) multiple of this base frequency (typically two or four) to transfer data faster. The internal frequency of microprocessors is usually based on FSB frequency. To calculate internal frequency the CPU multiplies bus frequency by a number called the clock multiplier. For calculation, the CPU uses actual bus frequenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Motherboard
A motherboard, also called a mainboard, a system board, a logic board, and informally a mobo (see #Nomenclature, "Nomenclature" section), is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expandable systems. It holds and allows communication between many of the crucial electronic components of a system, such as the central processing unit (CPU) and computer memory, memory, and provides connectors for other peripherals. Unlike a backplane, a motherboard usually contains significant sub-systems, such as the CPU, the chipset's input/output and Memory controller, memory controllers, interface (computing), interface connectors, and other components integrated for general use. Nomenclature ''Oxford English Dictionary'' traces the origin of the word ''motherboard'' to 1965, its earliest-found attestation occurring in the magazine ''Electronics (magazine), Electronics''. The term alludes to its importance and size compared to the components attached to i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Central Processing Unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary Processor (computing), processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes Instruction (computing), instructions of a computer program, such as arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output (I/O) operations. This role contrasts with that of external components, such as main memory and I/O circuitry, and specialized coprocessors such as graphics processing units (GPUs). The form, CPU design, design, and implementation of CPUs have changed over time, but their fundamental operation remains almost unchanged. Principal components of a CPU include the arithmetic–logic unit (ALU) that performs arithmetic operation, arithmetic and Bitwise operation, logic operations, processor registers that supply operands to the ALU and store the results of ALU operations, and a control unit that orchestrates the #Fetch, fetching (from memory), #Decode, decoding and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Front-side Bus
The front-side bus (FSB) is a computer communication interface ( bus) that was often used in Intel-chip-based computers during the 1990s and 2000s. The EV6 bus served the same function for competing AMD CPUs. Both typically carry data between the central processing unit (CPU) and a memory controller hub, known as the northbridge. Depending on the implementation, some computers may also have a back-side bus that connects the CPU to the cache. This bus and the cache connected to it are faster than accessing the system memory (or RAM) via the front-side bus. The speed of the front side bus is often used as an important measure of the performance of a computer. The original front-side bus architecture was replaced by HyperTransport, Intel QuickPath Interconnect, and Direct Media Interface, followed by Intel Ultra Path Interconnect and AMD's Infinity Fabric. History The term came into use by Intel Corporation about the time the Pentium Pro and Pentium II products were announ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Copper Heat Sink With Pipes
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable, unalloyed metallic form. This means that copper is a native metal. This led to very early human use in several regions, from . Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, ; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, ; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create bronze, . Commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electrical Network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical components (e.g., batteries, resistors, inductors, capacitors, switches, transistors) or a model of such an interconnection, consisting of electrical elements (e.g., voltage sources, current sources, resistances, inductances, capacitances). An electrical circuit is a network consisting of a closed loop, giving a return path for the current. Thus all circuits are networks, but not all networks are circuits (although networks without a closed loop are often referred to as "open circuits"). A resistive network is a network containing only resistors and ideal current and voltage sources. Analysis of resistive networks is less complicated than analysis of networks containing capacitors and inductors. If the sources are constant ( DC) sources, the result is a DC network. The effective resistance and current distribution properties of arbitrary resistor networks can be modeled in terms of their graph measures and g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |