|
Over-accumulation
Overaccumulation is one of the potential causes of the crisis of capital accumulation. In crisis theory, a crisis of capital occurs due to what Karl Marx refers to as the internal contradictions inherent in the capitalist system which result in the reconfiguration of production. The contradiction in this situation is realized because of the condition of capitalism that requires the accumulation of capital through the continual reinvestment of surplus value. Accumulation can reach a point where the reinvestment of capital no longer produces returns. When a market becomes flooded with capital, a massive devaluation occurs. This overaccumulation is a condition that occurs when surpluses of devalued capital and labor exist side by side with seemingly no way to bring them together. The inability to procure adequate value stems from a lack of demand. The term "overaccumulation" is also used in a neoclassical context. Examples The Great Depression of the 1930s and 40s resulted, in par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Accumulation
Capital accumulation is the dynamic that motivates the pursuit of profit, involving the investment of money or any financial asset with the goal of increasing the initial monetary value of said asset as a financial return whether in the form of profit, rent, interest, royalties or capital gains. The aim of capital accumulation is to create new fixed and working capitals, broaden and modernize the existing ones, grow the material basis of social-cultural activities, as well as constituting the necessary resource for reserve and insurance. The process of capital accumulation forms the basis of capitalism, and is one of the defining characteristics of a capitalist economic system.''Capital'', Encyclopedia on Marxists.org: http://marxists.org/glossary/terms/c/a.htm#capital Definition The definition of capital accumulation is subject to controversy and ambiguities, because it could refer to: *a ''net addition'' to existing wealth *a ''redistribution'' of wealth. Most often, capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crisis Theory
Crisis theory, concerning the causes and consequences of the tendency for the rate of profit to fall in a capitalist system, is associated with Marxian critique of political economy, and was further popularised through Marxist economics. History Earlier analysis by Jean Charles Léonard de Sismondi provided the first suggestions of the systemic roots of Crisis. "The distinctive feature of Sismondi's analysis is that it is geared to an explicit dynamic model in the modern sense of this phrase ... Sismondi's great merit is that he used, systematically and explicitly, a schema of periods, that is, that he was the first to practice the particular method of dynamics that is called period analysis". Marx praised and built on Sismondi's theoretical insights. Rosa Luxemburg and Henryk Grossman both subsequently drew attention to both Sismondi's work on the nature of capitalism, and as a reference point for Karl Marx. Grossman in particular pointed out how Sismondi had contributed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marxian Economics
Marxian economics, or the Marxian school of economics, is a Heterodox economics, heterodox school of political economic thought. Its foundations can be traced back to Karl Marx, Karl Marx's Critique of political economy#Marx's critique of political economy, critique of political economy. However, unlike Critique of political economy, critics of political economy, Marxian economists tend to accept the concept of economy, the economy prima facie. Marxian economics comprises several different theories and includes multiple schools of thought, which are sometimes opposed to each other; in many cases Marxian analysis is used to complement, or to supplement, other economic approaches. Because one does not necessarily have to be politically Marxism, Marxist to be economically Marxian, the two adjectives coexist in usage, rather than being synonymous: They share a semantic field, while also allowing both connotation, connotative and denotation, denotative differences. Marxian economics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for Profit (economics), profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, private property, Property rights (economics), property rights recognition, voluntary exchange, and wage labor. In a market economy, decision-making and investments are determined by owners of wealth, property, or ability to maneuver capital or production ability in Capital market, capital and financial markets—whereas prices and the distribution of goods and services are mainly determined by competition in goods and services markets. Economists, historians, political economists and sociologists have adopted different perspectives in their analyses of capitalism and have recognized various forms of it in practice. These include ''Laissez-faire capitalism, laissez-faire'' or free-market capitalism, anarcho-capitalism, state capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
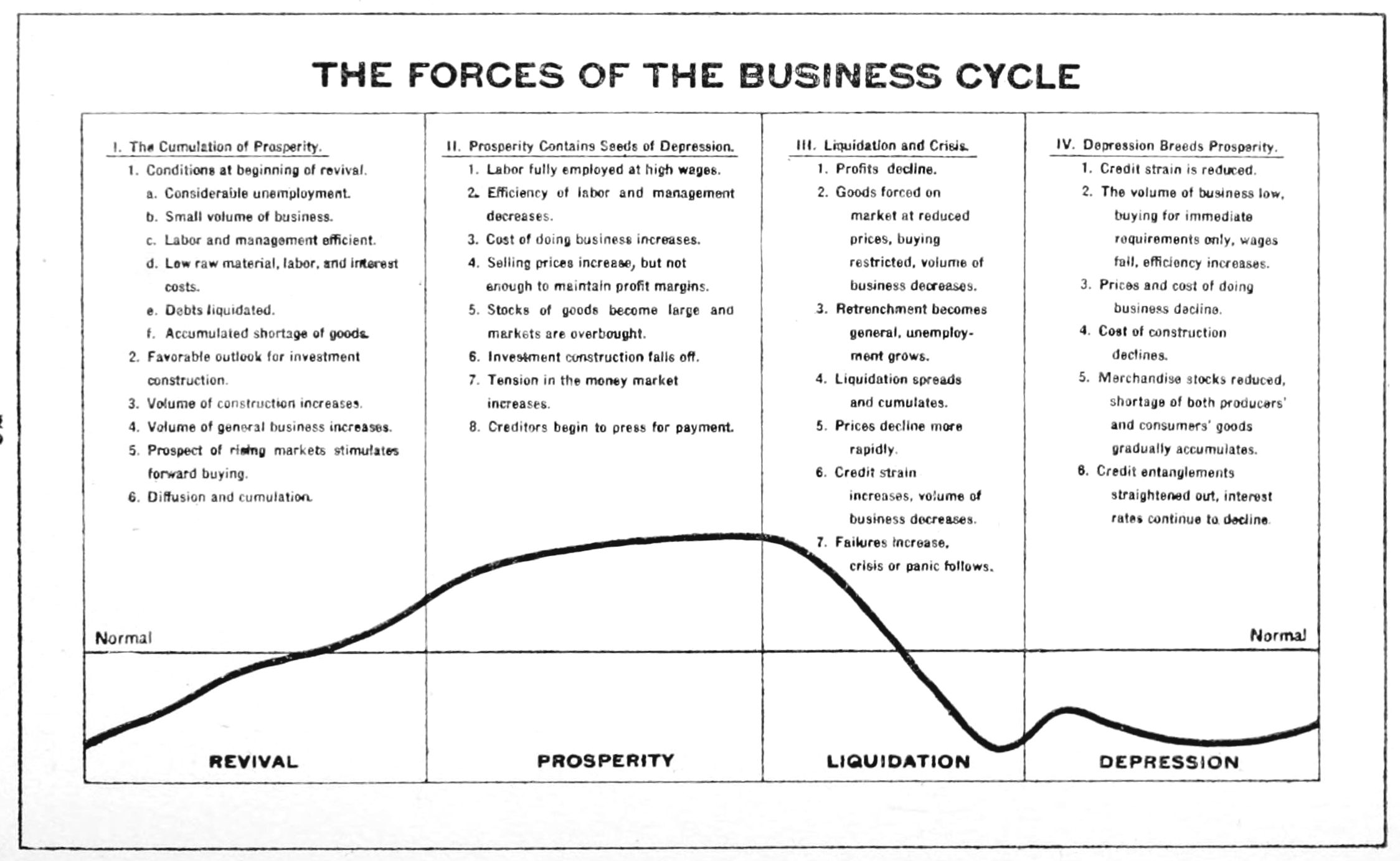
Business Cycle
Business cycles are intervals of Economic expansion, expansion followed by recession in economic activity. These changes have implications for the welfare of the broad population as well as for private institutions. Typically business cycles are measured by examining trends in a broad economic indicator such as Real Gross Domestic Production. Business cycle fluctuations are usually characterized by general upswings and downturns in a span of macroeconomic variables. The individual episodes of expansion/recession occur with changing duration and intensity over time. Typically their periodicity has a wide range from around 2 to 10 years (the technical phrase "stochastic cycle" is often used in statistics to describe this kind of process.) As in [Harvey, Trimbur, and van Dijk, 2007, ''Journal of Econometrics''], such flexible knowledge about the frequency of business cycles can actually be included in their mathematical study, using a Bayesian statistical paradigm. There are numer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Accumulation
Capital accumulation is the dynamic that motivates the pursuit of profit, involving the investment of money or any financial asset with the goal of increasing the initial monetary value of said asset as a financial return whether in the form of profit, rent, interest, royalties or capital gains. The aim of capital accumulation is to create new fixed and working capitals, broaden and modernize the existing ones, grow the material basis of social-cultural activities, as well as constituting the necessary resource for reserve and insurance. The process of capital accumulation forms the basis of capitalism, and is one of the defining characteristics of a capitalist economic system.''Capital'', Encyclopedia on Marxists.org: http://marxists.org/glossary/terms/c/a.htm#capital Definition The definition of capital accumulation is subject to controversy and ambiguities, because it could refer to: *a '' net addition'' to existing wealth *a ''redistribution'' of wealth. Most often, capita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underconsumption
Underconsumption is a theory in economics that recessions and stagnation arise from an inadequate consumer demand, relative to the amount produced. In other words, there is a problem of overproduction and overinvestment during a demand crisis. The theory formed the basis for the development of Keynesian economics and the theory of aggregate demand after the 1930s. Underconsumption theory narrowly refers to heterodox economists in Britain in the 19th century, particularly from 1815 onwards, who advanced the theory of underconsumption and rejected classical economics in the form of Ricardian economics. The economists did not form a unified school, and their theories were rejected by mainstream economics of the time. Underconsumption is an old concept in economics that goes back to the 1598 French mercantilist text ''Les Trésors et richesses pour mettre l'Estat en Splendeur'' (''The Treasures and riches to put the State in Splendor'') by Barthélemy de Laffemas, if not earlier. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overproduction
In economics, overproduction, oversupply, excess of supply or glut refers to excess of supply over demand of products being offered to the market. This leads to lower prices and/or unsold goods along with the possibility of unemployment. The demand side equivalent is underconsumption Underconsumption is a theory in economics that recessions and stagnation arise from an inadequate consumer demand, relative to the amount produced. In other words, there is a problem of overproduction and overinvestment during a demand crisis. The ...; some consider supply and demand two sides to the same coin – excess supply is only relative to a given demand, and insufficient demand is only relative to a given supply – and thus consider overproduction and underconsumption equivalent. Overproduction is often attributed as due to previous overinvestment – creation of excess productive capacity, which must then either lie idle (or under capacity), which is unprofit (economics), profitable, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagion began around September and led to the Wall Street stock market crash of October 24 (Black Thursday). It was the longest, deepest, and most widespread depression of the 20th century. Between 1929 and 1932, worldwide gross domestic product (GDP) fell by an estimated 15%. By comparison, worldwide GDP fell by less than 1% from 2008 to 2009 during the Great Recession. Some economies started to recover by the mid-1930s. However, in many countries, the negative effects of the Great Depression lasted until the beginning of World War II. Devastating effects were seen in both rich and poor countries with falling personal income, prices, tax revenues, and profits. International trade fell by more than 50%, unemployment in the U.S. rose to 23% and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crisis Theory
Crisis theory, concerning the causes and consequences of the tendency for the rate of profit to fall in a capitalist system, is associated with Marxian critique of political economy, and was further popularised through Marxist economics. History Earlier analysis by Jean Charles Léonard de Sismondi provided the first suggestions of the systemic roots of Crisis. "The distinctive feature of Sismondi's analysis is that it is geared to an explicit dynamic model in the modern sense of this phrase ... Sismondi's great merit is that he used, systematically and explicitly, a schema of periods, that is, that he was the first to practice the particular method of dynamics that is called period analysis". Marx praised and built on Sismondi's theoretical insights. Rosa Luxemburg and Henryk Grossman both subsequently drew attention to both Sismondi's work on the nature of capitalism, and as a reference point for Karl Marx. Grossman in particular pointed out how Sismondi had contributed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Economic Theory
The ''Journal of Economic Theory'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed academic journal covering the field of economic theory. Karl Shell has served as editor-in-chief of the journal since it was established in 1968. Since 2000, he has shared the editorship with Jess Benhabib, Alessandro Lizzeri, Christian Hellwig, and more recently with Alessandro Pavan, Ricardo Lagos, Marciano Siniscalchi, and Xavier Vives. The journal is published by Elsevier. In 2020, Tilman Börgers was chief editor of the journal. Abstracting and indexing According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 1.458. See also *List of economics journals The following is a list of scholarly journals in economics containing most of the prominent academic journals in economics. Popular magazines or other publications related to economics, finance, or business are not listed. A *'' Affilia'' *''A ... References External links * Economics journals Elsevier academic jou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Economics
Neoclassical economics is an approach to economics in which the production, consumption and valuation (pricing) of goods and services are observed as driven by the supply and demand model. According to this line of thought, the value of a good or service is determined through a hypothetical maximization of utility by income-constrained individuals and of profits by firms facing production costs and employing available information and factors of production. This approach has often been justified by appealing to rational choice theory, a theory that has come under considerable question in recent years. Neoclassical economics historically dominated macroeconomics and, together with Keynesian economics, formed the neoclassical synthesis which dominated mainstream economics as "neo-Keynesian economics" from the 1950s to the 1970s.Clark, B. (1998). ''Principles of political economy: A comparative approach''. Westport, Connecticut: Praeger. Nadeau, R. L. (2003). ''The Wealth of Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |