|
Out-of-pocket Expense
An out-of-pocket expense (or out-of-pocket cost, OOP) is the direct payment of money that may or may not be later reimbursed from a third-party source. For example, when operating a vehicle, gasoline, parking fees and tolls are considered out-of-pocket expenses for a trip. Car insurance, oil changes, and interest are not, since the outlay of cash covers expenses accrued over a longer period of time. The services rendered and other in-kind expenses are not considered out-of-pocket expenses; the same goes for depreciation of capital goods or depletion. Organizations often reimburse out-of-pocket expenses incurred on their behalf, especially expenses incurred by employees on their employers' behalf. In the United States, out-of-pocket expenses for such things as charity, medical bills, and education may be deductions on US income taxes, according to IRS regulations. To be out of pocket is to have expended personal resources, often unexpectedly or unfairly, at the end of some ente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reimbursement
Reimbursement is the act of compensating someone for an out-of-pocket expense by giving them an amount of money equal to what was spent. Companies, governments and nonprofit organizations may compensate their employees or officers for necessary and reasonable expenses; under US law, these expenses may be deducted from taxes by the organization and treated as untaxed income for the recipient provided that accountability conditions are met. UK law provides for deductions for travel and subsistence. Reimbursement is also provided for supply, day care, mobile, medical, or education expenses, as determined by the payer. Similarly, a university, academic conference, or business conference may reimburse the expenses of an invited speaker or attendee. Reimbursement is also used in insurance, when a provider pays for expenses after they have been paid directly by the policy holder or another party. This is especially relevant in health insurance, due to urgency, high costs, and administ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Income Taxes
Income taxes in the United States are imposed by the federal government, and most states. The income taxes are determined by applying a tax rate, which may increase as income increases, to taxable income, which is the total income less allowable deductions. Income is broadly defined. Individuals and corporations are directly taxable, and estates and trusts may be taxable on undistributed income. Partnerships are not taxed (with some exceptions in the case of Federal income taxation), but their partners are taxed on their shares of partnership income. Residents and citizens are taxed on worldwide income, while nonresidents are taxed only on income within the jurisdiction. Several types of credits reduce tax, and some types of credits may exceed tax before credits. An alternative tax applies at the federal and some state levels. In the United States, the term "payroll tax" usually refers to FICA taxes that are paid to fund Social Security and Medicare, while "income tax" ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Finance
Personal finance is the financial management which an individual or a family unit performs to budget, save, and spend monetary resources over time, taking into account various financial risks and future life events. When planning personal finances, the individual would consider the suitability to his or her needs of a range of banking products ( checking, savings accounts, credit cards and consumer loans) or investment in private equity, ( companies' shares, bonds, mutual funds) and insurance (life insurance, health insurance, disability insurance) products or participation and monitoring of and- or employer-sponsored retirement plans, social security benefits, and income tax management. History Before a specialty in personal finance was developed, various disciplines which are closely related to it, such as family economics, and consumer economics were taught in various colleges as part of home economics for over 100 years. The earliest known research in personal financ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Good
The economic concept of a capital good (also called complex product systems (CoPS),H. Rush, "Managing innovation in complex product systems (CoPS)," IEE Colloquium on EPSRC Technology Management Initiative (Engineering & Physical Sciences Research Council), London, UK, 1997, pp. 4/1-4/4, doi: 10.1049/ic:19971215. and means of production) is as a "...series of heterogeneous commodities, each having specific technical characteristics ..." in the form of a durable good that is used in the production of goods or services. Capital goods are a particular form of economic good and are tangible property. A society acquires capital goods by saving wealth that can be invested in the means of production. People use them to produce other goods or services within a certain period. Machinery, tools, buildings, computers, or other kinds of equipment that are involved in the production of other things for sale are capital goods. The owners of the capital good can be individuals, households, corpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Car Costs
The car internal costs are all the costs consumers pay to own and operate a car. Normally these expenditures are divided by fixed or standing costs and variable or running costs. Fixed costs are those ones which do not depend on the distance traveled by the vehicle and which the owner must pay to keep the vehicle ready for use on the road, like insurance or road taxes. Variable or running costs are those that depend on the use of the car, like fuel or tolls. Compared to other popular modes of passenger transportation, especially buses or trains, the car has a relatively high cost per passenger-distance traveled. Motorists in the United Kingdom spend, on average, roughly 1/3 of their average net income to operate a car, while motorists in Portugal spend approximately 1/2 of their net income. For the average car owner, depreciation constitutes about half the cost of running a car. The typical motorist underestimates this fixed cost by a significant margin. The IRS considers tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
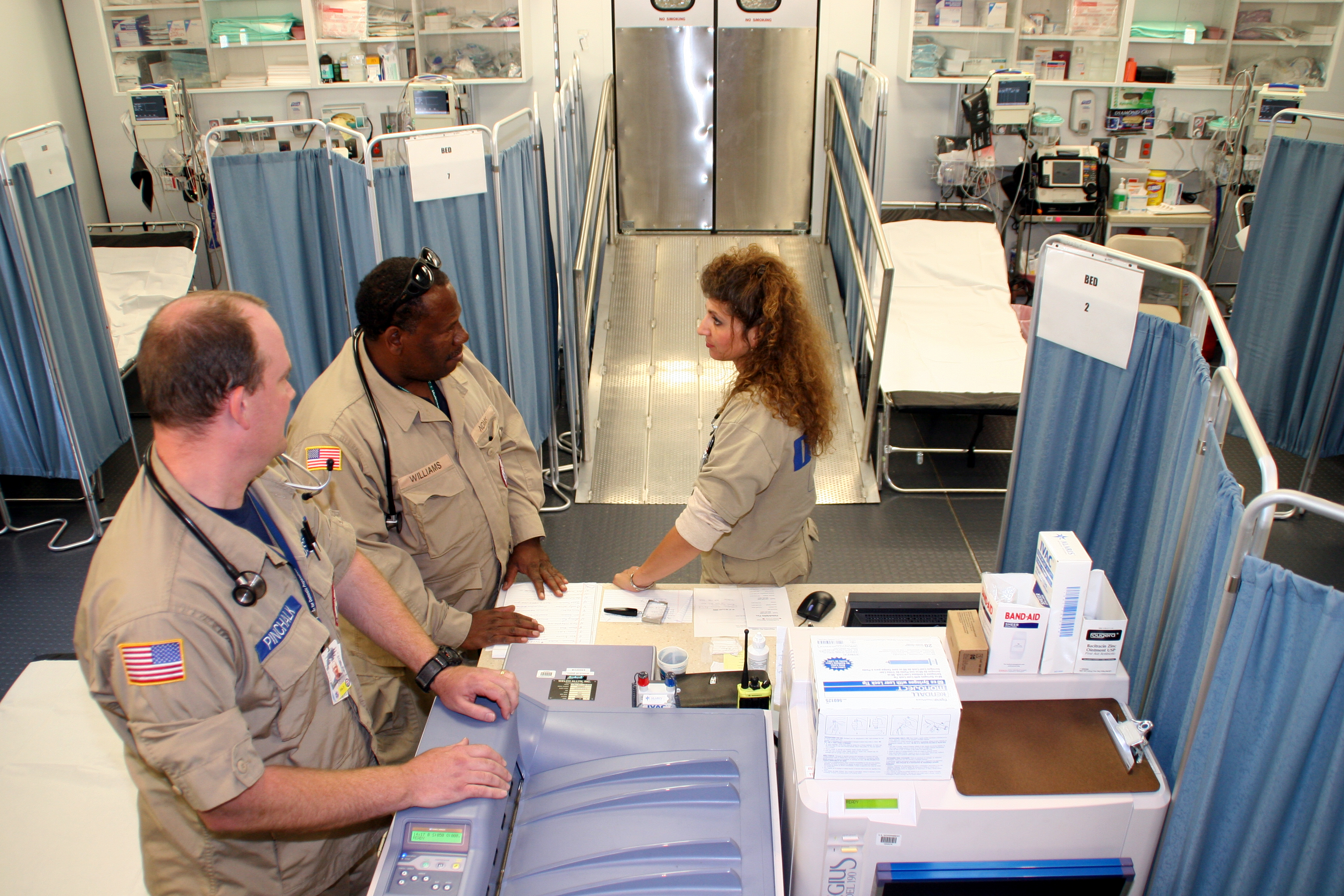
Emergency Department
An emergency department (ED), also known as an accident and emergency department (A&E), emergency room (ER), emergency ward (EW) or casualty department, is a medical treatment facility specializing in emergency medicine, the acute care of patients who present without prior appointment; either by their own means or by that of an ambulance. The emergency department is usually found in a hospital or other primary care center. Due to the unplanned nature of patient attendance, the department must provide initial treatment for a broad spectrum of illnesses and injuries, some of which may be life-threatening and require immediate attention. In some countries, emergency departments have become important entry points for those without other means of access to medical care. The emergency departments of most hospitals operate 24 hours a day, although staffing levels may be varied in an attempt to reflect patient volume. History Accident services were provided by workmen's compensation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicare Part D
Medicare Part D, also called the Medicare prescription drug benefit, is an optional United States federal-government program to help Medicare beneficiaries pay for self-administered prescription drugs. Part D was enacted as part of the Medicare Modernization Act of 2003 and went into effect on January 1, 2006. Under the program, drug benefits are provided by private insurance plans that receive premiums from both enrollees and the government. Part D plans typically pay most of the cost for prescriptions filled by their enrollees. However, plans are later reimbursed for much of this cost through rebates paid by manufacturers and pharmacies. Part D enrollees cover a portion of their own drug expenses by paying cost-sharing. The amount of cost-sharing an enrollee pays depends on the retail cost of the filled drug, the rules of their plan, and whether they are eligible for additional Federal income-based subsidies. Prior to 2010, enrollees were required to pay 100% of their retail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Care System
Health, according to the World Health Organization, is "a state of complete physical, Mental health, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity".World Health Organization. (2006)''Constitution of the World Health Organization''– ''Basic Documents'', Forty-fifth edition, Supplement, October 2006. A variety of definitions have been used for different purposes over time. Health can be promoted by encouraging healthful activities, such as regular physical exercise and adequate sleep, and by reducing or avoiding unhealthful activities or situations, such as smoking or excessive Stress (biology), stress. Some factors affecting health are due to Agency (sociology), individual choices, such as whether to engage in a high-risk behavior, while others are due to Social structure, structural causes, such as whether the society is arranged in a way that makes it easier or harder for people to get necessary healthcare services. Still, other factors are be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic compounds obtained by the fractional distillation of petroleum, enhanced with a variety of additives. On average, U.S. refineries produce, from a barrel of crude oil, about 19 to 20 gallons of gasoline; 11 to 13 gallons of distillate fuel (most of which is sold as diesel fuel); and 3 to 4 gallons of jet fuel. The product ratio depends on the processing in an oil refinery and the crude oil assay. A barrel of oil is defined as holding 42 US gallons, which is about 159 liters or 35 imperial gallons. The characteristic of a particular gasoline blend to resist igniting too early (which causes knocking and reduces efficiency in reciprocating engines) is measured by its octane rating, which is produced in several grades. Tetraethyl lead and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depletion (accounting)
Depletion is an accounting and tax concept used most often in the mining, timber, and petroleum industries. It is similar to depreciation in that it is a cost recovery system for accounting and tax reporting: "The depletion deduction" allows an owner or operator to account for the reduction of a product's reserves. Types of depletion For tax purposes, the two types of depletion are percentage depletion and cost depletion. For mineral property, the method leading to the largest deduction is generally used. For standing timber, use of the cost depletion method is required. Depletion, for both accounting purposes and United States tax purposes, is a method of recording the gradual expense or use of natural resources over time. Depletion is the using up of natural resources by mining, quarrying, drilling, or felling. According to the IRS Newswire, over 50 percent of oil and gas extraction businesses use cost depletion to figure their depletion deduction. Mineral property include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Goods
The economic concept of a capital good (also called complex product systems (CoPS),H. Rush, "Managing innovation in complex product systems (CoPS)," IEE Colloquium on EPSRC Technology Management Initiative (Engineering & Physical Sciences Research Council), London, UK, 1997, pp. 4/1-4/4, doi: 10.1049/ic:19971215. and means of production) is as a "...series of heterogeneous commodities, each having specific technical characteristics ..." in the form of a durable good that is used in the production of goods or services. Capital goods are a particular form of economic good and are tangible property. A society acquires capital goods by saving wealth that can be invested in the means of production. People use them to produce other goods or services within a certain period. Machinery, tools, buildings, computers, or other kinds of equipment that are involved in the production of other things for sale are capital goods. The owners of the capital good can be individuals, households, corp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |