|
Osteocalcin
Osteocalcin, also known as bone gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing protein (BGLAP), is a small (49-amino-acid) noncollagenous protein hormone found in bone and dentin, first identified as a calcium-binding protein. Because osteocalcin has gla domains, its synthesis is vitamin K dependent. In humans, osteocalcin is encoded by the ''BGLAP'' gene. Its receptors include GPRC6A, GPR158, and possibly a third, yet-to-be-identified receptor. There is evidence that GPR37 might be the third osteocalcin receptor. Function Osteocalcin is secreted solely by osteoblasts and thought to play a role in the body's metabolic regulation. In its carboxylated form it binds calcium directly and thus concentrates in bone. In its uncarboxylated form, osteocalcin acts as a hormone in the body, signalling in the pancreas, fat, muscle, testes, and brain. * In the pancreas, osteocalcin acts on beta cells, causing beta cells in the pancreas to release more insulin. * In fat cells, osteocalcin triggers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoblasts
Osteoblasts (from the Greek language, Greek combining forms for "bone", ὀστέο-, ''osteo-'' and βλαστάνω, ''blastanō'' "germinate") are cell (biology), cells with a single Cell nucleus, nucleus that synthesize bone. However, in the process of bone formation, osteoblasts function in groups of connected cells. Individual cells cannot make bone. A group of organized osteoblasts together with the bone made by a unit of cells is usually called the osteon. Osteoblasts are specialized, terminally differentiated products of mesenchymal stem cells. They synthesize dense, crosslinked collagen and specialized proteins in much smaller quantities, including osteocalcin and osteopontin, which compose the organic matrix of bone. In organized groups of disconnected cells, osteoblasts produce hydroxylapatite, the bone mineral, that is deposited in a highly regulated manner, into the organic matrix forming a strong and dense mineralized tissues, mineralized tissue, the mineralized mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin K
Vitamin K refers to structurally similar, fat-soluble vitamers found in foods and marketed as dietary supplements. The human body requires vitamin K for post-synthesis modification of certain proteins that are required for blood coagulation (K from ''Koagulation'', German for "coagulation") or for controlling binding of calcium in bones and other tissues. The complete synthesis involves final modification of these so-called "Gla proteins" by the enzyme gamma-glutamyl carboxylase that uses vitamin K as a cofactor. Vitamin K is used in the liver as the intermediate VKH2 to deprotonate a glutamate residue and then is reprocessed into vitamin K through a vitamin K oxide intermediate. The presence of uncarboxylated proteins indicates a vitamin K deficiency. Carboxylation allows them to bind (chelate) calcium ions, which they cannot do otherwise. Without vitamin K, blood coagulation is seriously impaired, and uncontrolled bleeding occurs. Research suggests that deficiency of v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPRC6A
G protein-coupled receptor family C group 6 member A (GPRC6A) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GPRC6A'' gene. This protein functions as a receptor of L-α-amino acids, cations (e.g., calcium), osteocalcin, and steroids. It is a membrane androgen receptor. Clinical significance GPRC6A has also been linked to prostate cancer progression, and it has been shown to mediate rapid, non-genomic prostate cancer cell responses to testosterone. See also * ZIP9 Zinc transporter ZIP9, also known as Zrt- and Irt-like protein 9 (ZIP9) and solute carrier family 39 member 9, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC39A9'' gene. This protein is the 9th member out of 14 ZIP family proteins, which is ... References Further reading * * * * * External links * * G protein-coupled receptors {{transmembranereceptor-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactoferrin
Lactoferrin (LF), also known as lactotransferrin (LTF), is a multifunctional protein of the transferrin family. Lactoferrin is a globular glycoprotein with a molecular mass of about 80 kDa that is widely represented in various secretory fluids, such as milk, saliva, tears, and nasal secretions. Lactoferrin is also present in secondary granules of PMNs and is secreted by some acinar cells. Lactoferrin can be purified from milk or produced recombinantly. Human colostrum (''"first milk"'') has the highest concentration, followed by human milk, then cow milk (150 mg/L). Lactoferrin is one of the components of the immune system of the body; it has antimicrobial activity (bacteriocide, fungicide) and is part of the innate defense, mainly at mucoses. In particular, lactoferrin provides antibacterial activity to human infants. Lactoferrin interacts with DNA and RNA, polysaccharides and heparin, and shows some of its biological functions in complexes with these ligands. Lactoferri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gla Domain
Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation/gamma-carboxyglutamic (GLA) domain is a protein domain that contains post-translational modifications of many glutamate residues by vitamin K-dependent carboxylation to form γ-carboxyglutamate (Gla). Proteins with this domain are known informally as Gla proteins. The Gla residues are responsible for the high-affinity binding of calcium ions. The GLA domain binds calcium ions by chelating them between two carboxylic acid residues. These residues are part of a region that starts at the N-terminal extremity of the mature form of Gla proteins, and that ends with a conserved aromatic residue. This results in a conserved Gla-x(3)-Gla-x-Cys motif that is found in the middle of the domain, and which seems to be important for substrate recognition by the carboxylase. The 3D structures of several Gla domains have been solved. Calcium ions induce conformational changes in the Gla domain and are necessary for the Gla domain to fold properly. A common structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fight-or-flight Response
The fight-or-flight or the fight-flight-or-freeze response (also called hyperarousal or the acute stress response) is a physiological reaction that occurs in response to a perceived harmful event, attack, or threat to survival. It was first described by Walter Bradford Cannon. His theory states that animals react to threats with a general discharge of the sympathetic nervous system, preparing the animal for fighting or fleeing. More specifically, the adrenal medulla produces a hormonal cascade that results in the secretion of catecholamines, especially norepinephrine and epinephrine. The hormones estrogen, testosterone, and cortisol, as well as the neurotransmitters dopamine and serotonin, also affect how organisms react to stress. The hormone osteocalcin might also play a part. This response is recognised as the first stage of the general adaptation syndrome that regulates stress responses among vertebrates and other organisms. Name Originally understood as the fight-o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossification
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in the formation of normal, healthy bone tissue: Intramembranous ossification is the direct laying down of bone into the primitive connective tissue ( mesenchyme), while endochondral ossification involves cartilage as a precursor. In fracture healing, endochondral osteogenesis is the most commonly occurring process, for example in fractures of long bones treated by plaster of Paris, whereas fractures treated by open reduction and internal fixation with metal plates, screws, pins, rods and nails may heal by intramembranous osteogenesis. Heterotopic ossification is a process resulting in the formation of bone tissue that is often atypical, at an extraskeletal location. Calcification is often confused with ossification. Calcification is sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Male Fertility
Fertility is the capability to produce offspring through reproduction following the onset of sexual maturity. The fertility rate is the average number of children born by a female during her lifetime and is quantified demographically. Fertility is addressed when there is a difficulty or an inability to reproduce naturally, which is referred to as infertility. Infertility is widespread, with fertility specialists available all over the world to assist mothers and couples who experience difficulties having a baby. Human fertility depends on factors of nutrition, sexual behaviour, consanguinity, culture, instinct, endocrinology, timing, economics, personality, way of life, and emotions. Fertility differs from fecundity, which is defined as the ''potential'' for reproduction (influenced by gamete production, fertilization and carrying a pregnancy to term). Where a woman or the lack of fertility is infertility while a lack of fecundity would be called sterility. Demography In de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
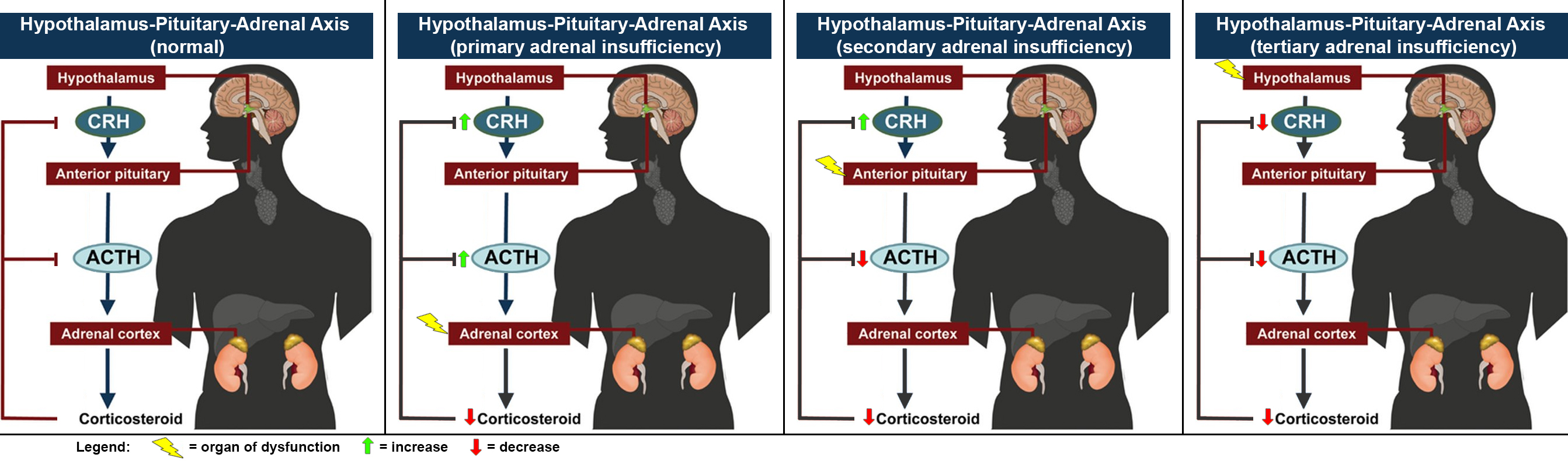
Adrenal Insufficiency
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones. The adrenal gland normally secretes glucocorticoids (primarily cortisol), mineralocorticoids (primarily aldosterone), and androgens. These hormones are important in regulating blood pressure, electrolytes, and metabolism as a whole. Deficiency of these hormones leads to symptoms ranging from abdominal pain, vomiting, muscle weakness and fatigue, low blood pressure, depression, mood and personality changes (in mild cases) to organ failure and shock (in severe cases). An adrenal crisis may occur if the body is subjected to stress, such as an accident, injury, surgery, or severe infection; this is a life-threatening medical condition resulting from severe deficiency of cortisol in the body. Death may quickly follow. Adrenal insufficiency can be caused by dysfunction of the adrenal gland itself, whether by destruction (e.g. Addison's disease), failure of development ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teriparatide
Teriparatide, sold under the brand name Forteo, is a form of parathyroid hormone (PTH) consisting of the first (N-terminus) 34 amino acids, which is the bioactive portion of the hormone. It is an effective anabolic (promoting bone formation) agent used in the treatment of some forms of osteoporosis. It is also occasionally used off-label to speed fracture healing. Teriparatide is identical to a portion of human parathyroid hormone and intermittent use activates osteoblasts more than osteoclasts, which leads to an overall increase in bone. Medical uses It is effective in growing bone (e.g., 8% increase in bone density in the spine after one year) and reducing the risk of fragility fractures. When studied, teriparatide only showed bone mineral density (BMD) improvement during the first 18 months of use. Teriparatide should only be used for a period of 2 years maximum. After 2 years, another agent such a bisphosphonate or denosumab should be used in cases of osteoporosis although re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Mineral Density
Bone density, or bone mineral density, is the amount of bone mineral in bone tissue. The concept is of mass of mineral per volume of bone (relating to density in the physics sense), although clinically it is measured by proxy according to optical density per square centimetre of bone surface upon imaging. Bone density measurement is used in clinical medicine as an indirect indicator of osteoporosis and fracture risk. It is measured by a procedure called densitometry, often performed in the radiology or nuclear medicine departments of hospitals or clinics. The measurement is painless and non-invasive and involves low radiation exposure. Measurements are most commonly made over the lumbar spine and over the upper part of the hip. The forearm may be scanned if the hip and lumbar spine are not accessible. There is a statistical association between poor bone density and higher probability of fracture. Fractures of the legs and pelvis due to falls are a significant public health pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)