|
Osmotic Power Plant
Osmotic power, salinity gradient power or blue energy is the energy available from the difference in the salt concentration between seawater and river water. Two practical methods for this are reverse electrodialysis (RED) and pressure retarded osmosis (PRO). Both processes rely on osmosis with membranes. The key waste product is brackish water. This byproduct is the result of natural forces that are being harnessed: the flow of fresh water into seas that are made up of salt water. In 1954, Pattle suggested that there was an untapped source of power when a river mixes with the sea, in terms of the lost osmotic pressure, however it was not until the mid ‘70s where a practical method of exploiting it using selectively permeable membranes by Loeb was outlined. The method of generating power by pressure retarded osmosis was invented by Prof. Sidney Loeb in 1973 at the Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beersheba, Israel. The idea came to Prof. Loeb, in part, as he observed the J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure Retarded Osmosis
Pressure retarded osmosis (PRO) is a technique to separate a solvent (for example, fresh water) from a solution that is more concentrated (e.g. sea water) and also pressurized. A semipermeable membrane allows the solvent to pass to the concentrated solution side by osmosis. The technique can be used to generate power from the salinity gradient energy resulting from the difference in the salt concentration between sea and river water. In PRO, the water potential between fresh water and sea water corresponds to a pressure of 26 Bar (unit), bars. This pressure is equivalent to a column of water (hydraulic head) 270 meters high. However, the optimal working pressure is only half of this, 11 to 15 bar. History This method of generating power was invented by Sidney Loeb, Prof. Sidney Loeb in 1973 at the Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beersheba, Israel. In 2014 researchers verified that 95% of a PRO system's theoretical power output can be produced with a membrane that is half ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure-retarded Osmosis
Pressure retarded osmosis (PRO) is a technique to separate a solvent (for example, fresh water) from a solution that is more concentrated (e.g. sea water) and also pressurized. A semipermeable membrane allows the solvent to pass to the concentrated solution side by osmosis. The technique can be used to generate power from the salinity gradient energy resulting from the difference in the salt concentration between sea and river water. In PRO, the water potential between fresh water and sea water corresponds to a pressure of 26 bars. This pressure is equivalent to a column of water (hydraulic head) 270 meters high. However, the optimal working pressure is only half of this, 11 to 15 bar. History This method of generating power was invented by Prof. Sidney Loeb in 1973 at the Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beersheba, Israel. In 2014 researchers verified that 95% of a PRO system's theoretical power output can be produced with a membrane that is half (or less) the size neede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
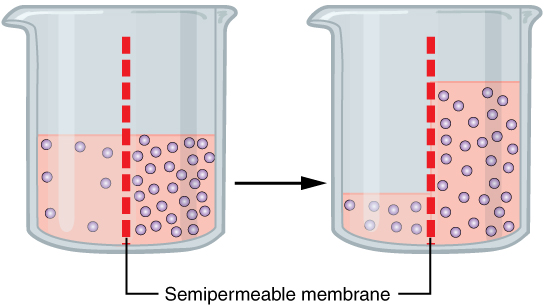
Osmosis
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region of higher solute concentration), in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. It may also be used to describe a physical process in which any solvent moves across a selectively permeable membrane (permeable to the solvent, but not the solute) separating two solutions of different concentrations. Osmosis can be made to do work. Osmotic pressure is defined as the external pressure required to be applied so that there is no net movement of solvent across the membrane. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property, meaning that the osmotic pressure depends on the molar concentration of the solute but not on its identity. Osmosis is a vital process in biological systems, as biological membranes are semiperm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seawater
Seawater, or salt water, is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has approximately of dissolved salts (predominantly sodium () and chloride () ions). The average density at the surface is 1.025 kg/L. Seawater is denser than both fresh water and pure water (density 1.0 kg/L at ) because the dissolved salts increase the mass by a larger proportion than the volume. The freezing point of seawater decreases as salt concentration increases. At typical salinity, it freezes at about . The coldest seawater still in the liquid state ever recorded was found in 2010, in a stream under an Antarctic glacier: the measured temperature was . Seawater pH is typically limited to a range between 7.5 and 8.4. However, there is no universally accepted reference pH-scale for seawater and the difference between measurement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statkraft Osmotic Power Prototype In Hurum
Statkraft osmotic power prototype is the world's first osmotic power plant, based on the energy of osmosis. The power plant is run by Statkraft. The power plant is located at Tofte in Hurum, Norway, with rooms at the factory area at Södra Cell Tofte cellulose factory. The power plant uses the osmotic gradient that occurs when fresh water and salt water meet, separated by a permeable membrane. The salt water pulls fresh water through the membrane and the pressure increases on the salt water side; this pressure increase can be used to produce electrical power with the use of a normal hydroelectric turbine/generator setup. The plant is a prototype developed together with Sintef and began test power production on 24 November 2009. Mette-Marit, Crown Princess of Norway, officially opened the plant. This plant had been planned since the summer of 2008, with a water usage of 10 litres of fresh water and 20 litres of salt water per second. It is expected to give a power output of betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mette-Marit, Crown Princess Of Norway
Mette-Marit, Crown Princess of Norway (born Mette-Marit Tjessem Høiby, , on 19 August 1973) is the wife of Crown Prince Haakon. Haakon is the heir apparent to the throne, which means that should he ascend to the throne, she will automatically become Queen consort of Norway. A Norwegian commoner and single mother with a disadvantaged past, she was a controversial figure at the time of her engagement to Haakon in 2000. She became Crown Princess of Norway upon her marriage in 2001. The couple have two children, Ingrid Alexandra and Sverre Magnus, who are second and third in line to the Norwegian throne respectively. In October 2018, she was diagnosed with a form of pulmonary fibrosis. She is being treated at Oslo University Hospital and has restricted her royal duties. Background and education Mette-Marit Tjessem Høiby was born in Kristiansand in the southern part of Norway, the daughter of Sven O. Høiby, who had been unemployed for some time but who had previously worke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reversed Electrodialysis
Reversal may refer to: * Medical reversal, when a medical intervention falls out of use after improved clinical trials demonstrate its ineffectiveness or harmfulness. * Reversal (law), the setting aside of a decision of a lower court by a higher court * In drama, "reversal" refers to Aristotle's concept of Peripeteia * Reversal film, a type of photographic film also known as ''slide'' or ''transparency'' film * ''The Reversal'', a novel by Michael Connelly * Reversal of polarization (other) * Reversal (wrestling), in which the defensive contender achieves an offensive position * ''Reversal'' (film), a movie about wrestling * Reversal, an options-trading strategy * Reversal of a word in formal language * "Reversal" (''Arrow''), an episode of ''Arrow'' * Russian reversal is a type of joke, usually starting with the words "In Soviet Russia", in which the subject and objects of a statement are reversed, commonly as a snowclone pattern See also *Reverse (other) *Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
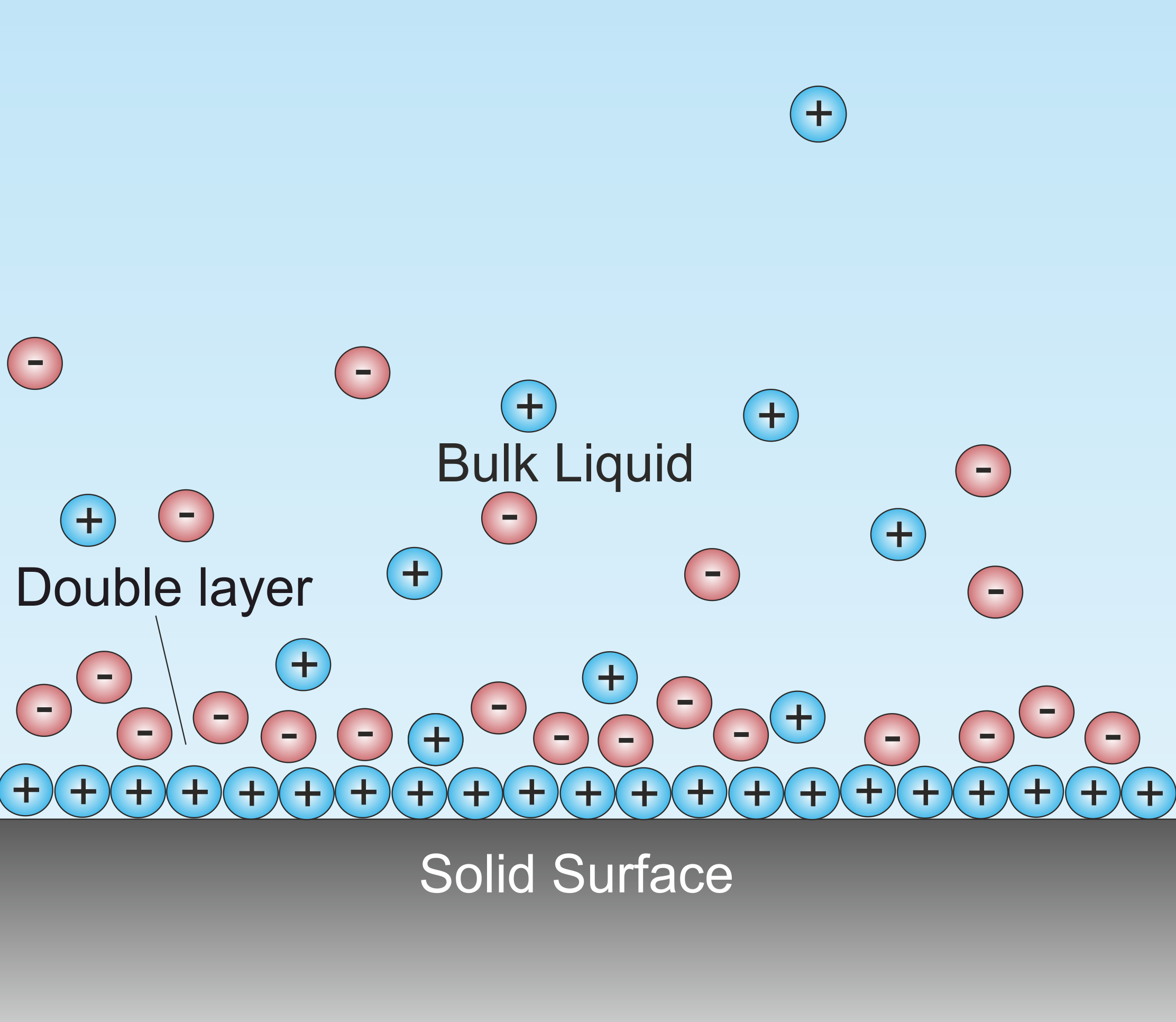
Double Layer (interfacial)
A double layer (DL, also called an electrical double layer, EDL) is a structure that appears on the surface of an object when it is exposed to a fluid. The object might be a solid particle, a gas bubble, a liquid droplet, or a porous body. The DL refers to two parallel layers of charge surrounding the object. The first layer, the surface charge (either positive or negative), consists of ions adsorbed onto the object due to chemical interactions. The second layer is composed of ions attracted to the surface charge via the Coulomb force, electrically screening the first layer. This second layer is loosely associated with the object. It is made of free ions that move in the fluid under the influence of electric attraction and thermal motion rather than being firmly anchored. It is thus called the "diffuse layer". Interfacial DLs are most apparent in systems with a large surface area to volume ratio, such as a colloid or porous bodies with particles or pores (respectively) on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or air). Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials depending on the type of battery. The electrophore, invented by Johan Wilcke, was an early version of an electrode used to study static electricity. Anode and cathode in electrochemical cells Electrodes are an essential part of any battery. The first electrochemical battery made was devised by Alessandro Volta and was aptly named the Voltaic cell. This battery consisted of a stack of copper and zinc electrodes separated by brine-soaked paper disks. Due to fluctuation in the voltage provided by the voltaic cell it wasn't very practical. The first practical battery was invented in 1839 and named the Daniell cell after John Frederic Daniell. Still making use of the zinc–copper electrode combination. Since then many more batteries have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Utility
A public utility company (usually just utility) is an organization that maintains the infrastructure for a public service (often also providing a service using that infrastructure). Public utilities are subject to forms of public control and regulation ranging from local community-based groups to statewide government monopolies. Public utilities are meant to supply goods/services that are considered essential; water, gas, electricity, telephone, and other communication systems represent much of the public utility market. The transmission lines used in the transportation of electricity, or natural gas pipelines, have natural monopoly characteristics. If the infrastructure already exists in a given area, minimal benefit is gained through competing. In other words, these industries are characterized by ''economies of scale'' in production. There are many different types of public utilities. Some, especially large companies, offer multiple products, such as electricity and natu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)