|
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
The glucose tolerance test (GTT, not to be confused with GGT test) is a medical test in which glucose is given and blood samples taken afterward to determine how quickly it is cleared from the blood. The test is usually used to test for diabetes, insulin resistance, impaired beta cell function, and sometimes reactive hypoglycemia and acromegaly, or rarer disorders of carbohydrate metabolism. In the most commonly performed version of the test, an ''oral glucose tolerance test'' (OGTT), a standard dose of glucose is ingested by mouth and blood levels are checked two hours later. Many variations of the GTT have been devised over the years for various purposes, with different standard doses of glucose, different routes of administration, different intervals and durations of sampling, and various substances measured in addition to blood glucose. History The glucose tolerance test was first described in 1923 by Jerome W. Conn. The test was based on the previous work in 1913 by A. T. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight, where it is used to make cellulose in cell walls, the most abundant carbohydrate in the world. In energy metabolism, glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms. Glucose for metabolism is stored as a polymer, in plants mainly as starch and amylopectin, and in animals as glycogen. Glucose circulates in the blood of animals as blood sugar. The naturally occurring form of glucose is -glucose, while -glucose is produced synthetically in comparatively small amounts and is less biologically active. Glucose is a monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group, and is therefore an aldohexose. The glucose molecule can exist in an open-chain (acyclic) as well as ring (cyclic) form. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salicylates
Salicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4CO2H. A colorless, bitter-tasting solid, it is a precursor to and a metabolite of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). It is a plant hormone, and has been listed by the EPA Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Chemical Substance Inventory as an experimental teratogen. The name is from Latin ''salix'' for willow tree. It is an ingredient in some anti-acne products. Salts and esters of salicylic acid are known as salicylates. Uses Medicine Salicylic acid as a medication is commonly used to remove the outer layer of the skin. As such, it is used to treat warts, psoriasis, acne vulgaris, ringworm, dandruff, and ichthyosis. Similar to other hydroxy acids, salicylic acid is an ingredient in many skincare products for the treatment of seborrhoeic dermatitis, acne, psoriasis, calluses, corns, keratosis pilaris, acanthosis nigricans, ichthyosis, and warts. Uses in manufacturing Salicylic acid is used as a food pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American College Of Obstetricians And Gynecologists
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) is a professional association of physicians specializing in obstetrics and gynecology in the United States. Several Latin American countries are also represented within Districts of the organization. It is a 501(c)(3) organization with a membership of more than 60,000 obstetrician-gynecologists and women's health care professionals. It was founded in 1951. __TOC__ Background A companion 501(c)(6) organization, the American ''Congress'' of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, was founded in 2008 and became operational in 2010. The two organizations coexist, and member individuals automatically belong to both. Both are not-for-profit. The College as a 501(c)(3) focuses on education (with limited political work), whereas the Congress as a 501(c)(6) is allowed to advocate for members' interests in terms of the business of medicine (BOM) through lobbying and other political work. Their main advocacy focuses on women's repro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impaired Glucose Tolerance
Prediabetes is a component of the metabolic syndrome and is characterized by elevated blood sugar levels that fall below the threshold to diagnose diabetes mellitus. It usually does not cause symptoms but people with prediabetes often have obesity (especially abdominal or visceral obesity), dyslipidemia with high triglycerides and/or low HDL cholesterol, and hypertension. It is also associated with increased risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD). Prediabetes is more accurately considered an early stage of diabetes as health complications associated with type 2 diabetes often occur before the diagnosis of diabetes. Prediabetes can be diagnosed by measuring hemoglobin A1c, fasting glucose, or glucose tolerance test. Many people may be diagnosed through routine screening tests. The primary treatment approach includes lifestyle changes such as exercise and dietary adjustments. Some medications can be used to reduce the risks associated with prediabetes. There is a high rate of pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia is a condition in which an excessive amount of glucose circulates in the blood plasma. This is generally a blood sugar level higher than 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL), but symptoms may not start to become noticeable until even higher values such as 13.9–16.7 mmol/L (~250–300 mg/dL). A subject with a consistent range between ~5.6 and ~7 mmol/L (100–126 mg/dL) ( American Diabetes Association guidelines) is considered slightly hyperglycemic, and above 7 mmol/L (126 mg/dL) is generally held to have diabetes. For diabetics, glucose levels that are considered to be too hyperglycemic can vary from person to person, mainly due to the person's renal threshold of glucose and overall glucose tolerance. On average, however, chronic levels above 10–12 mmol/L (180–216 mg/dL) can produce noticeable organ damage over time. Signs and symptoms The degree of hyperglycemia can change over time depending on the metabolic cause, for example, impaired ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impaired Fasting Glucose
Impaired fasting glucose is a type of prediabetes, in which a person's blood sugar levels during fasting are consistently above the normal range, but below the diagnostic cut-off for a formal diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Together with impaired glucose tolerance, it is a sign of insulin resistance. In this manner, it is also one of the conditions associated with metabolic syndrome. Those with impaired fasting glucose are at an increased risk of vascular complications of diabetes, though to a lesser extent. The risks are cumulative, with both higher blood glucose levels, and the total amount of time it spends elevated, increasing the overall complication rate. IFG can eventually progress to type 2 diabetes mellitus without intervention, which typically involves lifestyle modification. Those with impaired fasting glucose have a 1.5 fold increased risk of developing clinical diabetes within 10 years, when compared to the general population. Some studies suggest that without lifest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Glycosuria
Renal glycosuria is a rare condition in which the simple sugar glucose is excreted in the urine despite normal or low blood glucose levels. With normal kidney (renal) function, glucose is excreted in the urine only when there are abnormally elevated levels of glucose in the blood. However, in those with renal glycosuria, glucose is abnormally elevated in the urine due to improper functioning of the renal tubules, which are primary components of nephrons, the filtering units of the kidneys. Signs and symptoms In most affected individuals, the condition causes no apparent symptoms (asymptomatic) or serious effects. When renal glycosuria occurs as an isolated finding with otherwise normal kidney function, the condition is thought to be inherited as an autosomal recessive trait. Genetics It is associated with SLC5A2, coding the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2. Diagnosis A doctor normally can diagnose renal glycosuria when a routine urine test (Urinalysis) detects glucose in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucozade
Lucozade is a British brand of soft drink manufactured and marketed by the Japanese company Suntory. Created as "Glucozade" in the UK in 1927 by a Newcastle pharmacist, William Walker Hunter (trading as W. Owen & Son), it was acquired by the British pharmaceutical company Beecham's in 1938 and sold as Lucozade, an energy drink for the sick. Its advertising slogan was "Lucozade aids recovery". It was sold mostly in pharmacies up until the 1980s before it was more readily available as a sports drink in shops across the UK. A glucose and water solution, the product was sold until 1983 as a carbonated, slightly orange-flavoured drink in a glass bottle wrapped in orange cellophane. Pharmacists sold it, children were given it when ill, and hospital visitors would regularly arrive with a bottle. It was rebranded in 1978 as a "pick me up", and as a sports drink in 1983, to associate it with health rather than sickness. The company switched to a plastic bottle and introduced a range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a condition in which a woman without diabetes develops high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes generally results in few symptoms; however, it increases the risk of pre-eclampsia, depression, and of needing a Caesarean section. Babies born to mothers with poorly treated gestational diabetes are at increased risk of macrosomia, of having hypoglycemia after birth, and of jaundice. If untreated, diabetes can also result in stillbirth. Long term, children are at higher risk of being overweight and of developing type 2 diabetes. Gestational diabetes can occur during pregnancy because of insulin resistance or reduced production of insulin. Risk factors include being overweight, previously having gestational diabetes, a family history of type 2 diabetes, and having polycystic ovarian syndrome. Diagnosis is by blood tests. For those at normal risk, screening is recommended between 24 and 28 weeks' gestation. For those at high risk, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins. Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but can also occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. A pregnancy may end in a live birth, a miscarriage, an induced abortion, or a stillbirth. Childbirth typically occurs around 40 weeks from the start of the last menstrual period (LMP), a span known as the gestational age. This is just over nine months. Counting by fertilization age, the length is about 38 weeks. Pregnancy is "the presence of an implanted human embryo or fetus in the uterus"; implantation occurs on average 8–9 days after fertilization. An ''embryo'' is the term for the developing offspring during the first seven weeks following implantation (i.e. ten weeks' gestational age), after which the term '' fetus'' is used until birth. Signs a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
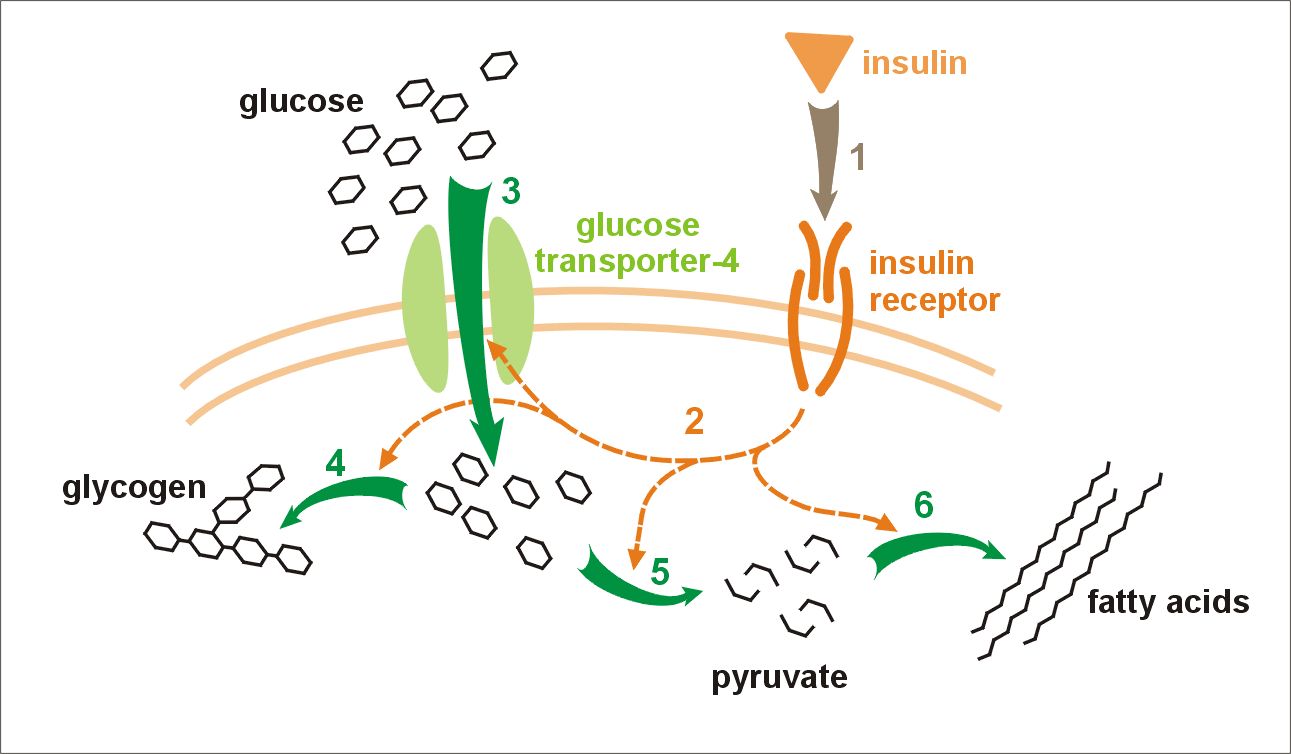
Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into liver, fat and skeletal muscle cells. In these tissues the absorbed glucose is converted into either glycogen via glycogenesis or fats ( triglycerides) via lipogenesis, or, in the case of the liver, into both. Glucose production and secretion by the liver is strongly inhibited by high concentrations of insulin in the blood. Circulating insulin also affects the synthesis of proteins in a wide variety of tissues. It is therefore an anabolic hormone, promoting the conversion of small molecules in the blood into large molecules inside the cells. Low insulin levels in the blood have the opposite effect by promoting widespread catabolism, espe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Sugar
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blood of a 70 kg (154 lb) human at all times. The body tightly regulates blood glucose levels as a part of metabolic homeostasis. Glucose is stored in skeletal muscle and liver cells in the form of glycogen; in fasting individuals, blood glucose is maintained at a constant level at the expense of glycogen stores in the liver and skeletal muscle. In humans, a blood glucose level of 4 grams, or about a teaspoon, is critical for normal function in a number of tissues, and the human brain consumes approximately 60% of blood glucose in fasting, sedentary individuals. A persistent elevation in blood glucose leads to glucose toxicity, which contributes to cell dysfunction and the pathology grouped together as complications of diabetes. Gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |